Translation
The default language of NocoBase is English. Currently, the main application supports English, Italian, Dutch, Simplified Chinese, and Japanese. We sincerely invite you to contribute translations for additional languages, enabling users around the world to enjoy an even more convenient NocoBase experience.
I. System Localization
1. System Interface and Plugin Translation
1.1 Translation Scope
This applies only to the localization of the NocoBase system interface and plugins, and does not cover other custom content (such as data tables or Markdown blocks).
1.2 Localization Content Overview
NocoBase uses Git to manage its localization content. The primary repository is: https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/main/locales
Each language is represented by a JSON file named according to its language code (e.g., de-DE.json, fr-FR.json). The file structure is organized by plugin modules, using key-value pairs to store translations. For example:
When translating, please gradually convert it to a structure similar to the following:
1.3 Translation Testing and Synchronization
-
After completing your translation, please test and verify that all texts display correctly. We've also released a translation validation plugin - search for
Locale testerin the plugin marketplace.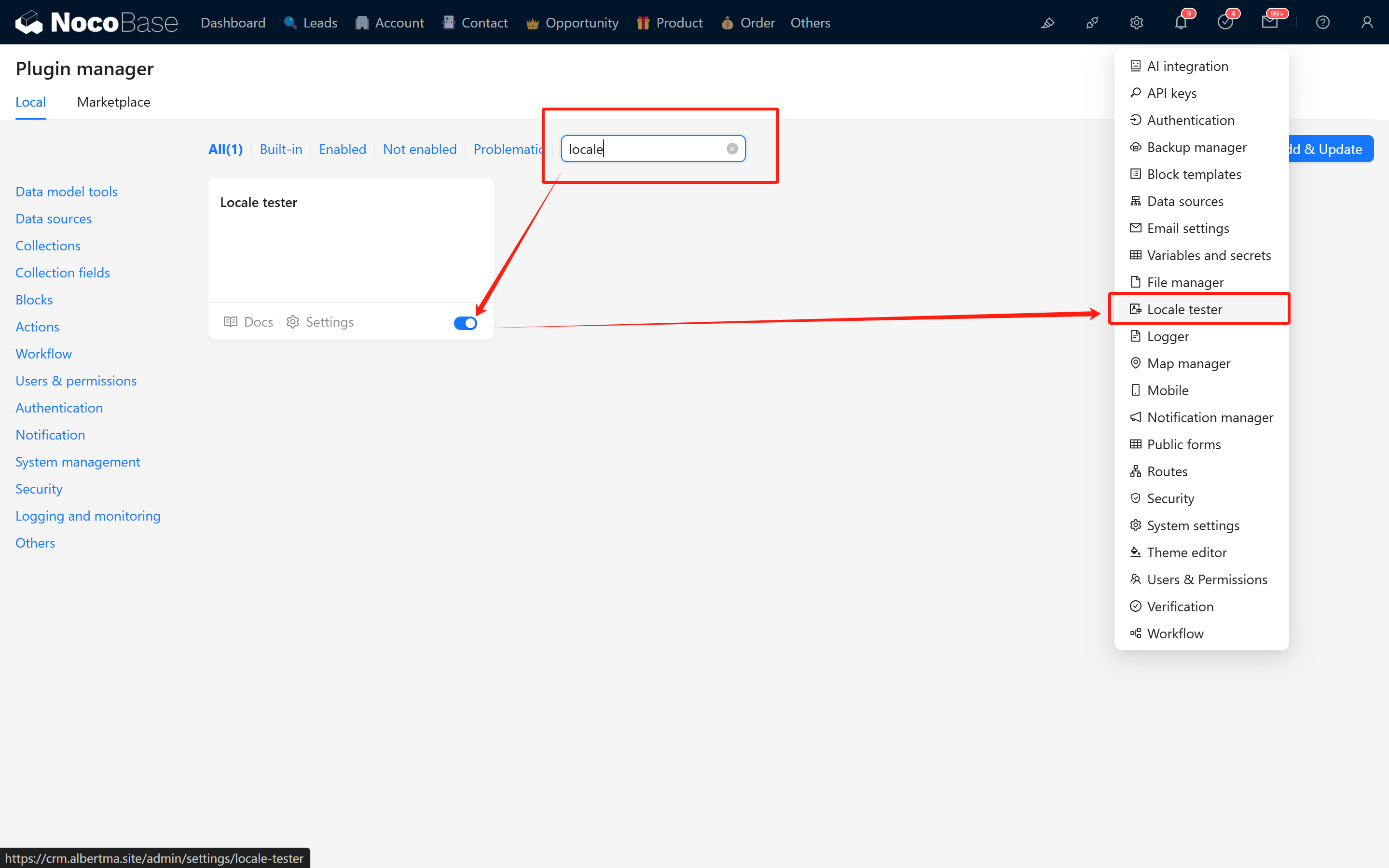 After installation, copy the JSON content from the corresponding localization file in the git repository, paste it inside, and click OK to verify if the translation content is effective.
After installation, copy the JSON content from the corresponding localization file in the git repository, paste it inside, and click OK to verify if the translation content is effective.
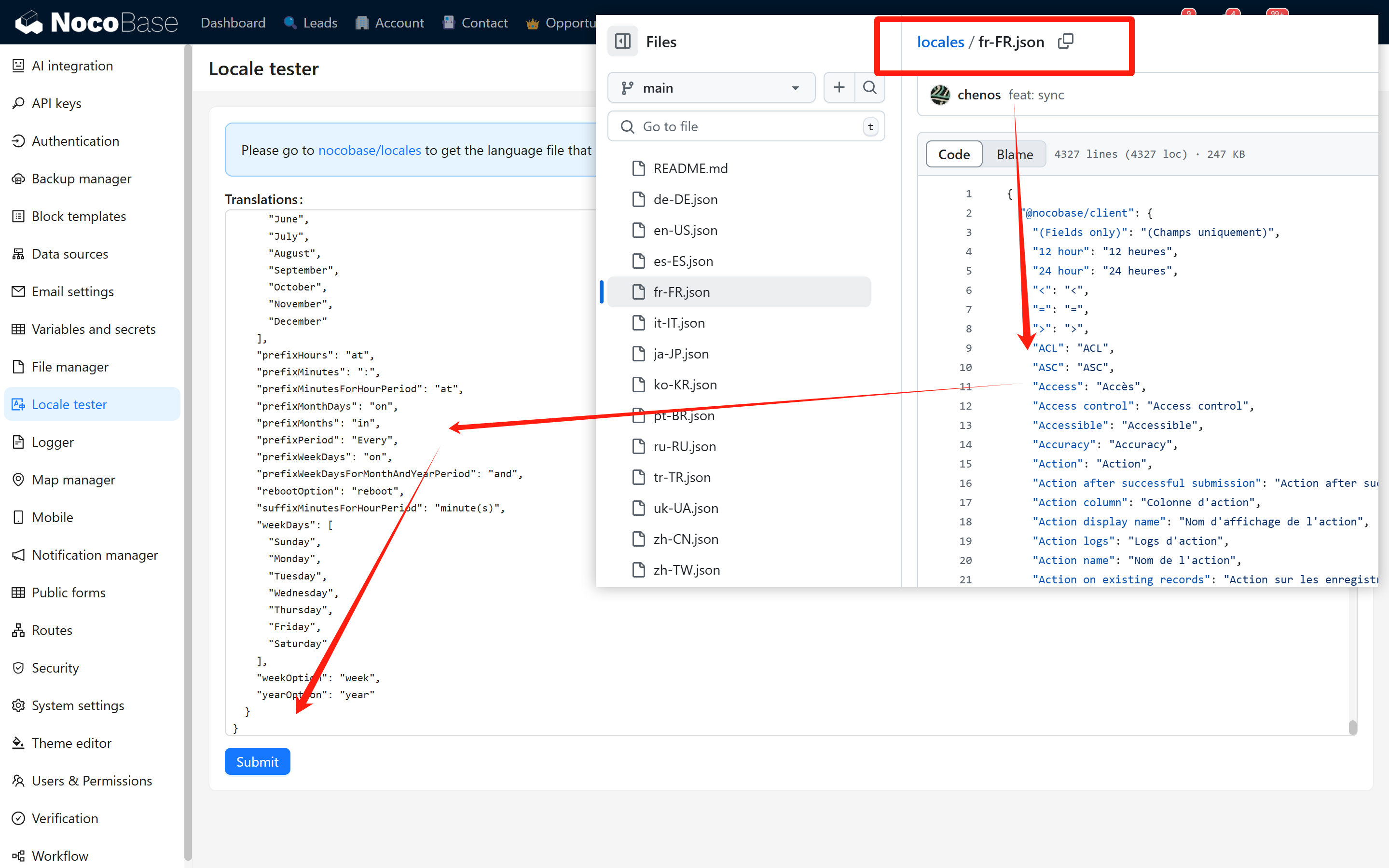
-
Once submitted, system scripts will automatically synchronize the localization content to the code repository.
1.4 NocoBase 2.0 Localization Plugin
Note: This section is under development. The localization plugin for NocoBase 2.0 has some differences from the 1.x version. Details will be provided in a future update.
II. Documentation Localization (NocoBase 2.0)
The documentation for NocoBase 2.0 is managed in a new structure. The documentation source files are located in the main NocoBase repository:
https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/next/docs
2.1 Documentation Structure
The documentation uses Rspress as the static site generator and supports 22 languages. The structure is organized as follows:
2.2 Translation Workflow
-
Sync with English source: All translations should be based on the English documentation (
docs/en/). When the English documentation is updated, translations should be updated accordingly. -
Branch strategy:
- Use the
developornextbranch as the reference for the latest English content - Create your translation branch from the target branch
- Use the
-
File structure: Each language directory should mirror the English directory structure. For example:
2.3 Contributing Translations
- Fork the repository: https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase
- Clone your fork and checkout the
developornextbranch - Navigate to the
docs/docs/directory - Find the language directory you want to contribute to (e.g.,
ja/for Japanese) - Translate the markdown files, keeping the same file structure as the English version
- Test your changes locally:
- Submit a Pull Request to the main repository
2.4 Translation Guidelines
- Keep formatting consistent: Maintain the same markdown structure, headings, code blocks, and links as the source
- Preserve frontmatter: Keep any YAML frontmatter at the top of files unchanged unless it contains translatable content
- Image references: Use the same image paths from
docs/public/- images are shared across all languages - Internal links: Update internal links to point to the correct language path
- Code examples: Generally, code examples should not be translated, but comments within code can be translated
2.5 Navigation Configuration
The navigation structure for each language is defined in _nav.json and _meta.json files within each language directory. When adding new pages or sections, make sure to update these configuration files.
III. Website Localization
The website pages and all content are stored in: https://github.com/nocobase/website
3.1 Getting Started and Reference Resources
When adding a new language, please refer to the existing language pages:
- English: https://github.com/nocobase/website/tree/main/src/pages/en
- Chinese: https://github.com/nocobase/website/tree/main/src/pages/cn
- Japanese: https://github.com/nocobase/website/tree/main/src/pages/ja
Global style modifications are located at:
- English: https://github.com/nocobase/website/blob/main/src/layouts/BaseEN.astro
- Chinese: https://github.com/nocobase/website/blob/main/src/layouts/BaseCN.astro
- Japanese: https://github.com/nocobase/website/blob/main/src/layouts/BaseJA.astro
The website's global component localization is available at: https://github.com/nocobase/website/tree/main/src/components
3.2 Content Structure and Localization Method
We use a mixed content management approach. English, Chinese, and Japanese content and resources are regularly synchronized from the CMS system and overwritten, while other languages can be edited directly in local files. Local content is stored in the content directory, organized as follows:
3.3 Content Translation Guidelines
- About Markdown Content Translation
- Create a new language file based on the default file (e.g.,
index.mdtoindex.fr.md) - Add localized properties in the corresponding fields in the JSON file
- Maintain consistency in file structure, links, and image references
- JSON Content Translation Many content metadata are stored in JSON files, which typically contain multilingual fields:
Translation Notes:
-
Field Naming Convention: Translation fields typically use the
{original_field}_{language_code}format- For example: title_fr (French title), description_de (German description)
-
When Adding a New Language:
- Add a corresponding language suffix version for each field that needs translation
- Do not modify the original field values (such as title, description, etc.), as they serve as default language (English) content
-
CMS Synchronization Mechanism:
- The CMS system periodically updates English, Chinese and Japanese content
- The system will only update/overwrite content for these three languages (some properties in the JSON), and will not delete language fields added by other contributors
- For example: if you added a French translation (title_fr), CMS synchronization will not affect this field
3.4 Configuring Support for a New Language
To add support for a new language, you need to modify the SUPPORTED_LANGUAGES configuration in the src/utils/index.ts file:
3.5 Layout Files and Styles
Each language needs corresponding layout files:
- Create a new layout file (e.g., for French, create
src/layouts/BaseFR.astro) - You can copy an existing layout file (such as
BaseEN.astro) and translate it - The layout file contains translations for global elements like navigation menus, footers, etc.
- Be sure to update the language switcher configuration to properly switch to the newly added language
3.6 Creating Language Page Directories
Create independent page directories for the new language:
- Create a folder named with the language code in the
srcdirectory (e.g.,src/fr/) - Copy the page structure from other language directories (e.g.,
src/en/) - Update page content, translating titles, descriptions and text into the target language
- Ensure pages use the correct layout component (e.g.,
.layout: '@/layouts/BaseFR.astro')
3.7 Component Localization
Some common components also need translation:
- Check components in the
src/components/directory - Pay special attention to components with fixed text (like navigation bars, footers, etc.)
- Components may use conditional rendering to display content in different languages:
3.8 Testing and Validation
After completing the translation, conduct thorough testing:
- Run the website locally (usually using
yarn dev) - Check how all pages display in the new language
- Verify that the language switching functionality works properly
- Ensure all links point to the correct language version pages
- Check responsive layouts to ensure translated text doesn't break page design
IV. How to Start Translating
If you want to contribute a new language translation to NocoBase, please follow these steps:
| Component | Repository | Branch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Interface | https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase/tree/main/locales | main | JSON locale files |
| Documentation (2.0) | https://github.com/nocobase/nocobase | develop / next | docs/docs/<lang>/ directory |
| Website | https://github.com/nocobase/website | main | See Section III |
After completing your translation, please submit a Pull Request to NocoBase. The new languages will appear in the system configuration, allowing you to select which languages to display.
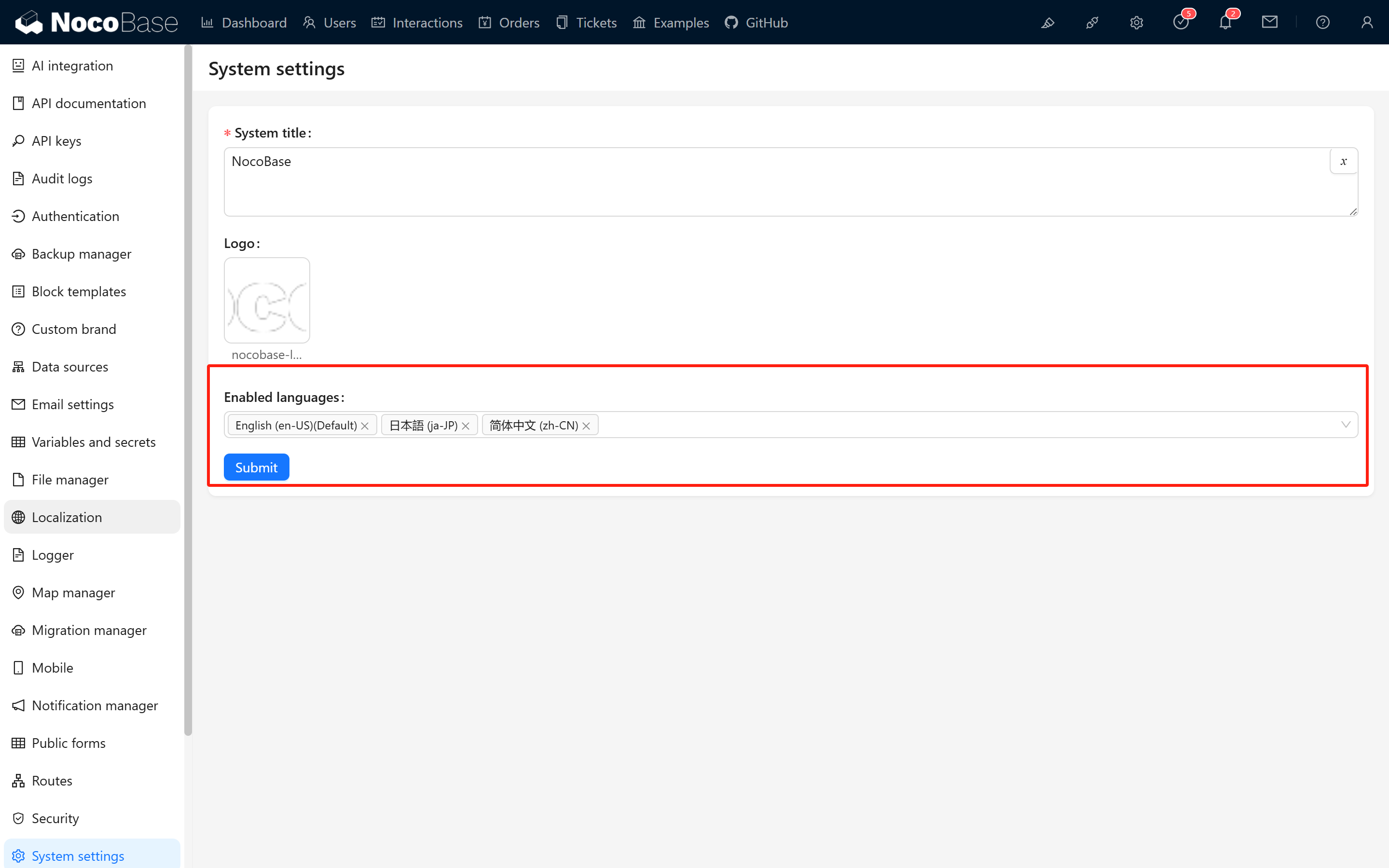
NocoBase 1.x Documentation
For NocoBase 1.x translation guide, please refer to:

