Workflow Webhook Integration
Through Webhook triggers, NocoBase can receive HTTP calls from third-party systems and automatically trigger workflows, enabling seamless integration with external systems.
Overview
Webhooks are a "reverse API" mechanism that allows external systems to proactively send data to NocoBase when specific events occur. Compared to active polling, Webhooks provide a more real-time and efficient integration approach.
Typical Use Cases
Form Data Submission
External survey systems, registration forms, and customer feedback forms push data to NocoBase via Webhook after user submission, automatically creating records and triggering follow-up processes (such as sending confirmation emails, assigning tasks, etc.).
Message Notifications
Events from third-party messaging platforms (such as WeCom, DingTalk, Slack) like new messages, mentions, or approval completions can trigger automated processes in NocoBase through Webhooks.
Data Synchronization
When data changes in external systems (such as CRM, ERP), Webhooks push updates to NocoBase in real-time to maintain data synchronization.
Third-Party Service Integration
- GitHub: Code pushes, PR creation events trigger automation workflows
- GitLab: CI/CD pipeline status notifications
- Form Submissions: External form systems submit data to NocoBase
- IoT Devices: Device status changes, sensor data reporting
Features
Flexible Trigger Mechanism
- Supports GET, POST, PUT, DELETE HTTP methods
- Automatically parses JSON, form data, and other common formats
- Configurable request validation to ensure trusted sources
Data Processing Capabilities
- Received data can be used as variables in workflows
- Supports complex data transformation and processing logic
- Can be combined with other workflow nodes to implement complex business logic
Security Assurance
- Supports signature verification to prevent forged requests
- Configurable IP whitelist
- HTTPS encrypted transmission
Usage Steps
1. Install Plugin
Locate and install the Workflow: Webhook plugin in the plugin manager.
Note: This is a commercial plugin. For detailed activation instructions, please refer to: Commercial Plugin Activation Guide
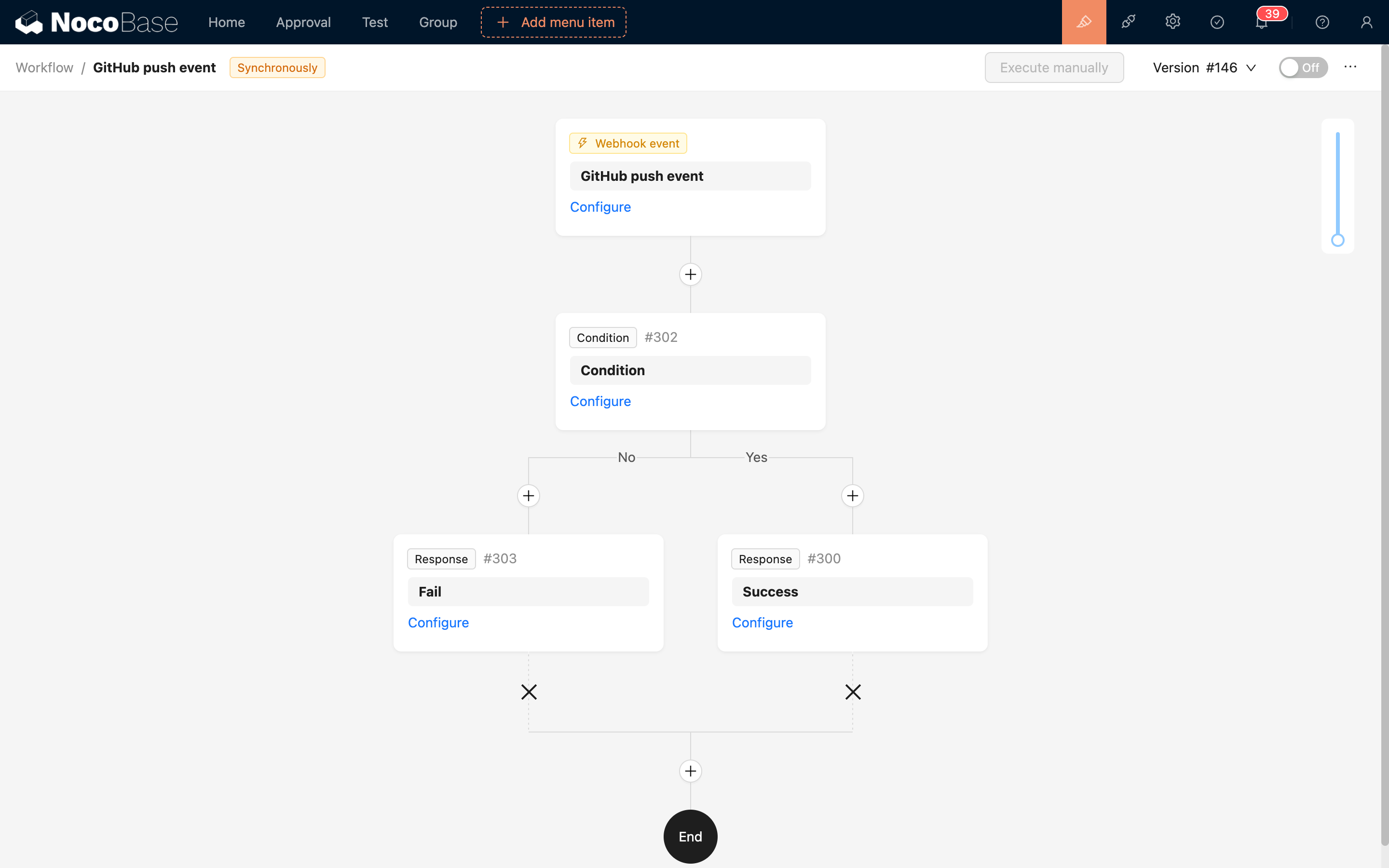
2. Create Webhook Workflow
- Navigate to Workflow Management
- Click Create Workflow
- Select Webhook Trigger as the trigger type
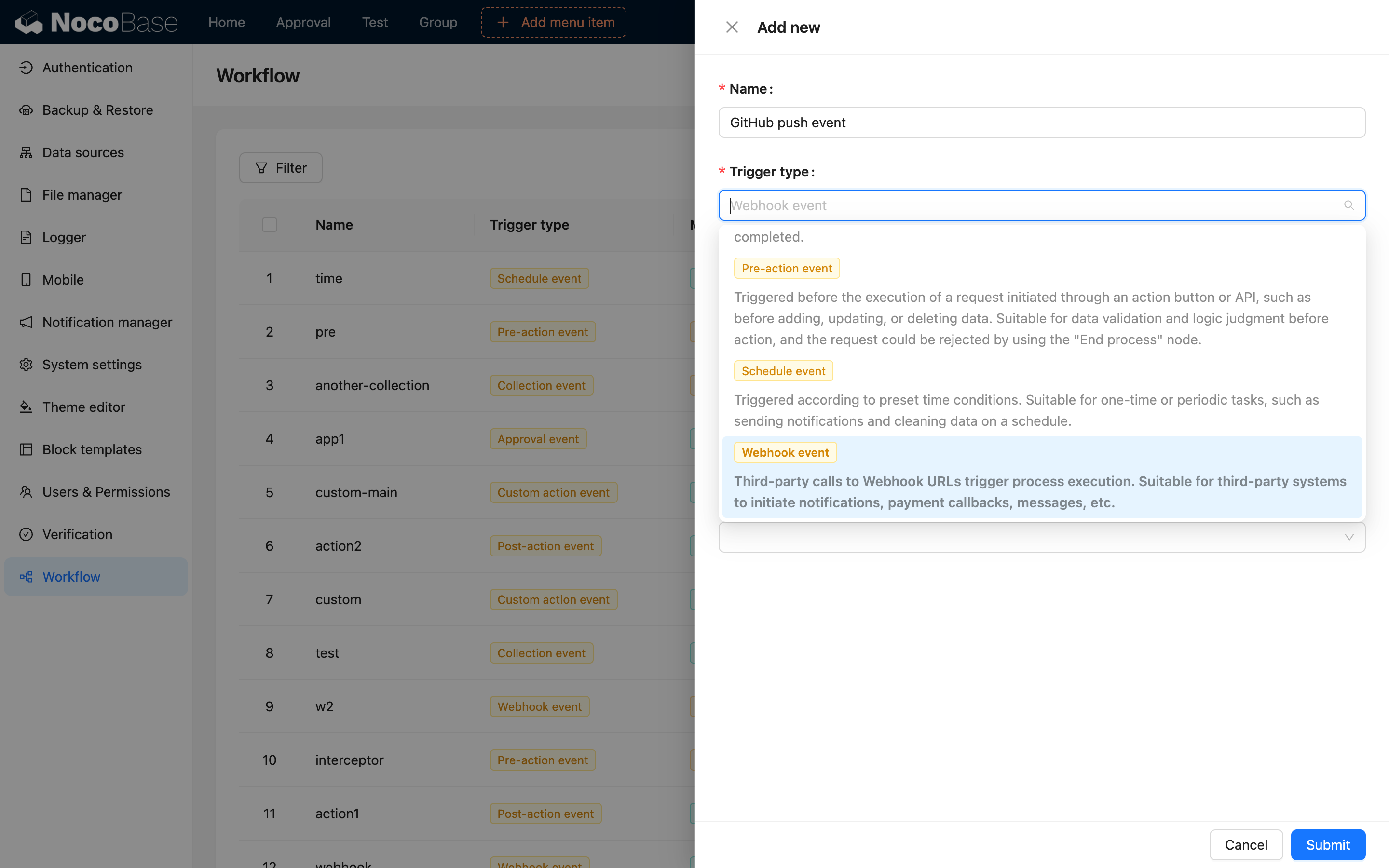
- Configure Webhook parameters
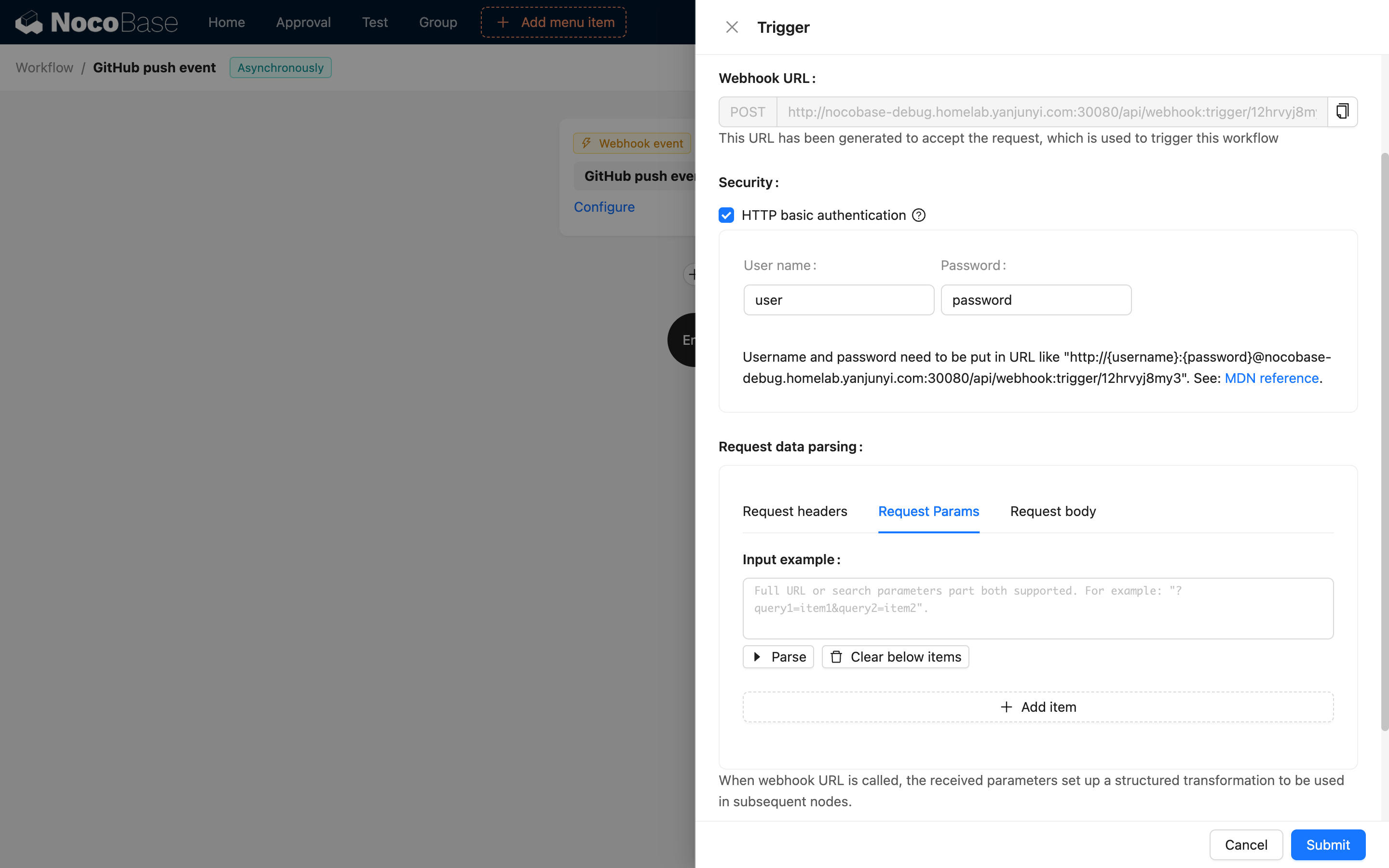
- Request Path: Custom Webhook URL path
- Request Method: Select allowed HTTP methods (GET/POST/PUT/DELETE)
- Sync/Async: Choose whether to wait for workflow completion before returning results
- Validation: Configure signature verification or other security mechanisms
3. Configure Workflow Nodes
Add workflow nodes based on business requirements, such as:
- Collection Operations: Create, update, delete records
- Conditional Logic: Branch based on received data
- HTTP Request: Call other APIs
- Notifications: Send emails, SMS, etc.
- Custom Code: Execute JavaScript code
4. Obtain Webhook URL
After workflow creation, the system generates a unique Webhook URL, typically in the format:
5. Configure in Third-Party System
Configure the generated Webhook URL in the third-party system:
- Set data submission callback address in form systems
- Configure Webhook in GitHub/GitLab
- Configure event push address in WeCom/DingTalk
6. Test Webhook
Test the Webhook using tools like Postman or cURL:
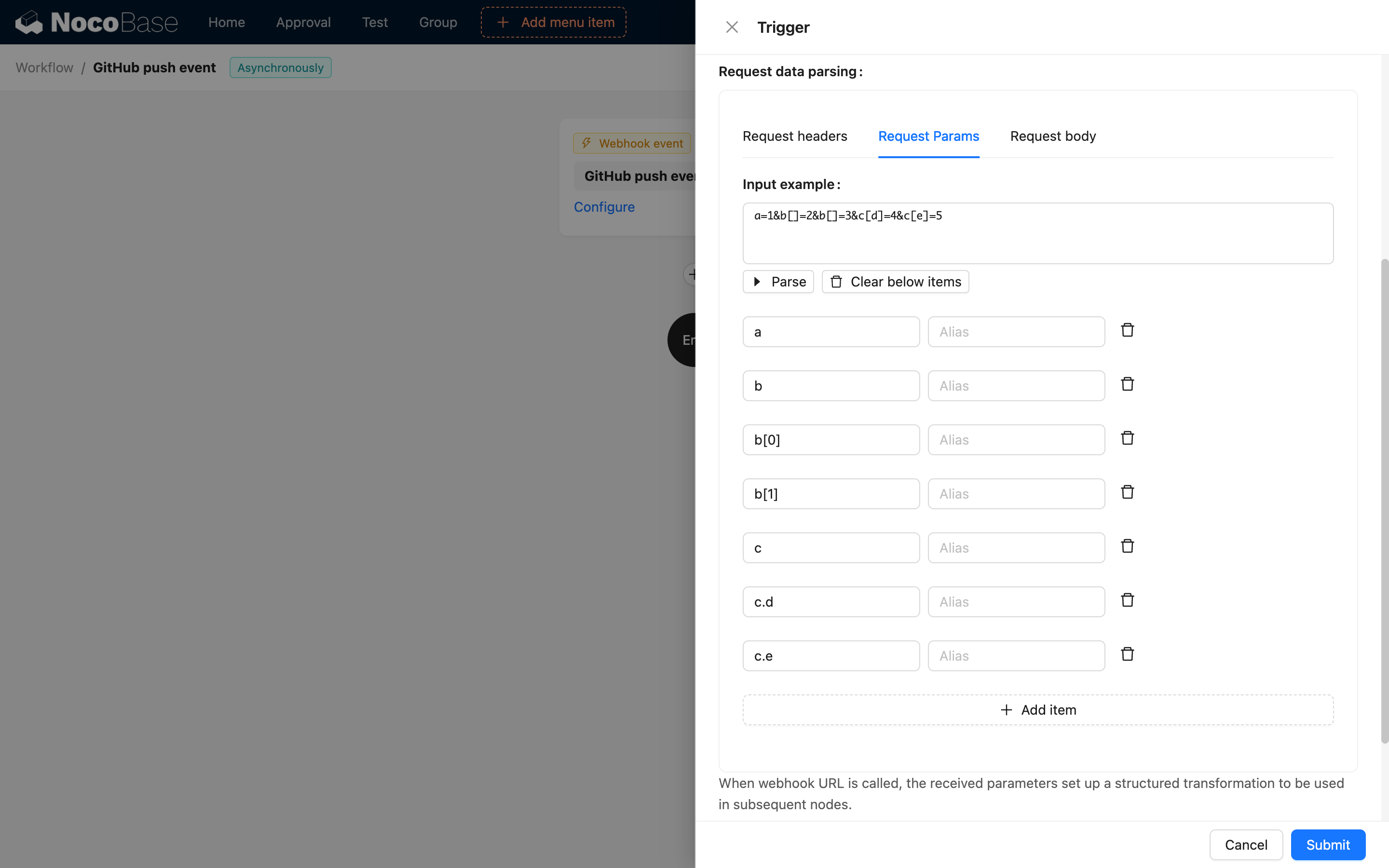
Accessing Request Data
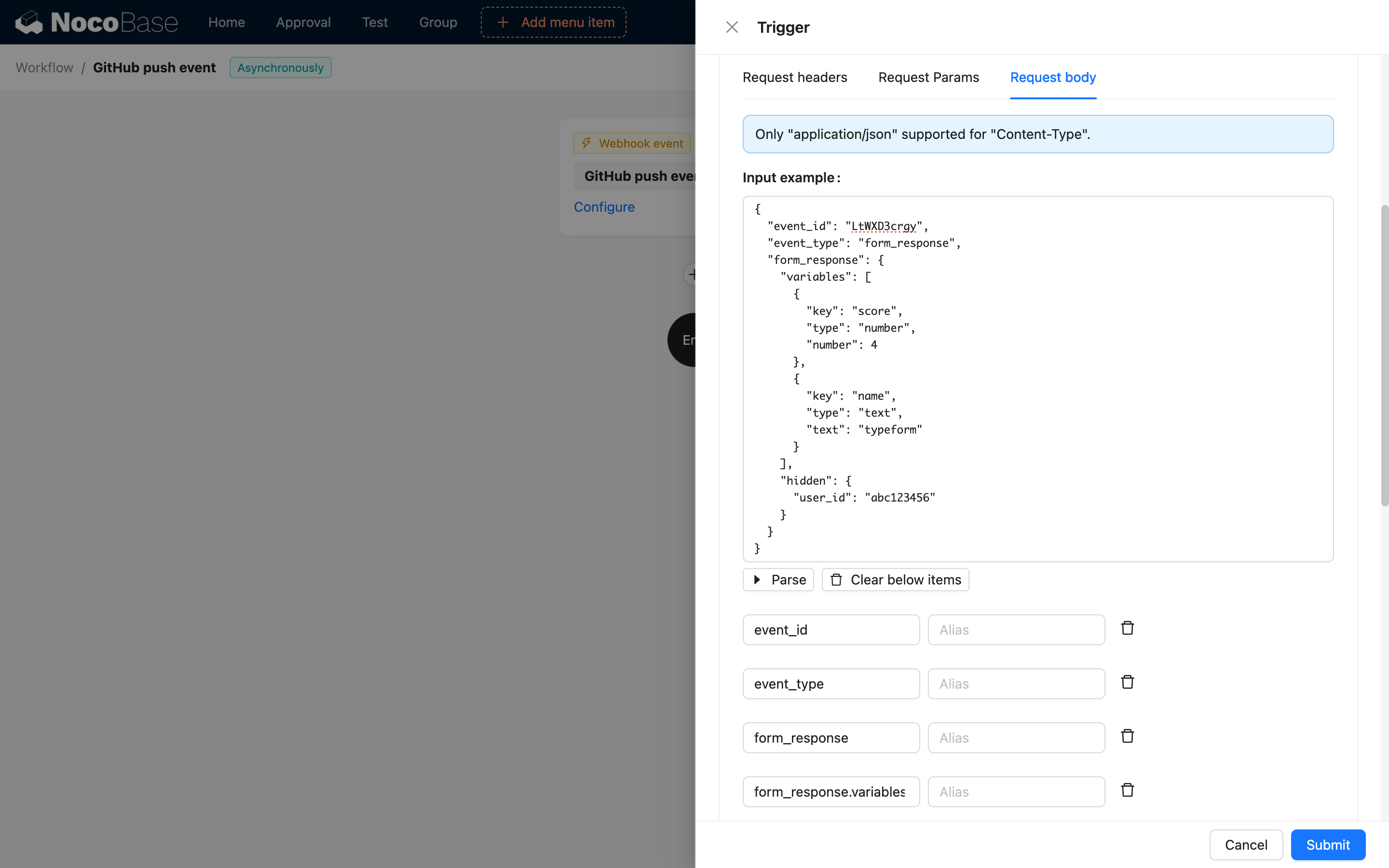
In workflows, access Webhook data through variables:
{{$context.data}}: Request body data{{$context.headers}}: Request headers{{$context.query}}: URL query parameters{{$context.params}}: Path parameters
Response Configuration
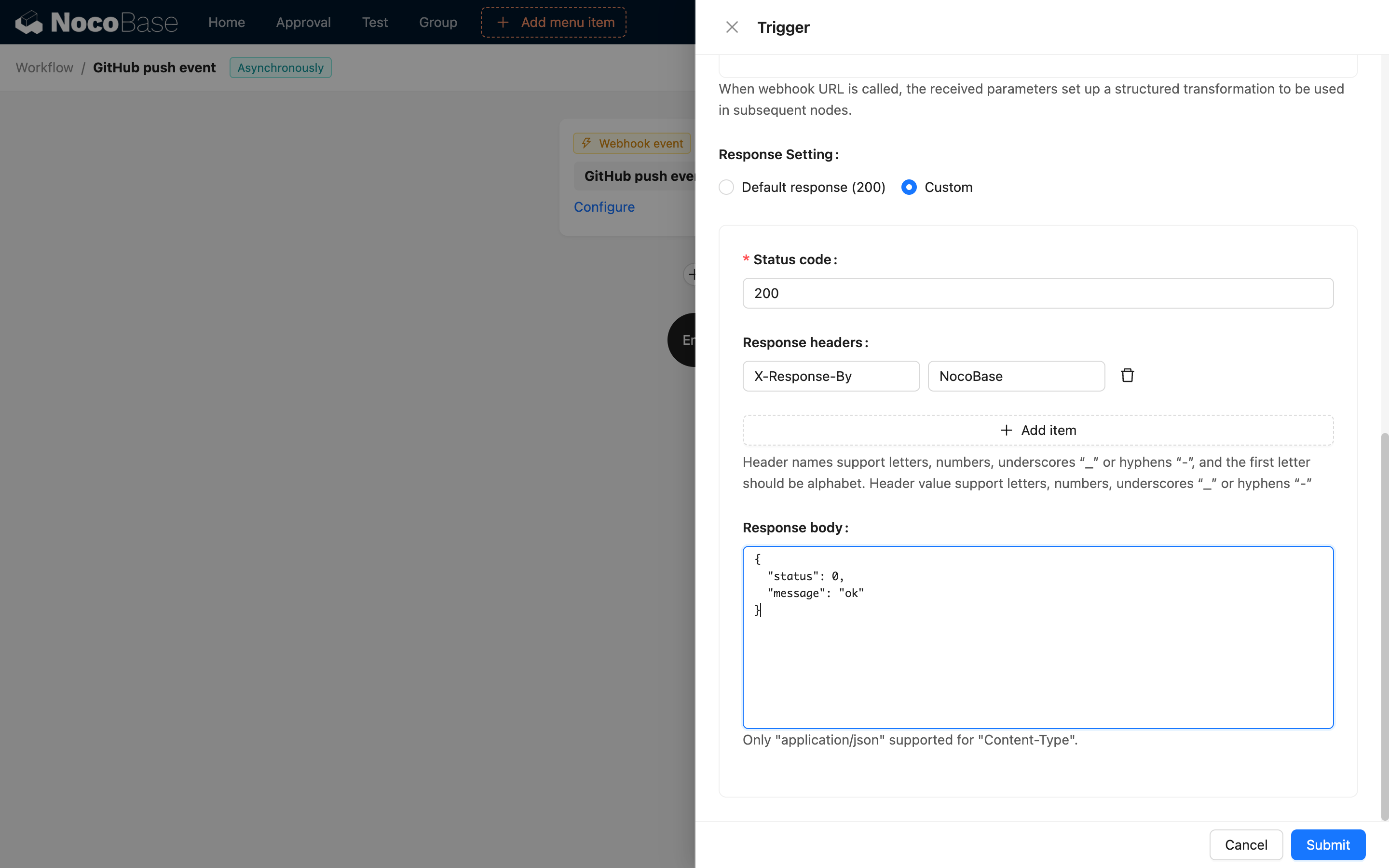
Synchronous Mode
Returns results after workflow execution completes, configurable:
- Response Status Code: 200, 201, etc.
- Response Data: Custom JSON response
- Response Headers: Custom HTTP headers
Asynchronous Mode
Returns immediate confirmation, workflow executes in background. Suitable for:
- Long-running workflows
- Scenarios not requiring execution results
- High-concurrency scenarios
Security Best Practices
1. Enable Signature Verification
Most third-party services support signature mechanisms:
2. Use HTTPS
Ensure NocoBase is deployed with HTTPS to protect data transmission.
3. Restrict Request Sources
Configure IP whitelist to allow only trusted sources.
4. Data Validation
Add data validation logic in workflows to ensure correct format and valid content.
5. Audit Logging
Record all Webhook requests for tracking and troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting
Webhook Not Triggering?
- Verify the Webhook URL is correct
- Confirm workflow status is "Enabled"
- Check third-party system's send logs
- Review firewall and network configuration
How to Debug Webhooks?
- Check workflow execution records for detailed information about requests and results
- Use Webhook testing tools (like Webhook.site) to verify requests
- Review key data and error messages in execution records
How to Handle Retries?
Some third-party services retry sending if they don't receive a successful response:
- Ensure workflow is idempotent
- Use unique identifiers for deduplication
- Record processed request IDs
Performance Optimization Tips
- Use asynchronous mode for time-consuming operations
- Add conditional logic to filter unnecessary requests
- Consider using message queues for high-concurrency scenarios
Example Scenarios
External Form Submission Processing
GitHub Code Push Notification