Many-to-Many
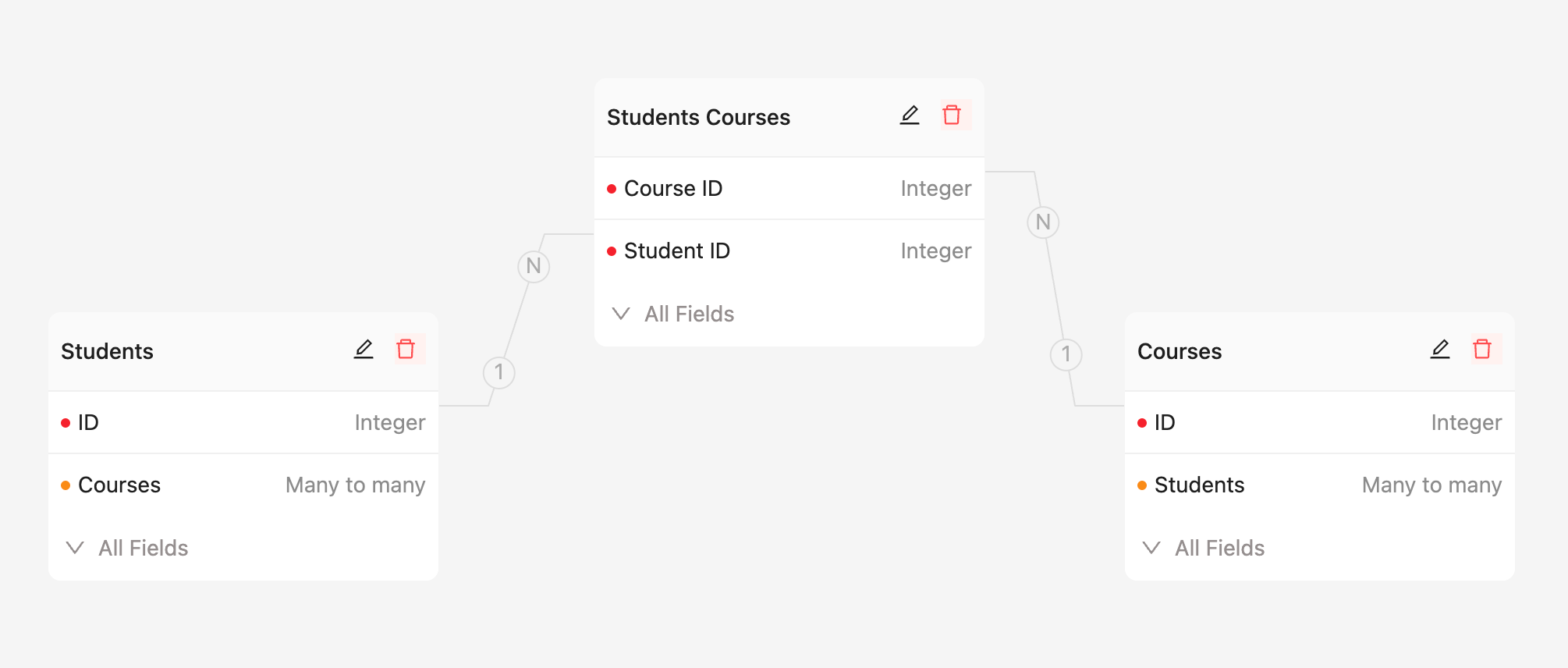
In a course enrollment system, there are two entities: students and courses. A student can enroll in multiple courses, and a course can have multiple students enrolled, constituting a many-to-many relationship. In a relational database, to represent the many-to-many relationship between students and courses, an intermediary collection, such as an enrollment collection, is usually used. This collection can record which courses each student has chosen and which students have enrolled in each course. This design effectively represents the many-to-many relationship between students and courses.
ER Diagram:
Field Configuration:
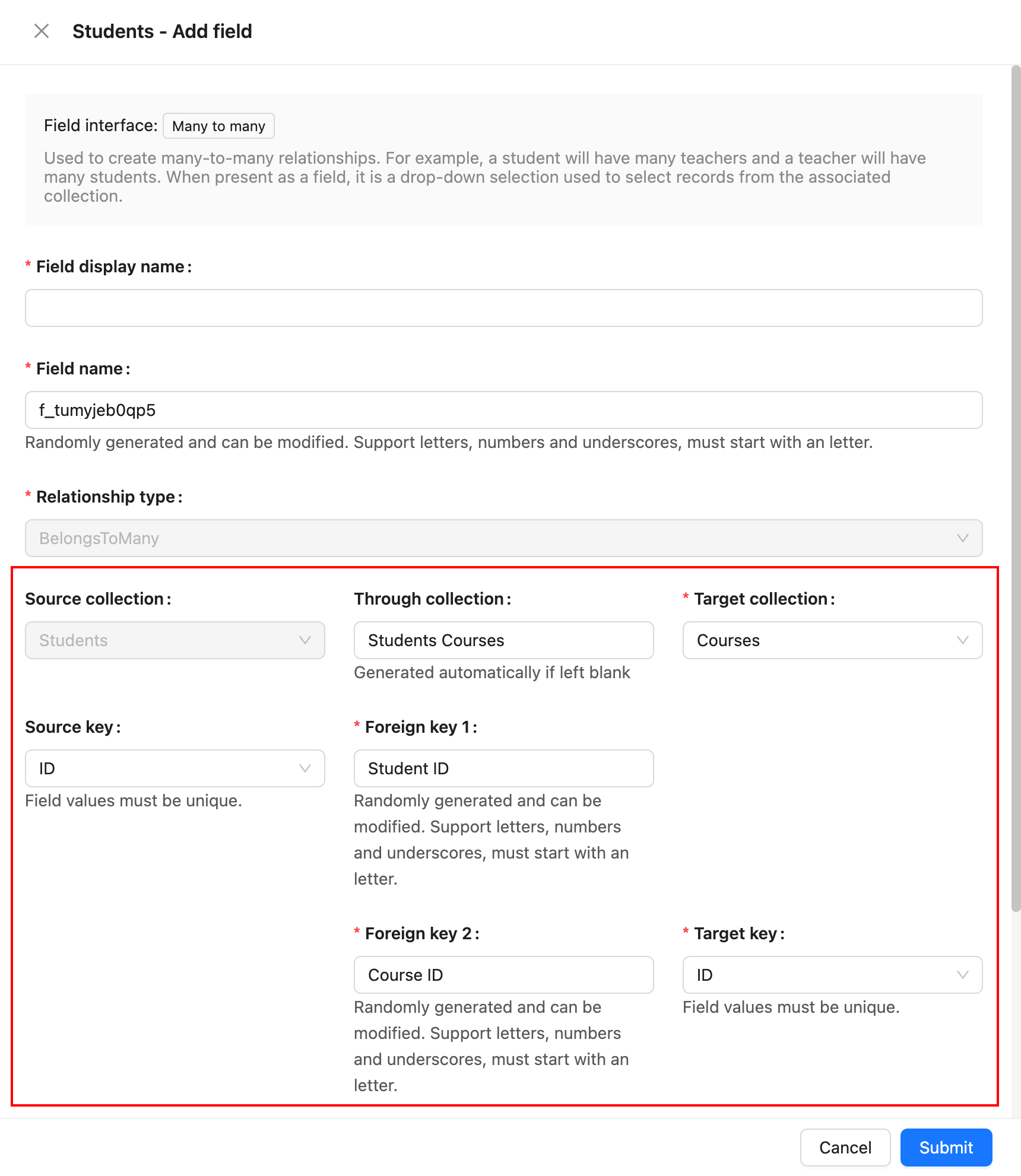
Parameter Description
Source Collection
The source collection, which is the collection where the current field resides.
Target Collection
The target collection, which is the collection to be associated with.
Through Collection
The intermediary collection, used when a many-to-many relationship exists between two entities. The intermediary collection has two foreign keys that are used to maintain the association between the two entities.
Source Key
The field in the source collection that is referenced by the foreign key. It must be unique.
Foreign Key 1
The field in the intermediary collection that establishes the association with the source collection.
Foreign Key 2
The field in the intermediary collection that establishes the association with the target collection.
Target Key
The field in the target collection that is referenced by the foreign key. It must be unique.
ON DELETE
ON DELETE refers to the rules applied to foreign key references in related child collections when records in the parent collection are deleted. It is an option used when defining a foreign key constraint. Common ON DELETE options include:
- CASCADE: When a record in the parent collection is deleted, all related records in the child collection are automatically deleted.
- SET NULL: When a record in the parent collection is deleted, the foreign key values in the related child collection records are set to NULL.
- RESTRICT: The default option, it prevents the deletion of a parent collection record if there are related records in the child collection.
- NO ACTION: Similar to RESTRICT, it prevents the deletion of a parent collection record if there are related records in the child collection.

