Sort Field
This feature is provided by the plugin «Collection field: Sort»Introduction
Sort fields are used to sort records in a collection, supporting sorting within groups.
Since the sort field is part of the same collection, a record cannot be assigned to multiple groups when using group sorting.
Installation
Built-in plugin, no separate installation required.
User Manual
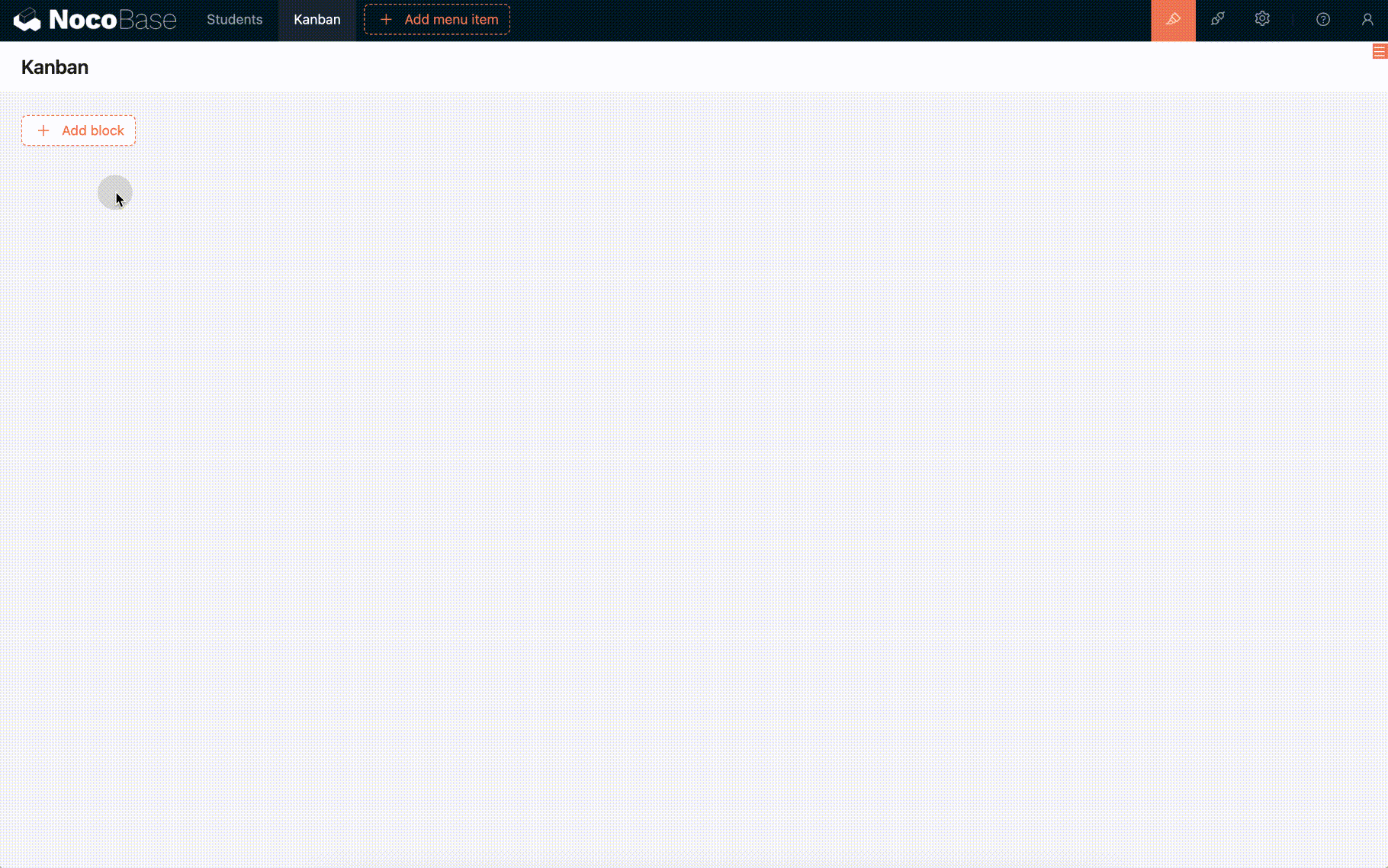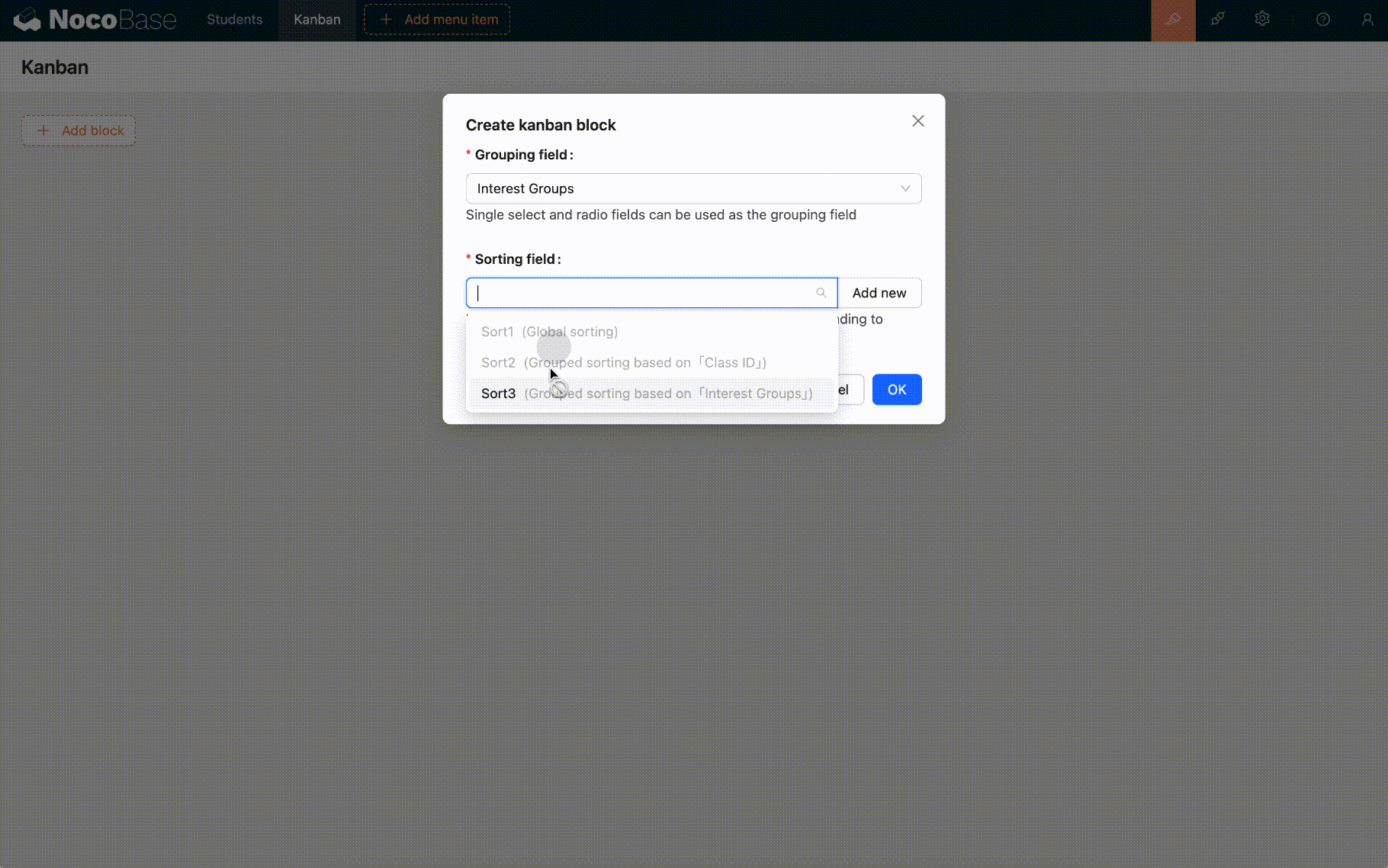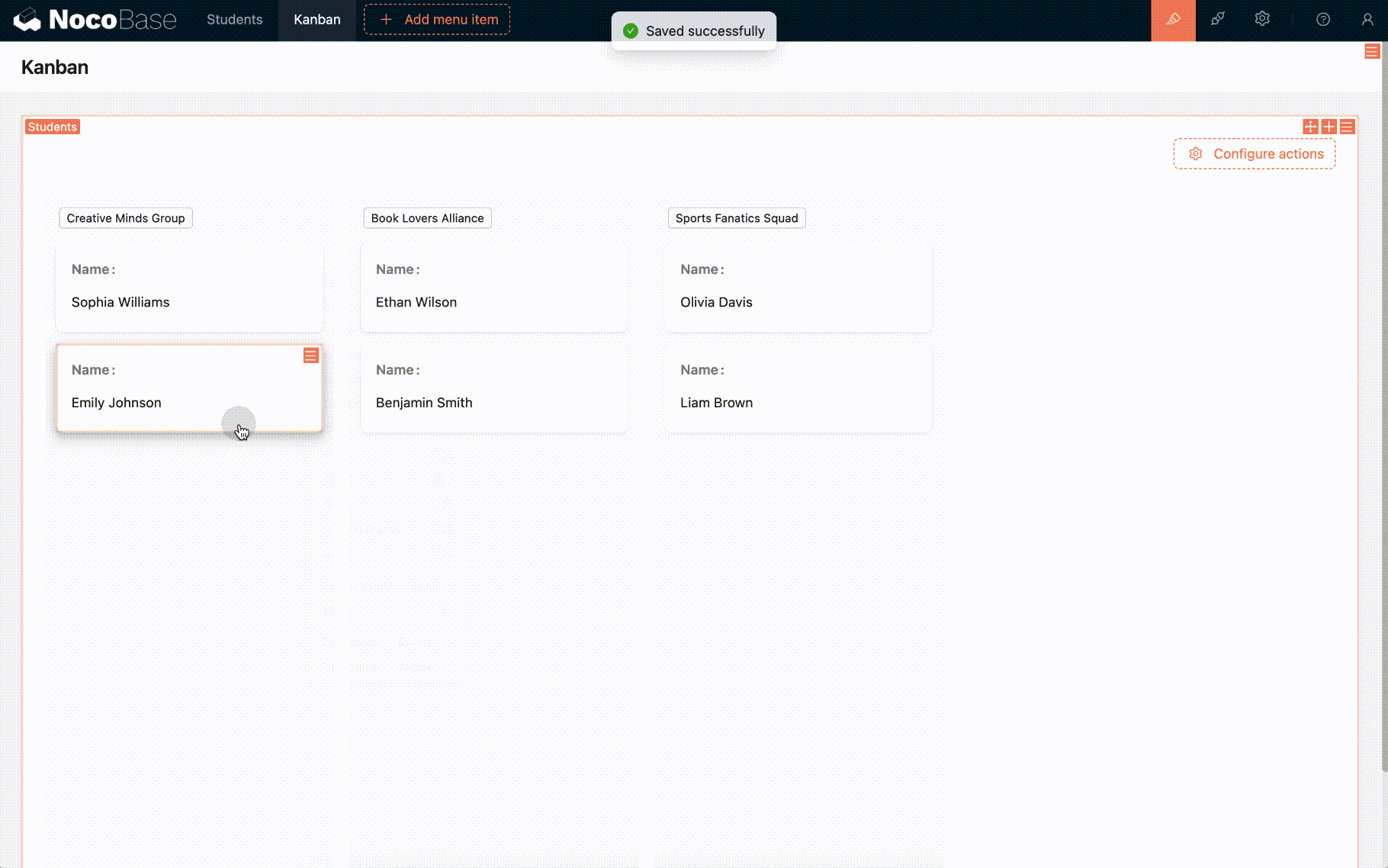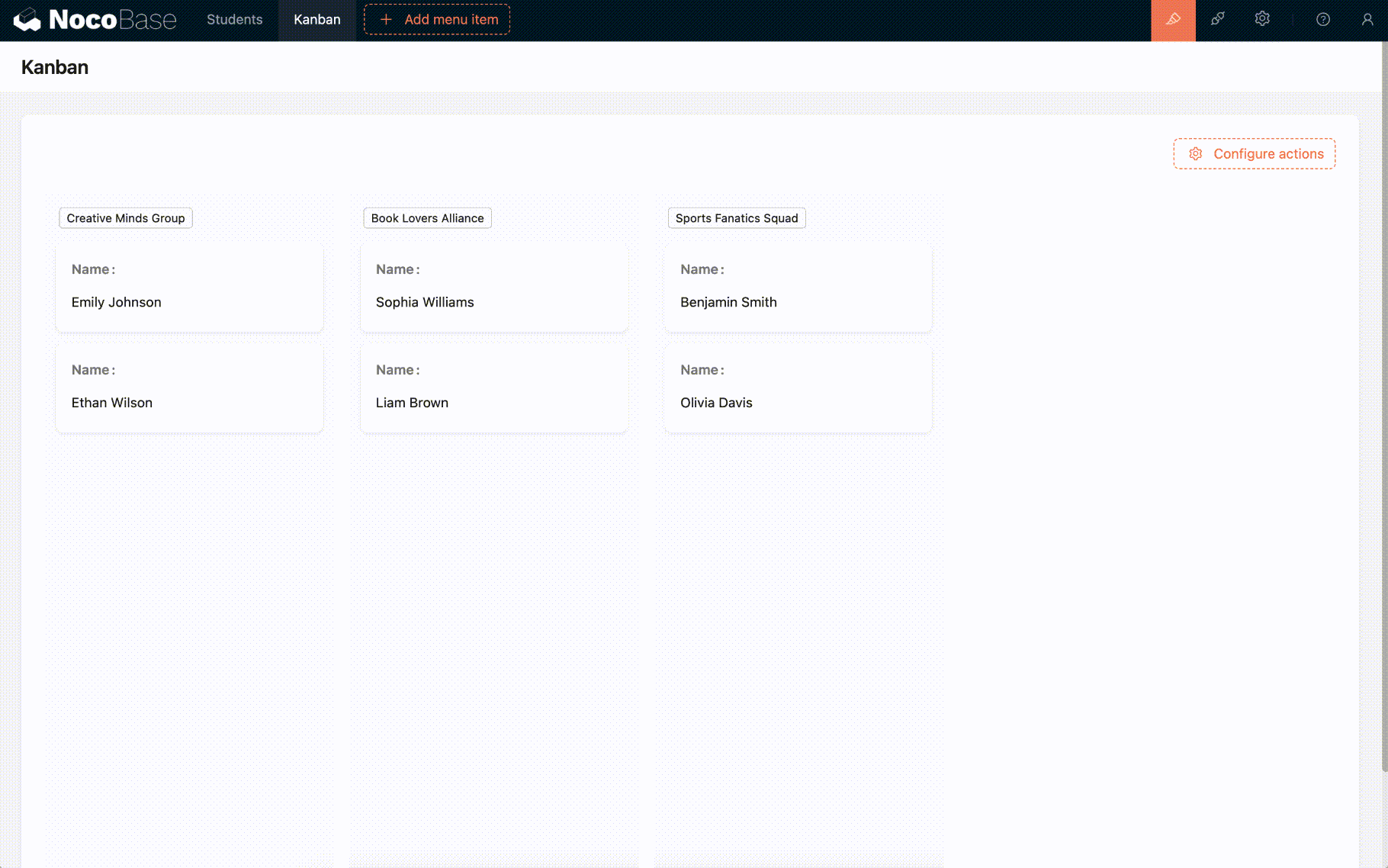
Create a Sort Field
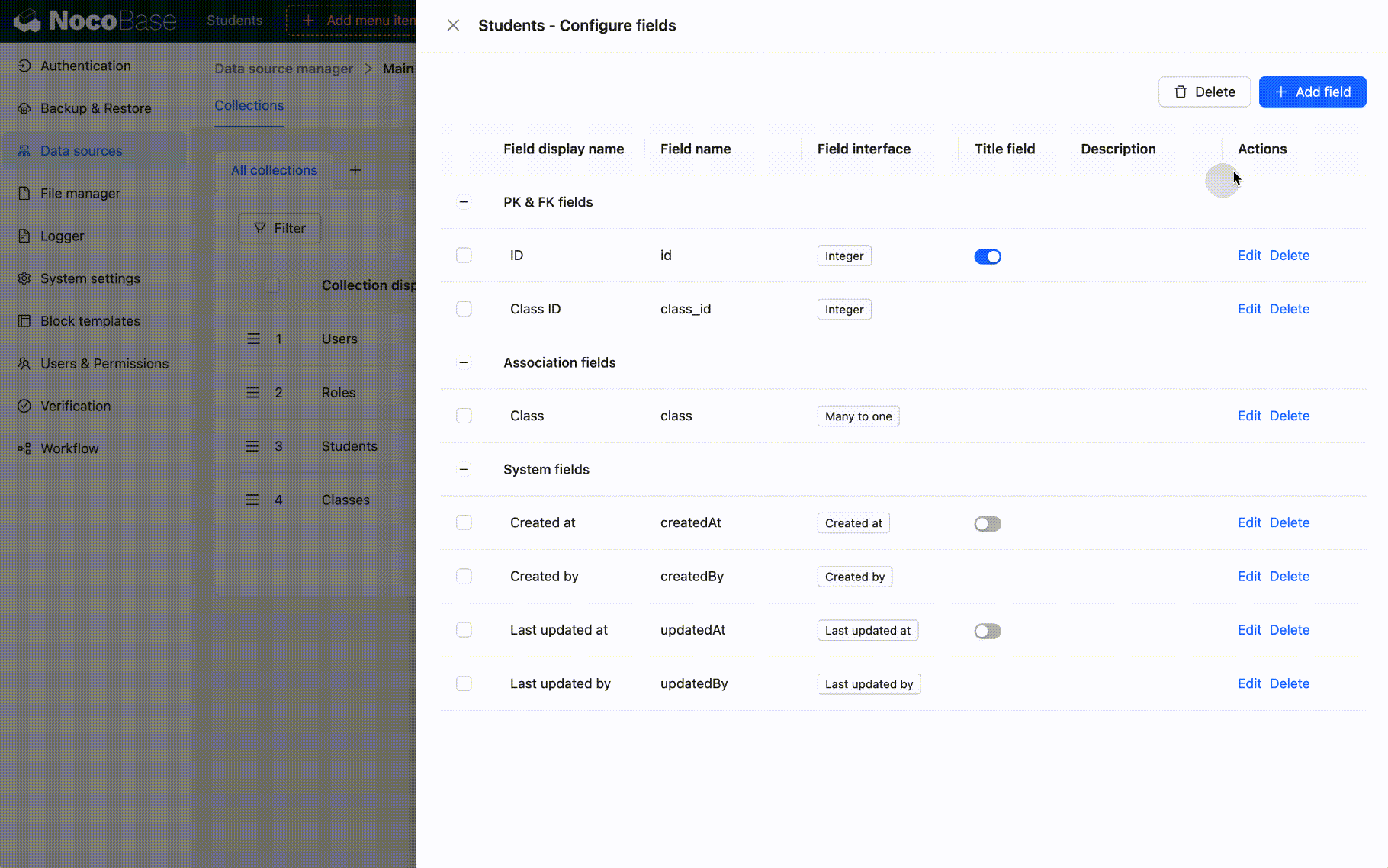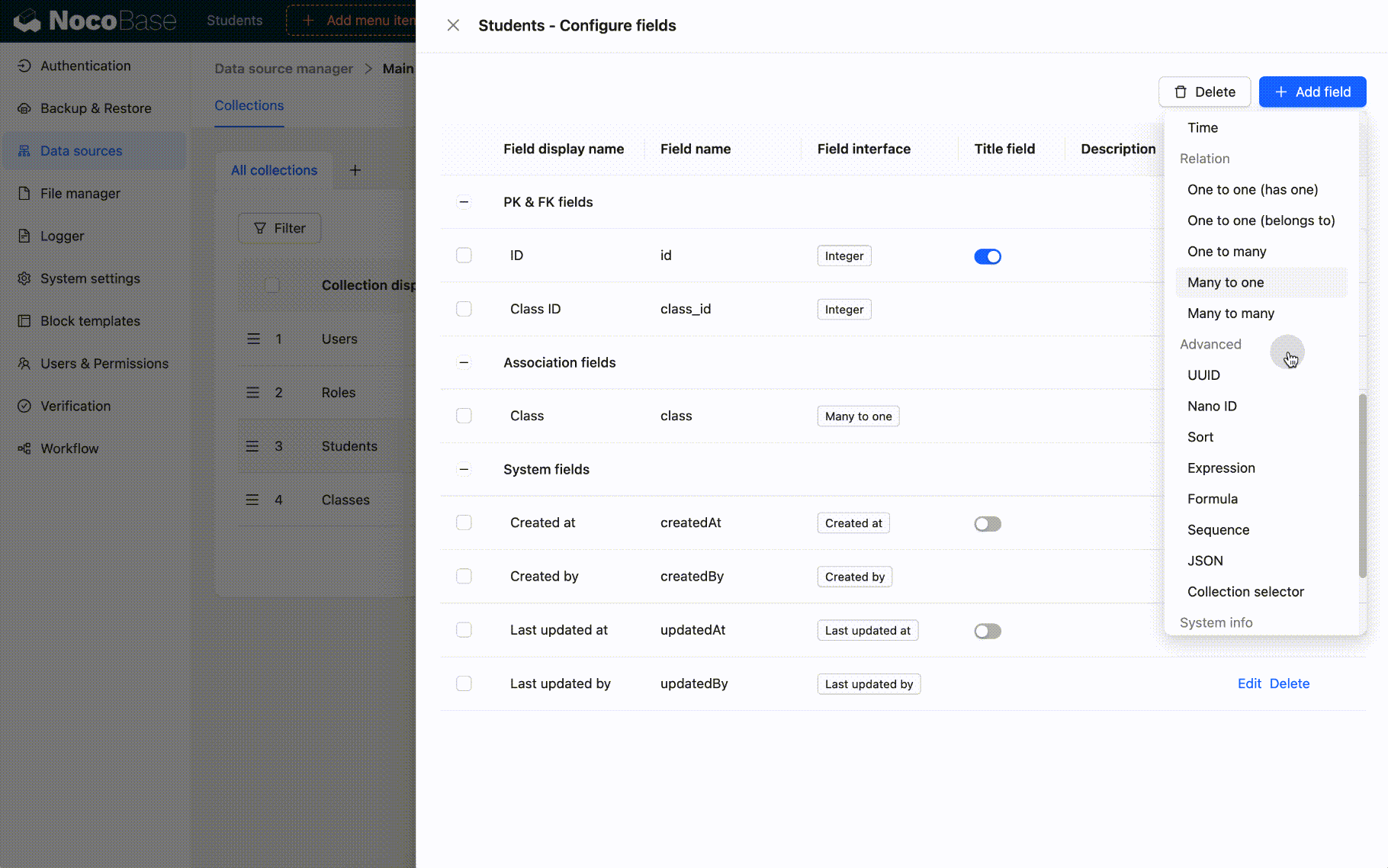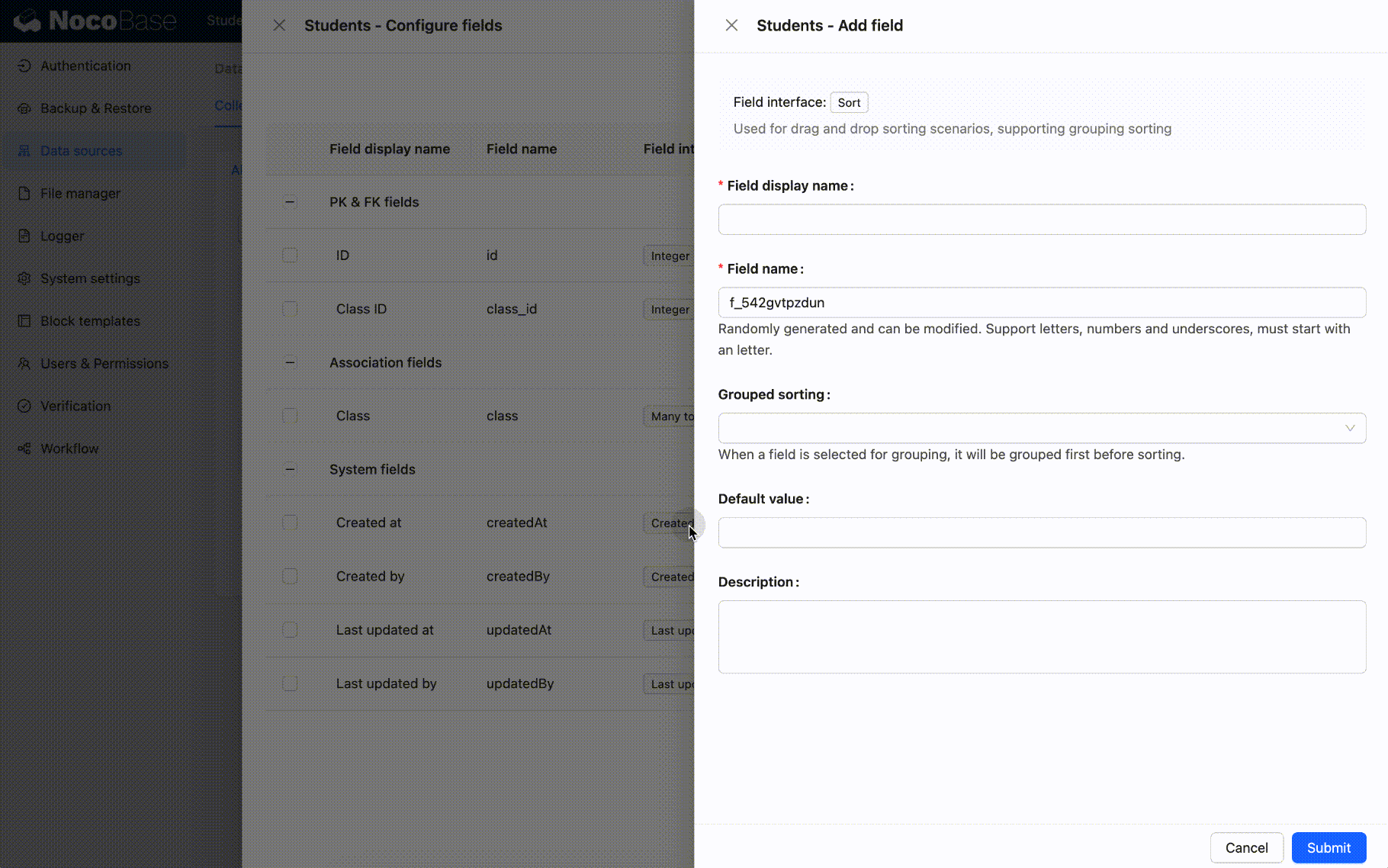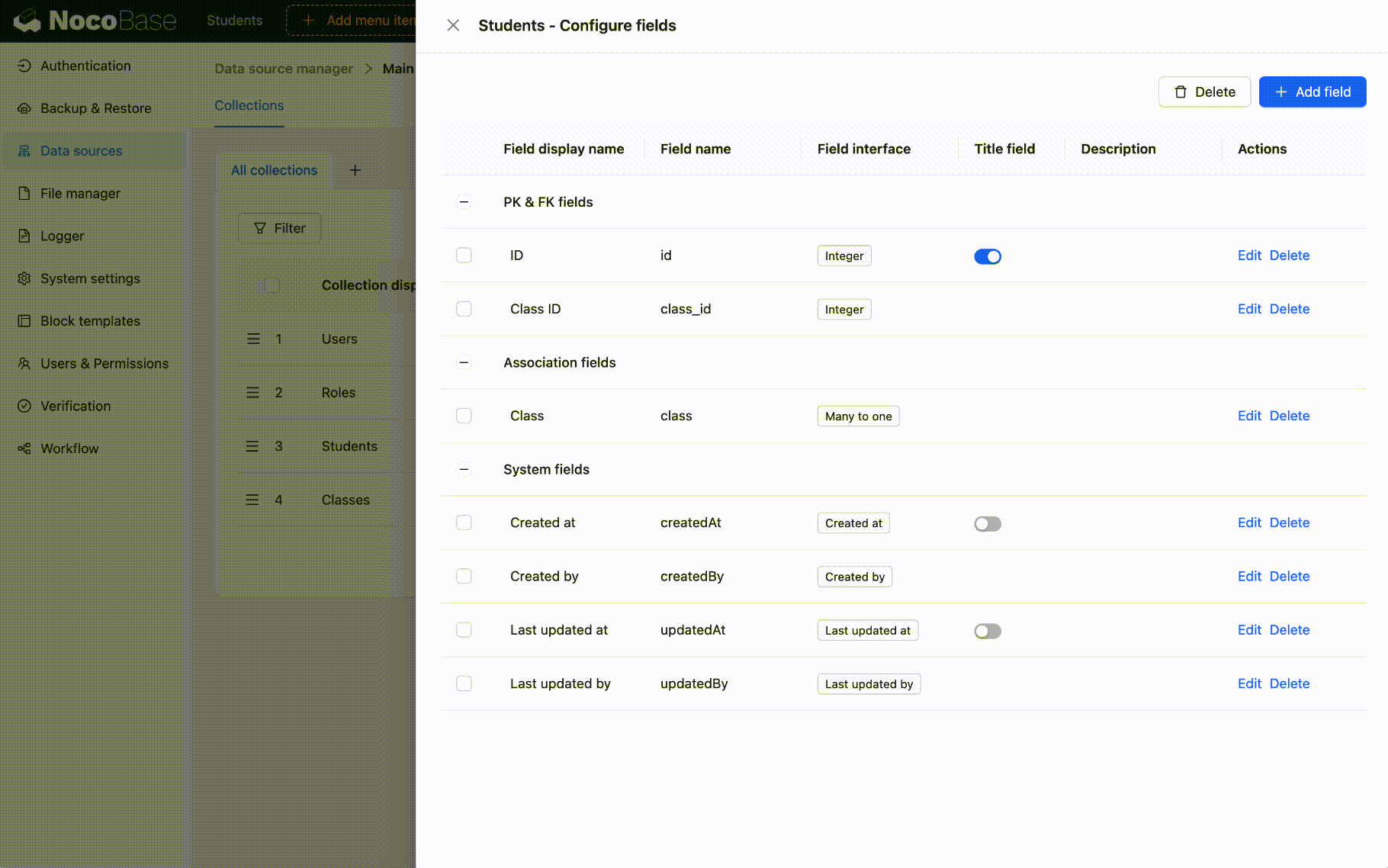
When creating sort fields, the sort values will be initialized:
- If group sorting is not selected, initialization will be based on the primary key field and creation date field.
- If group sorting is selected, the data will be grouped first, and then initialization will be based on the primary key field and creation date field.
- When creating a field, if the sort value initialization fails, the sort field will not be created.
- Within a certain range, if a record moves from position A to position B, the sort values of all records between A and B will change. If any part of this update fails, the entire move operation is rolled back, and the sort values of the related records will not change. :::
Example 1: Create the sort1 field
The sort1 field is not grouped.
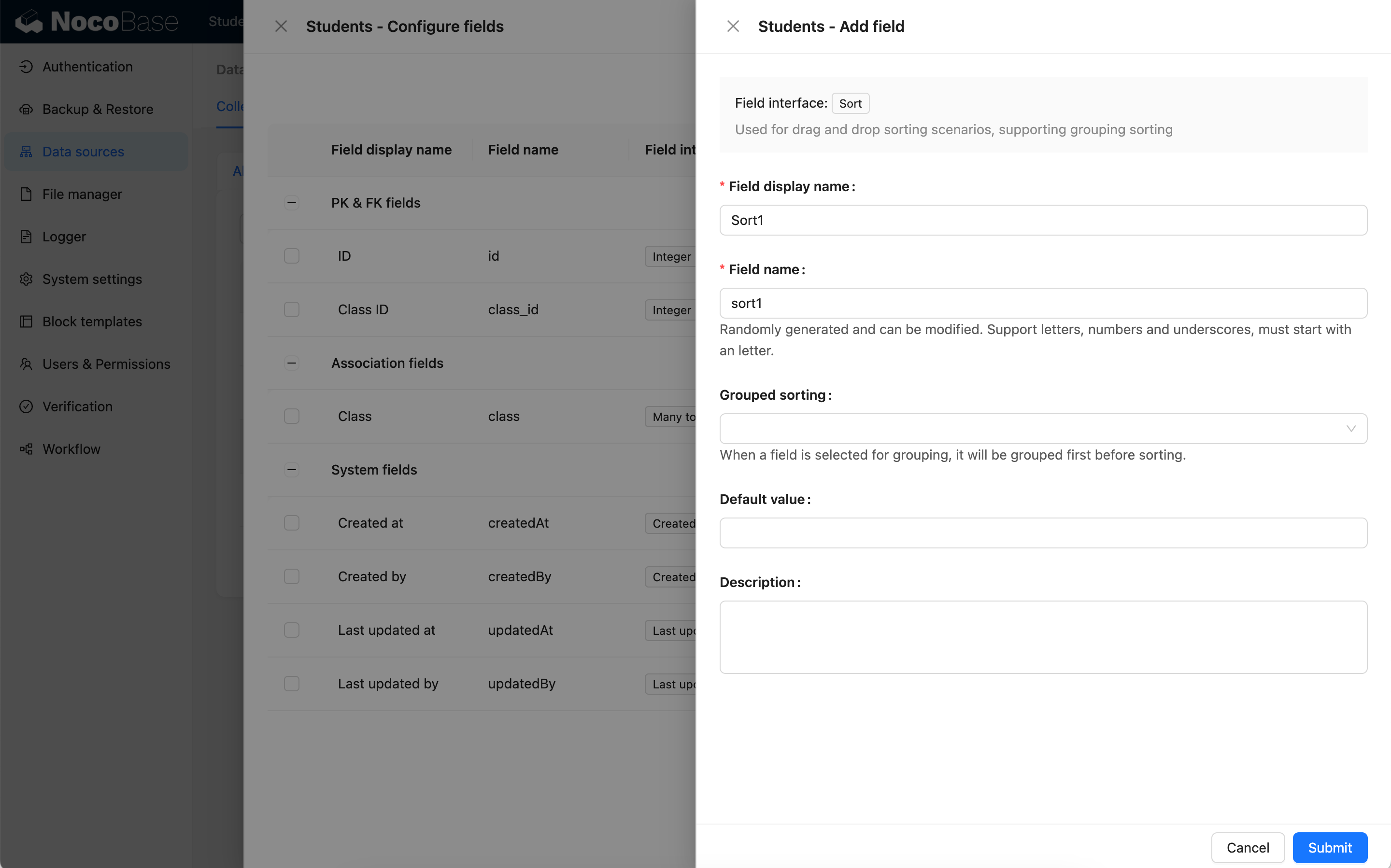
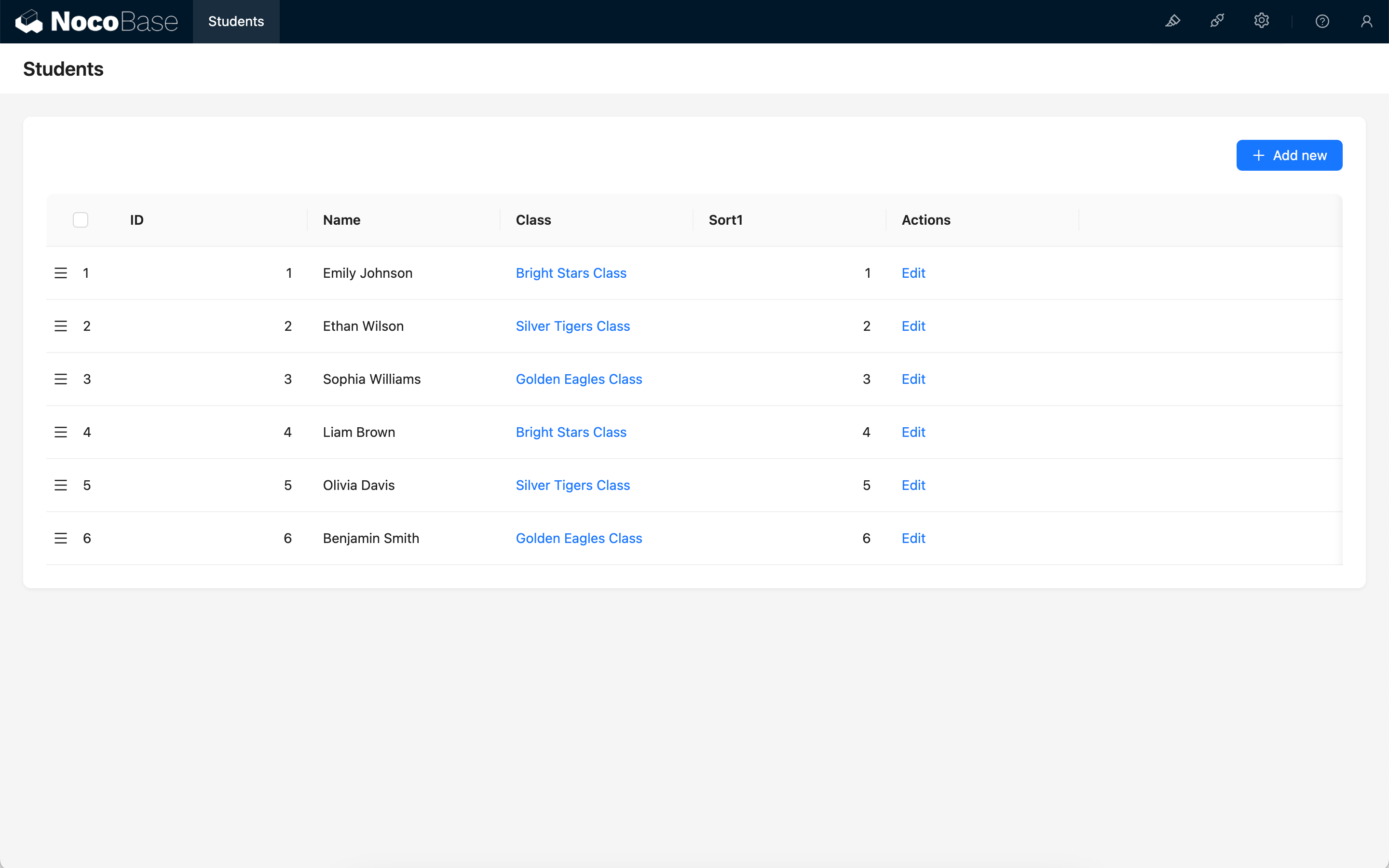
The sort fields of each record will be initialized based on the primary key field and creation date field.
Example 2: Create a sort2 field based on Class ID grouping
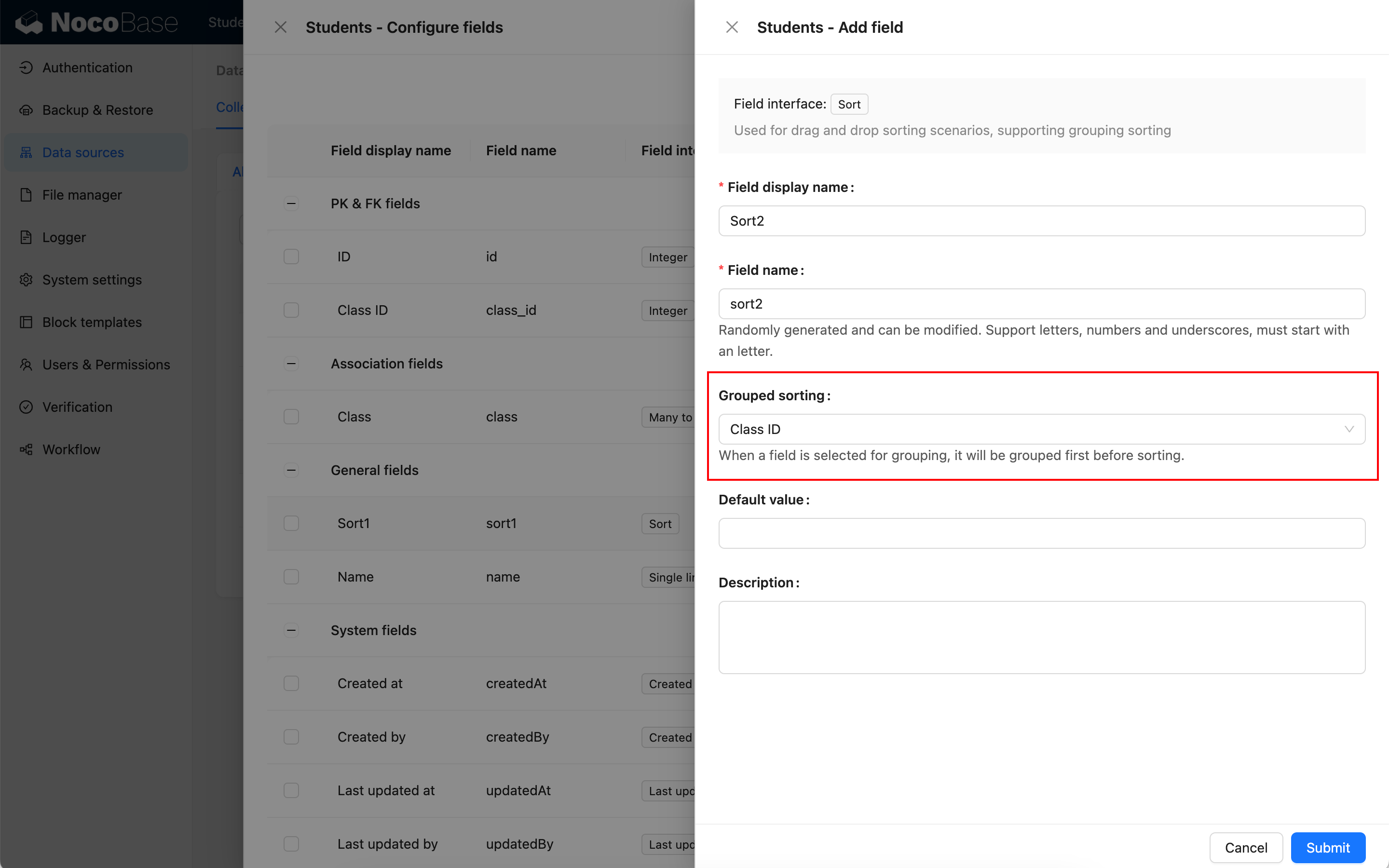
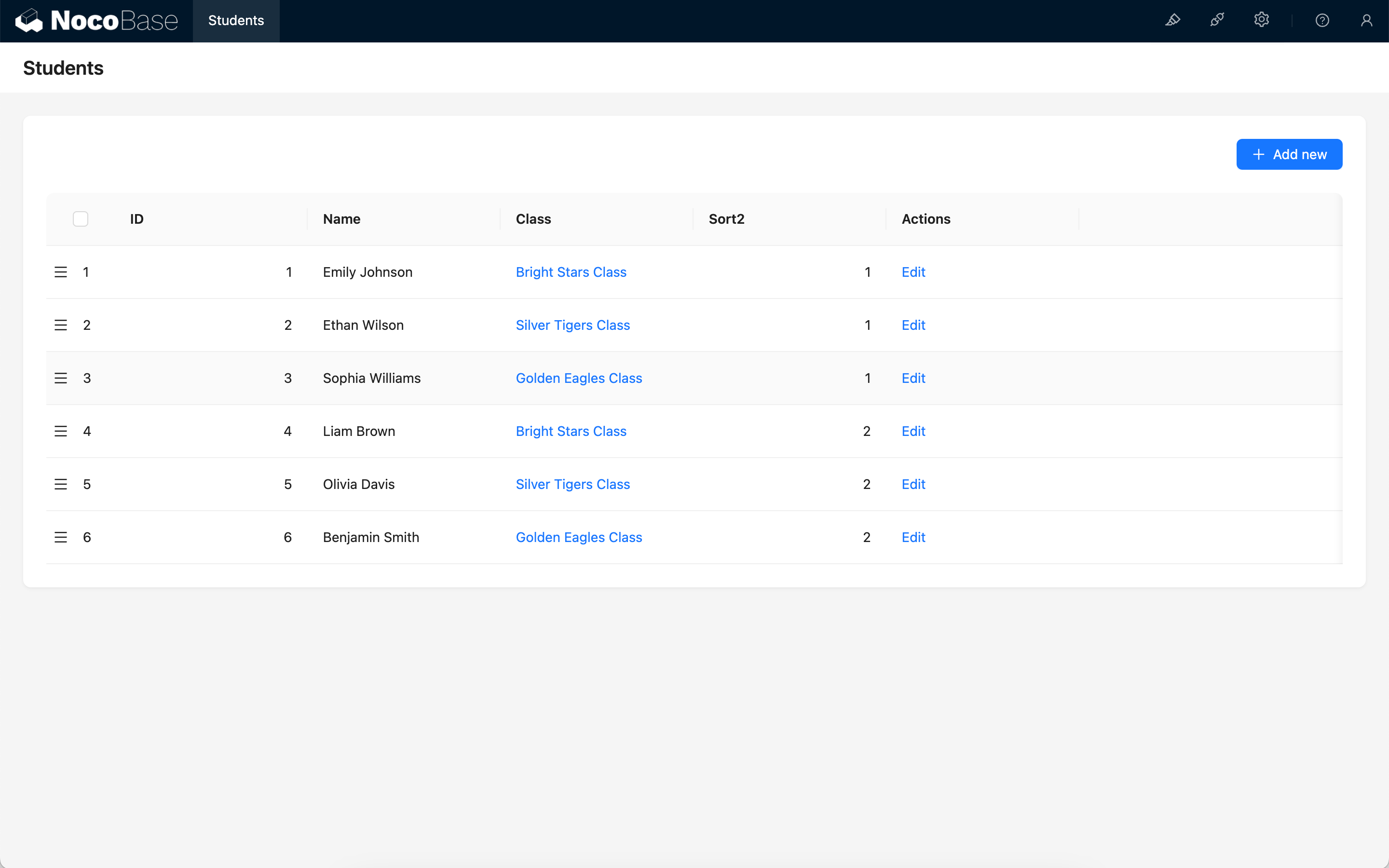
At this time, all records in the collection will be grouped first (grouped by Class ID), and then the sort field (sort2) will be initialized. The initial values of each record are:
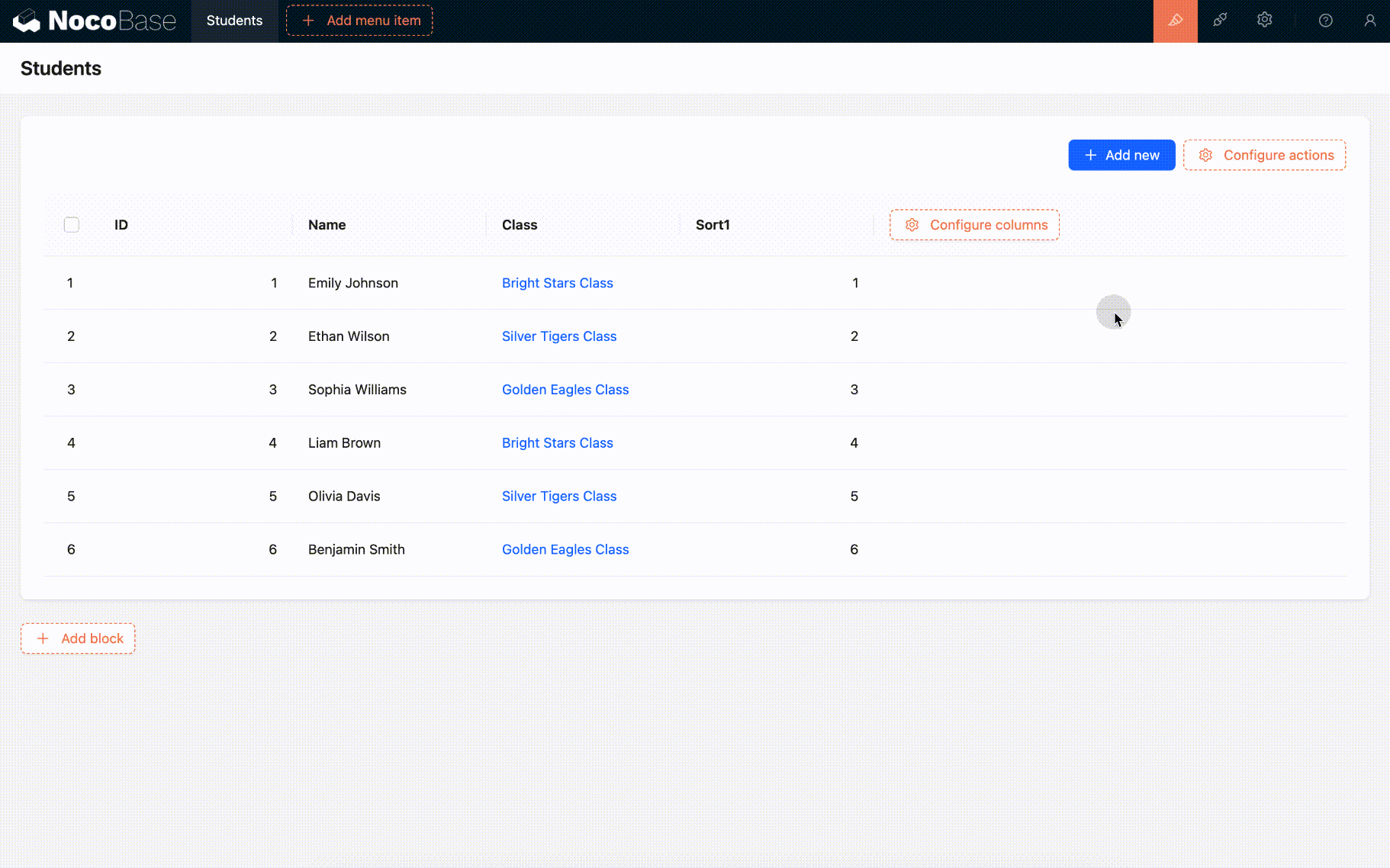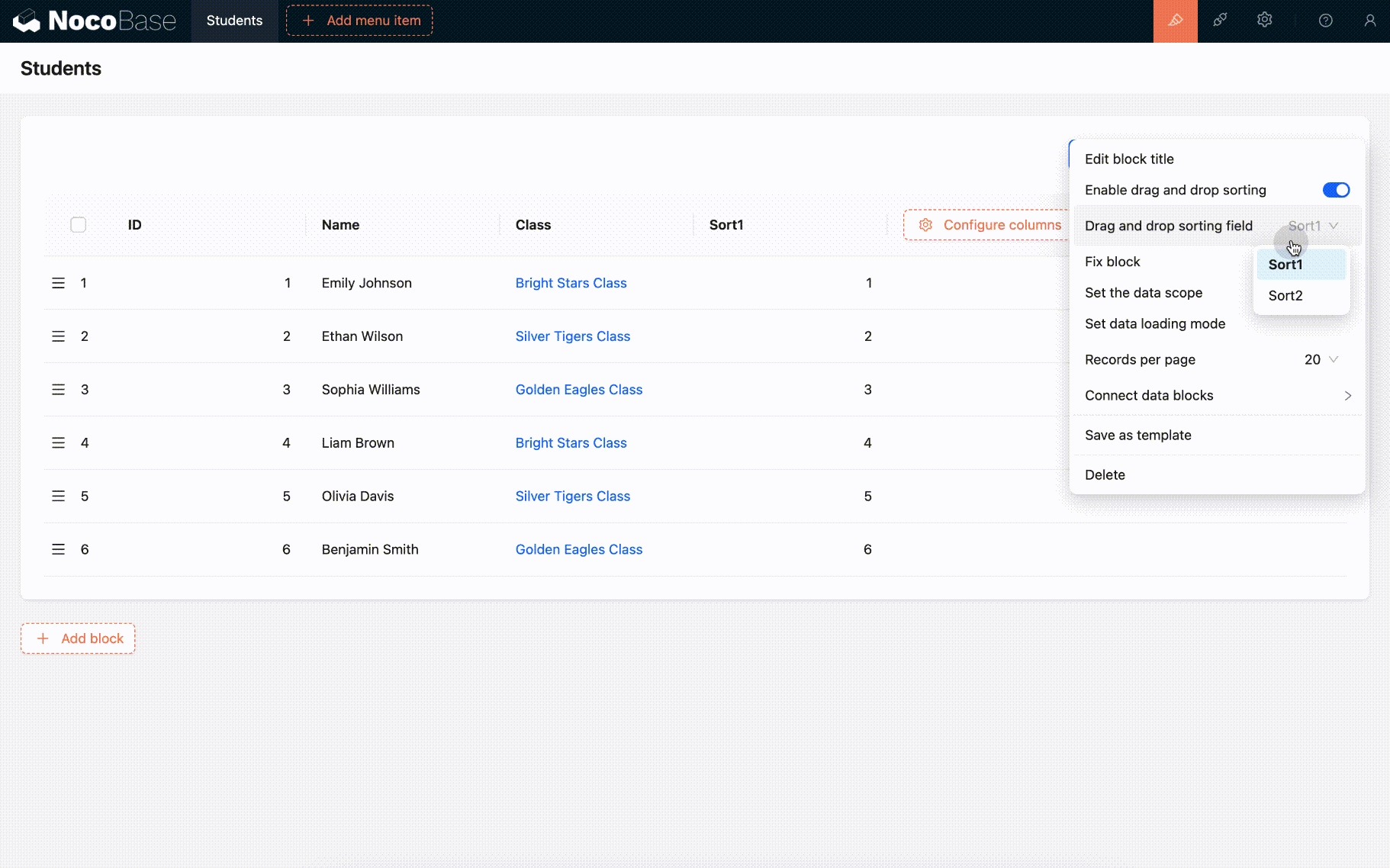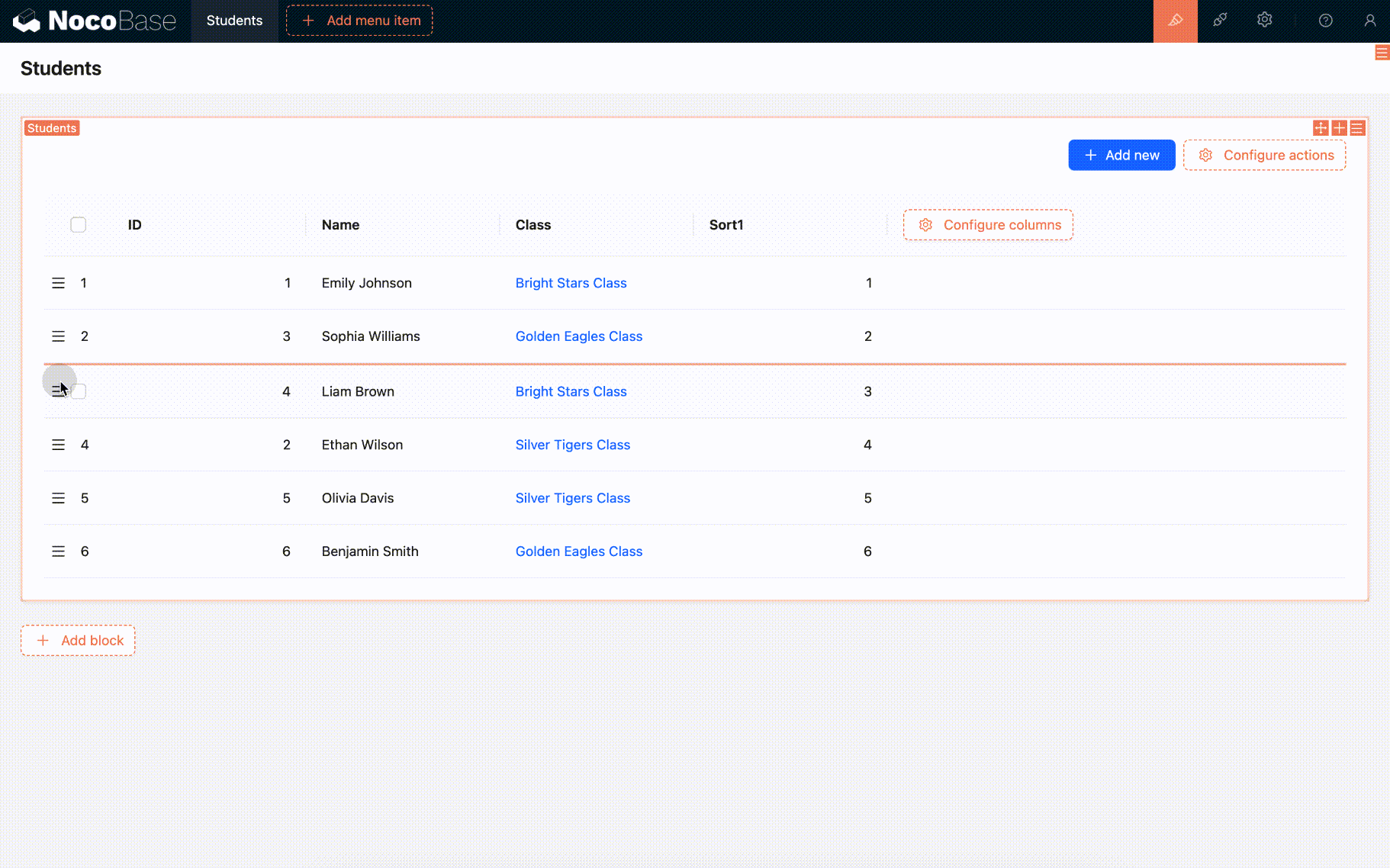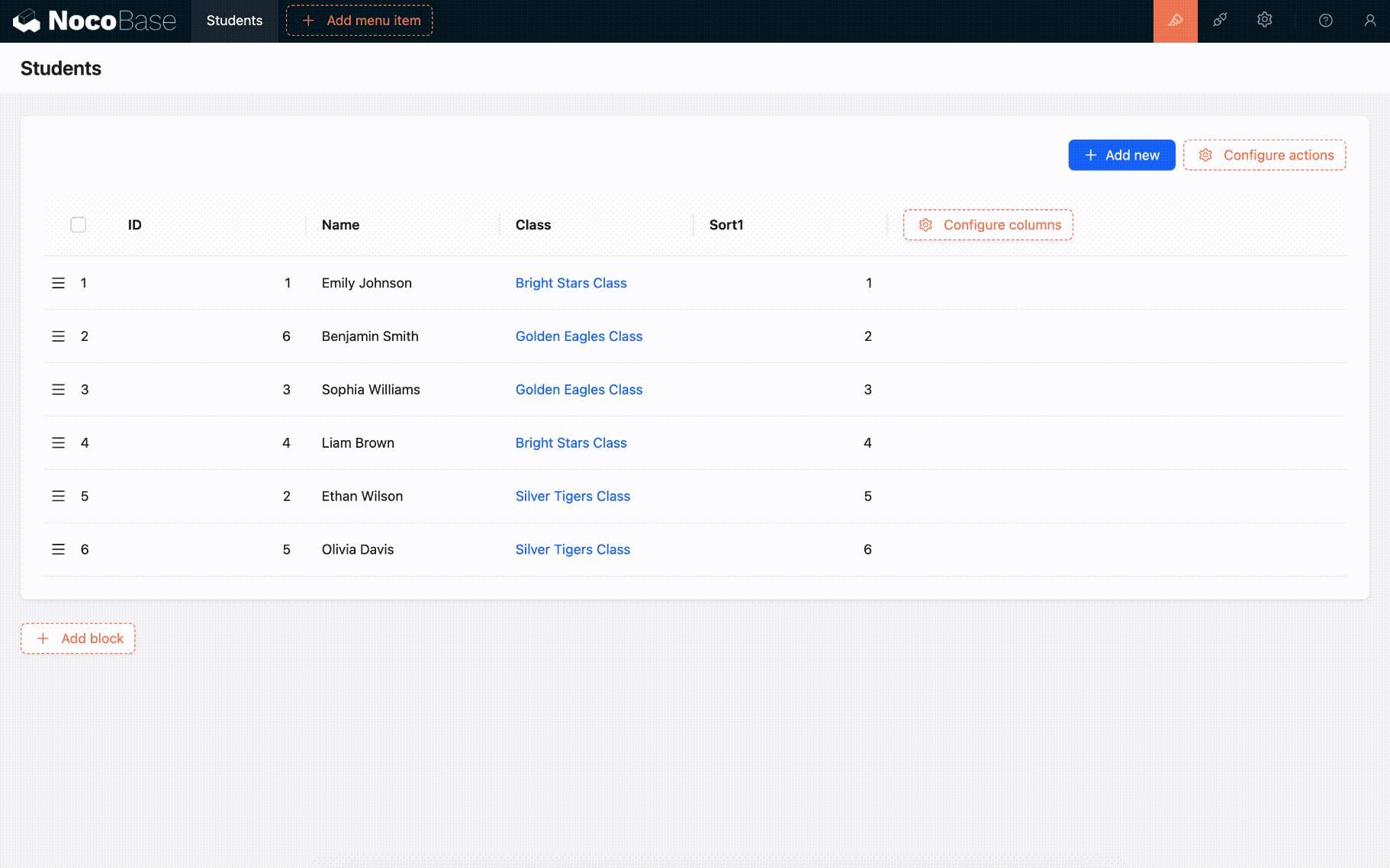
Drag-and-Drop Sorting
Sort fields are mainly used for drag-and-drop sorting of records in various blocks. The blocks that currently support drag-and-drop sorting include tables and boards.
:::warning
- When the same sort field is used for drag-and-drop sorting, using it across multiple blocks may disrupt the existing order.
- The field for table drag-and-drop sorting cannot be a sort field with a grouping rule.
- Exception: In a one-to-many relationship table block, the foreign key can serve as a group.
- Currently, only the board block supports drag-and-drop sorting within groups. :::
Drag-and-Drop Sorting of Table Rows
Table block
Relationship table block
:::warning In a one-to-many relationship block:
- If an ungrouped sort field is selected, all records may participate in the sorting.
- If records are first grouped by the foreign key and then sorted, the sorting rule will only affect the data within the current group.
The final effect is consistent, but the number of records participating in the sort is different. For more details, see Sorting Rule Explanation.
Drag-and-Drop Sorting of Board Cards
Sorting Rule Explanation
Displacement between ungrouped (or same-group) elements
Suppose there is a set of data:
When an element, say 5, moves forward to the position of 3, only the positions of items 3, 4, and 5 change. Item 5 takes the position of 3, and items 3 and 4 each shift back one position.
If we then move item 6 backward to the position of 8, item 6 takes the position of 8, and items 7 and 8 each shift forward one position.
Movement of elements between different groups
When sorting by group, if a record is moved to another group, its group assignment will also change. For example:
When item 1 is moved after item 6 (the default behavior), its group will also change from A to B.
Sort changes are unrelated to the data displayed on the interface
For example, consider a set of data:
The interface only displays a filtered view:
When item 1 is moved to the position of item 9, the positions of all intermediate items (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8) will also change, even though they are not visible.
The interface now displays the new order based on the filtered items:

