AI Agent · Prompt Engineering Guide
From "how to write" to "writing well," this guide teaches you how to write high-quality prompts in a simple, stable, and reusable way.
1. Why Prompts are Crucial
A prompt is the "job description" for an AI agent, directly determining its style, boundaries, and output quality.
Comparison Example:
❌ Unclear Prompt:
✅ Clear and Controllable Prompt:
Conclusion: A good prompt clearly defines "who it is, what to do, how to do it, and to what standard," making the AI's performance stable and controllable.
2. The "Nine Elements" Golden Formula for Prompts
A structure proven effective in practice:
2.1 Element Descriptions
| Element | What it Solves | Why it's Effective |
|---|---|---|
| Naming | Clarifies identity and style | Helps the AI establish a "sense of role" |
| Dual Instructions | Distinguishes "who I am" from "what I need to do" | Reduces role confusion |
| Simulated Confirmation | Restates understanding before execution | Prevents deviation |
| Repetition | Key points appear repeatedly | Increases priority |
| Hard Rules | MUST/ALWAYS/NEVER | Establishes a baseline |
| Background Information | Necessary knowledge and constraints | Reduces misunderstanding |
| Positive Reinforcement | Guides expectations and style | More stable tone and performance |
| Reference Examples | Provides a direct model to imitate | Output is closer to expectations |
| Negative Examples | Avoids common pitfalls | Corrects mistakes, becoming more accurate with use |
2.2 Quick Start Template
3. Practical Example: Viz (Data Analysis)
Let's combine the nine elements to create a complete, "ready-to-use" example.
Design Points
- "Authenticity" appears multiple times in the workflow, repetition, and rules sections (strong reminder)
- Choose a two-part "description + JSON" output for easy frontend integration
- Specify "read-only SQL" to reduce risk
4. How to Improve Prompts Over Time
4.1 Five-Step Iteration
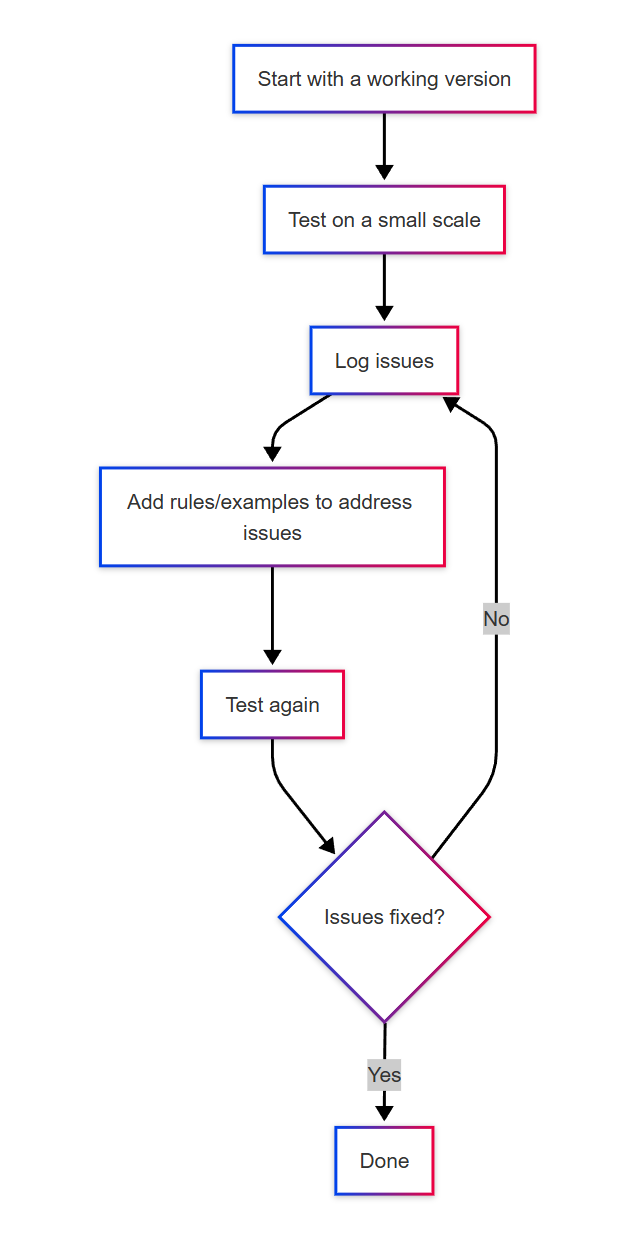
It is recommended to test 5–10 typical tasks at once, completing one round within 30 minutes.
4.2 Principles and Ratios
- Prioritize Positive Guidance: First, tell the AI what it should do
- Problem-Driven Improvement: Add constraints only when issues arise
- Moderate Constraints: Don't pile on "prohibitions" from the start
Empirical Ratio: 80% Positive : 20% Negative.
4.3 A Typical Optimization
Problem: Overloaded charts, poor readability Optimization:
- In "Background Information," add: one theme per chart
- In "Reference Examples," provide a "single-metric chart"
- If the problem persists, add a hard constraint in "Hard Rules/Repetition"
5. Advanced Techniques
5.1 Use XML/Tags for Clearer Structure (Recommended for Long Prompts)
When the content exceeds 1000 characters or can be confusing, using tags for partitioning is more stable:
5.2 Layered "Background + Task" Approach (A More Intuitive Way)
- Background (long-term stability): Who this agent is, its style, and what capabilities it has
- Task (on-demand): What to do now, which metrics to focus on, and what the default scope is
This naturally matches NocoBase's "Agent + Task" model: a fixed background with flexible tasks.
5.3 Modular Reuse
Break down common rules into modules to mix and match as needed:
Data Security Module
Output Structure Module
6. Golden Rules (Practical Conclusions)
- One AI for one type of job; specialization is more stable
- Examples are more effective than slogans; provide positive models first
- Use MUST/ALWAYS/NEVER to set boundaries
- Use a process-oriented approach to reduce uncertainty
- Start small, test more, modify less, and iterate continuously
- Don't over-constrain; avoid "hard-coding" behavior
- Log issues and changes to create versions
- 80/20: First, explain "how to do it right," then constrain "what not to do wrong"
7. FAQ
Q1: What's the ideal length?
- Basic agent: 500–800 characters
- Complex agent: 800–1500 characters
- Not recommended >2000 characters (can be slow and redundant) Standard: Cover all nine elements, but with no fluff.
Q2: What if the AI doesn't follow instructions?
- Use MUST/ALWAYS/NEVER to clarify boundaries
- Repeat key requirements 2–3 times
- Use tags/partitions to enhance structure
- Provide more positive examples, less abstract principles
- Evaluate if a more powerful model is needed
Q3: How to balance positive and negative guidance? First, write the positive parts (role, workflow, examples), then add constraints based on errors, and only constrain points that are "repeatedly wrong."
Q4: Should it be updated frequently?
- Background (identity/style/core capabilities): Long-term stability
- Task (scenario/metrics/scope): Adjust according to business needs
- Create a new version for any changes and log "why it was changed."
8. Next Steps
Hands-on Practice
- Choose a simple role (e.g., customer service assistant), write a "workable version" using the nine elements, and test it with 5 typical tasks
- Find an existing agent, collect 3–5 real issues, and perform a small iteration
Further Reading
- AI Agent · Administrator Configuration Guide: Put prompts into actual configuration
- Dedicated manuals for each AI agent: View complete role/task templates
Conclusion
Get it working, then refine it. Start with a "working" version, and continuously collect issues, add examples, and refine rules in real tasks. Remember: First, tell it how to do things right (positive guidance), then constrain it from doing things wrong (moderate restriction).

