快速开始:构建可编排的按钮组件
在 React 中,我们通常这样渲染一个按钮组件:
上述代码虽然简单,但属于静态组件,无法满足无代码平台对可配置性和编排能力的需求。
在 NocoBase 的 FlowEngine 中,我们可以通过 FlowModel + FlowDefinition 快速构建支持配置和事件驱动的组件,实现更强大的无代码能力。
第一步:使用 FlowModel 渲染组件
🧠 关键概念
FlowModel是 FlowEngine 中的核心组件模型,封装组件逻辑、渲染和配置能力。- 每个 UI 组件都可以通过
FlowModel进行实例化并统一管理。
📌 实现步骤
1. 创建自定义模型类
2. 创建 model 实例
3. 使用 <FlowModelRenderer /> 渲染
第二步:添加 PropsFlow,使按钮属性可配置
💡 为什么要用 PropsFlow?
使用 Flow 而非静态 props,可以实现属性的:
- 动态配置
- 可视化编辑
- 状态回放与持久化
🛠 关键改造点
1. 定义按钮属性的 Flow
2. 使用 stepParams 替代静态 props
✅ 使用
stepParams是 FlowEngine 推荐方式,可避免不可序列化数据(如 React 组件)的问题。
3. 启用属性配置界面
第三步:支持按钮事件流(EventFlow)
🎯 场景:点击按钮后弹出确认框
1. 监听 onClick 事件
使用无入侵的方式,添加 onClick
2. 定义事件流
补充说明:
- 事件流(EventFlow)可以让按钮的行为通过流程灵活配置,比如弹窗、消息、API 调用等。
- 你可以为不同事件(如
onClick,onMouseEnter等)注册不同的事件流,满足复杂业务需求。
3. 配置事件流参数
在创建模型时,可以通过 stepParams 配置事件流的默认参数:
模型对比图:ReactComponent vs FlowModel
Flow 并不会改变组件的实现方式。它只是为 ReactComponent 增加了对 PropsFlow 和 EventFlow 的支持,从而让组件的属性和事件都可以通过可视化方式配置和编排。
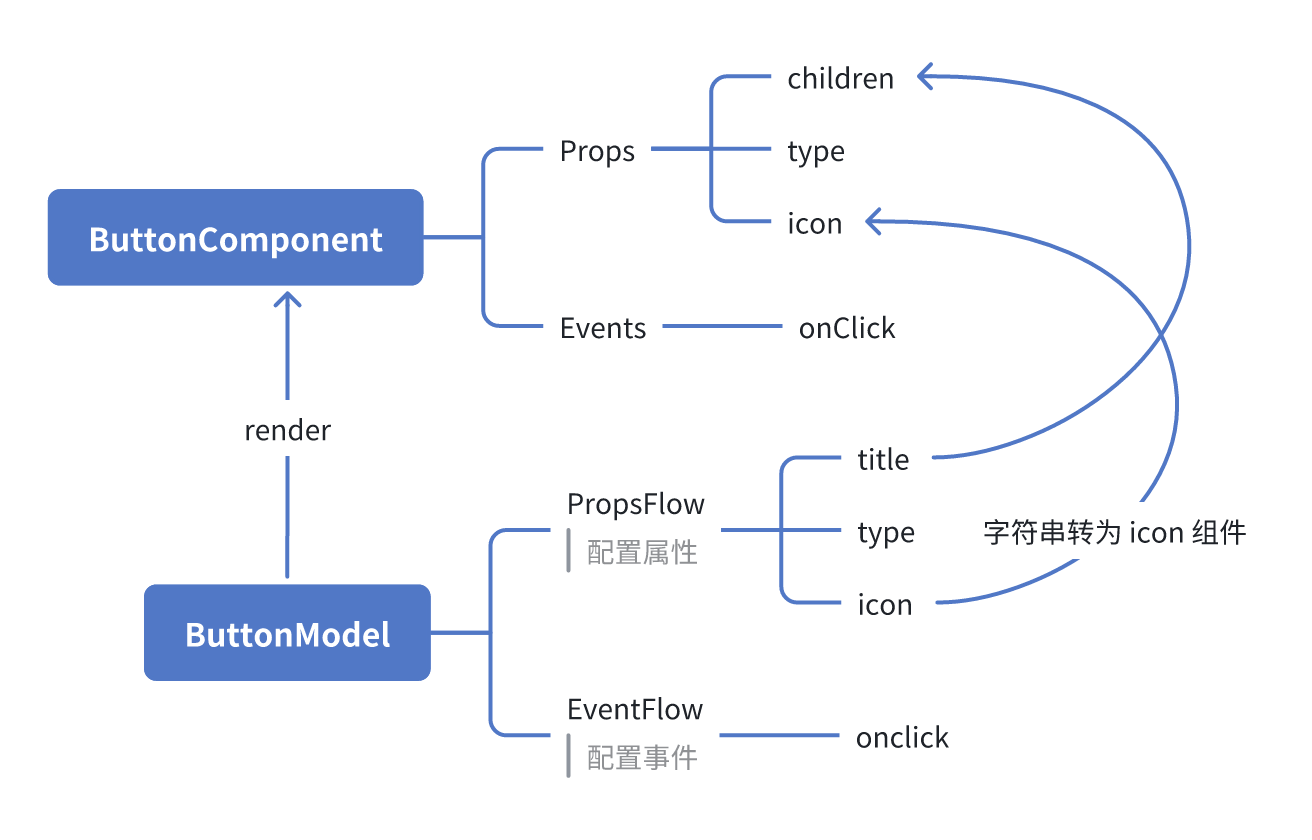
ReactComponent
FlowModel
总结
通过以上三步,我们完成了一个支持配置与事件编排的按钮组件,具备以下优势:
- 🚀 可视化配置属性(如标题、类型、图标)
- 🔄 事件响应可被流程接管(如点击弹窗)
- 🔧 支持后续拓展(如条件逻辑、变量绑定等)
这种模式也适用于表单、列表、图表等任何 UI 组件,在 NocoBase 的 FlowEngine 中,一切皆可编排。

