Execution Plan (History)
After a workflow is triggered, a corresponding execution plan is created to track the execution process of this task. Each execution plan has a status value to indicate the current execution status, which can be viewed in the list and details of the execution history:

When all nodes in the main process branch are executed to the end of the process with a "Completed" status, the entire execution plan will end with a "Completed" status. When a node in the main process branch has a final status such as "Failed", "Error", "Cancelled", or "Rejected", the entire execution plan will be terminated prematurely with the corresponding status. When a node in the main process branch has a "Waiting" status, the entire execution plan will be paused, but will still show a "Running" status, until the waiting node is resumed. Different node types handle the waiting state differently. For example, a manual node needs to wait for manual processing, while a delay node needs to wait for the specified time to pass before continuing.
The statuses of an execution plan are as follows:
| Status | Corresponding status of the last executed node in the main process | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Queued | - | The workflow has been triggered and an execution plan has been generated, waiting in the queue for the scheduler to arrange execution. |
| Running | Waiting | The node requires a pause, waiting for further input or a callback to continue. |
| Completed | Completed | No issues were encountered, and all nodes were executed one by one as expected. |
| Failed | Failed | Failed because the node configuration was not met. |
| Error | Error | The node encountered an unhandled program error and terminated prematurely. |
| Cancelled | Cancelled | A waiting node was cancelled externally by the workflow administrator, terminating prematurely. |
| Rejected | Rejected | In a manual processing node, it was manually rejected, and the subsequent process will not continue. |
In the Quick Start example, we already know that by viewing the details of a workflow's execution history, we can check whether all nodes were executed normally, as well as the execution status and result data of each executed node. In some advanced workflows and nodes, a node may have multiple results, such as the result of a loop node:
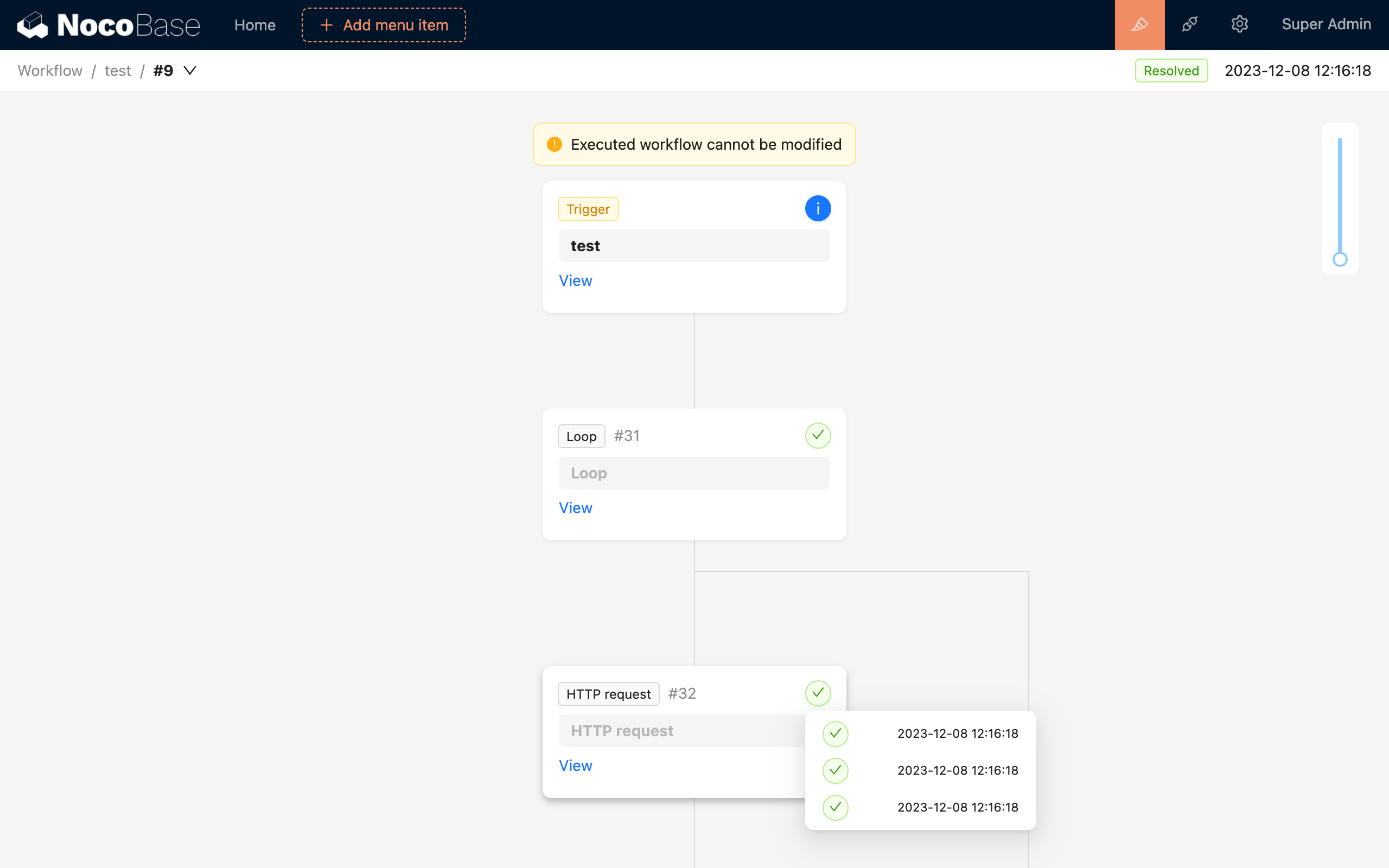
Workflows can be triggered concurrently, but they are executed sequentially in a queue. Even if multiple workflows are triggered at the same time, they will be executed one by one, not in parallel. Therefore, a "Queued" status means that other workflows are currently running and it needs to wait.
The "Running" status only indicates that the execution plan has started and is usually paused due to the waiting state of an internal node. It does not mean that this execution plan has preempted the execution resources at the head of the queue. Therefore, when there is a "Running" execution plan, other "Queued" execution plans can still be scheduled to start.
Node Execution Status
The status of an execution plan is determined by the execution of each of its nodes. In an execution plan after a trigger, each node produces an execution status after it runs, and this status determines whether the subsequent process will continue. Normally, after a node executes successfully, the next node will be executed, until all nodes are executed in sequence or the process is interrupted. When encountering flow control-related nodes, such as branches, loops, parallel branches, delays, etc., the execution flow to the next node is determined based on the conditions configured in the node and the runtime context data.
The possible statuses of a node after execution are as follows:
| Status | Is Final State | Terminates Prematurely | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waiting | No | No | The node requires a pause, waiting for further input or a callback to continue. |
| Completed | Yes | No | No issues were encountered, executed successfully, and continues to the next node until the end. |
| Failed | Yes | Yes | Failed because the node configuration was not met. |
| Error | Yes | Yes | The node encountered an unhandled program error and terminated prematurely. |
| Cancelled | Yes | Yes | A waiting node was cancelled externally by the workflow administrator, terminating prematurely. |
| Rejected | Yes | Yes | In a manual processing node, it was manually rejected, and the subsequent process will not continue. |
Except for the "Waiting" status, all other statuses are final states for node execution. Only when the final state is "Completed" will the process continue; otherwise, the entire workflow execution will be terminated prematurely. When a node is in a branch flow (parallel branch, condition, loop, etc.), the final state produced by the node's execution will be handled by the node that initiated the branch, and this determines the flow of the entire workflow.
For example, when we use a condition node in "'Yes' to continue" mode, if the result is "No" during execution, the entire workflow will be terminated prematurely with a "Failed" status, and subsequent nodes will not be executed, as shown in the figure below:
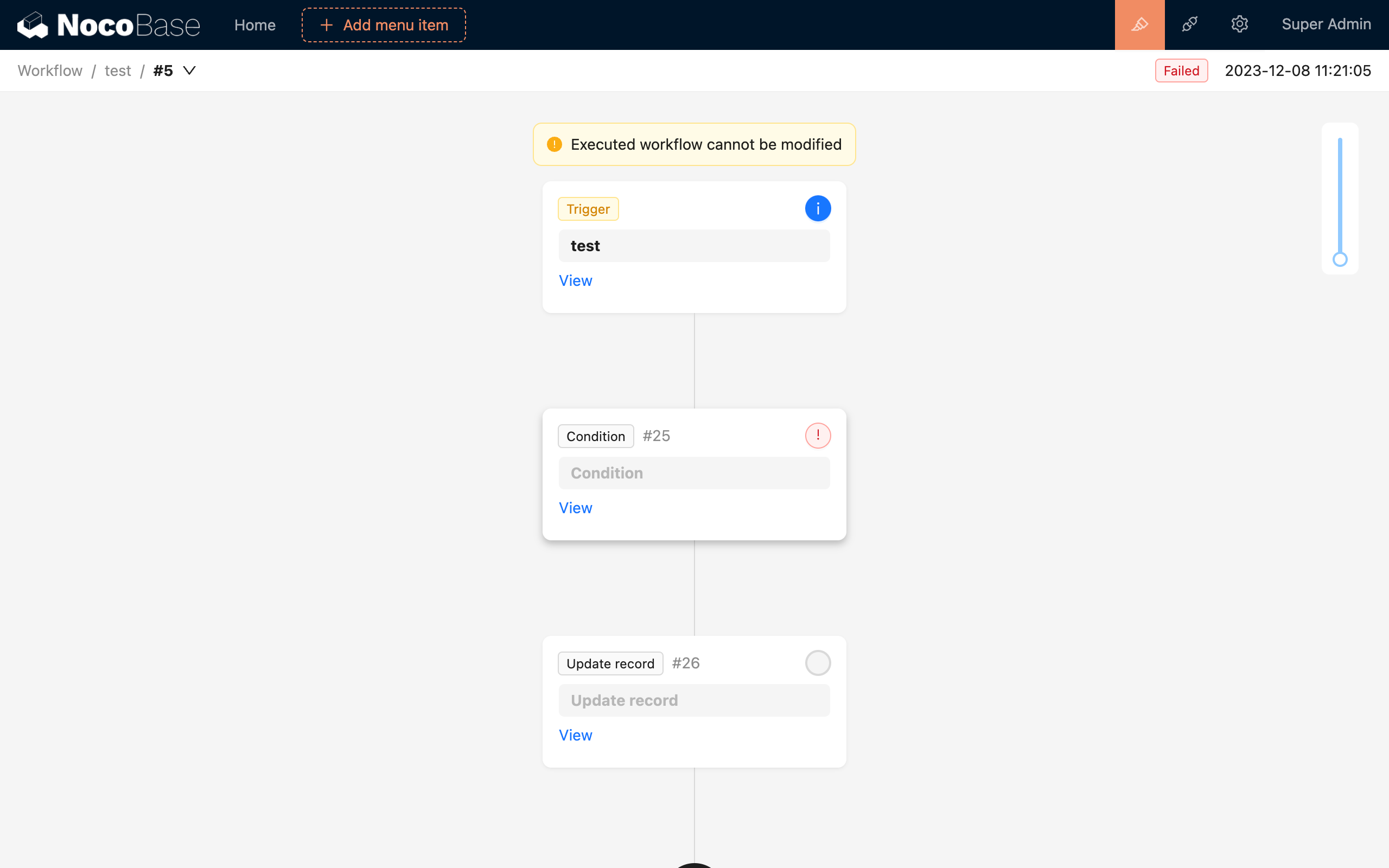
All terminating statuses other than "Completed" can be considered failures, but the reasons for failure are different. You can view the node's execution results to further understand the cause of the failure.

