Scheduled Task
Introduction
A scheduled task is an event triggered by a time condition, which comes in two modes:
- Custom time: Regular cron-like triggering based on system time.
- Collection time field: Triggering based on the value of a time field in a collection when the time is reached.
When the system reaches the time point (accurate to the second) that meets the configured trigger conditions, the corresponding workflow will be triggered.
Basic Usage
Create a scheduled task
When creating a workflow in the workflow list, select the "Scheduled Task" type:
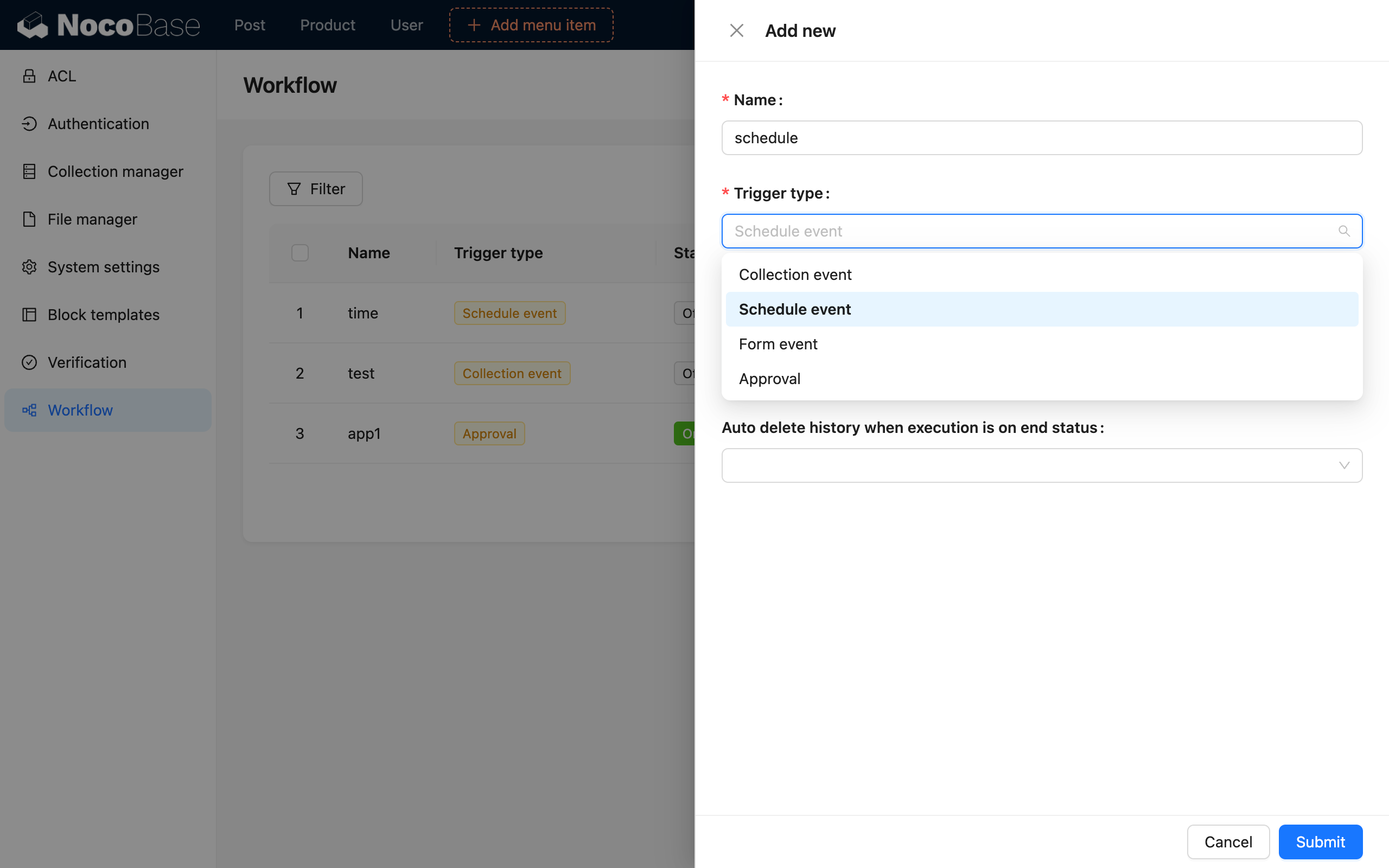
Custom time mode
For the regular mode, you first need to configure the start time to any point in time (accurate to the second). The start time can be set to a future time or a past time. When set to a past time, it will check if the time is due based on the configured repeat condition. If no repeat condition is configured and the start time is in the past, the workflow will no longer be triggered.
There are two ways to configure the repeat rule:
- By interval: Triggers at a fixed interval after the start time, such as every hour, every 30 minutes, etc.
- Advanced mode: That is, according to cron rules, it can be configured for a cycle that reaches a fixed rule-based date and time.
After configuring the repeat rule, you can also configure an end condition. It can be ended at a fixed point in time or limited by the number of times it has been executed.
Collection time field mode
Using a collection's time field to determine the start time is a trigger mode that combines regular scheduled tasks with collection time fields. Using this mode can simplify nodes in some specific processes and is also more intuitive in terms of configuration. For example, to change the status of overdue unpaid orders to cancelled, you can simply configure a scheduled task in the collection time field mode, selecting the start time as 30 minutes after the order is created.
Related Tips
Scheduled tasks in an inactive or shutdown state
If the configured time condition is met, but the entire NocoBase application service is in an inactive or shutdown state, the scheduled task that should have been triggered at that time point will be missed. Moreover, after the service is restarted, the missed tasks will not be triggered again. Therefore, when using it, you may need to consider handling for such situations or have fallback measures.
Repeat count
When the "by repeat count" end condition is configured, it calculates the total number of executions across all versions of the same workflow. For example, if a scheduled task has been executed 10 times in version 1, and the repeat count is also set to 10, the workflow will no longer be triggered. Even if copied to a new version, it will not be triggered unless the repeat count is changed to a number greater than 10. However, if it is copied as a new workflow, the execution count will be reset to 0. Without modifying the relevant configuration, the new workflow can be triggered another 10 times.
Difference between interval and advanced mode in repeat rules
The interval in the repeat rule is relative to the time of the last trigger (or the start time), while the advanced mode triggers at fixed points in time. For example, if it is configured to trigger every 30 minutes, and the last trigger was at 2021-09-01 12:01:23, then the next trigger time will be 2021-09-01 12:31:23. The advanced mode, i.e., cron mode, is configured to trigger at fixed time points, for example, it can be configured to trigger at 01 and 31 minutes of every hour.
Example
Suppose we need to check for orders that have not been paid for more than 30 minutes after creation every minute and automatically change their status to cancelled. We will implement this using both modes.
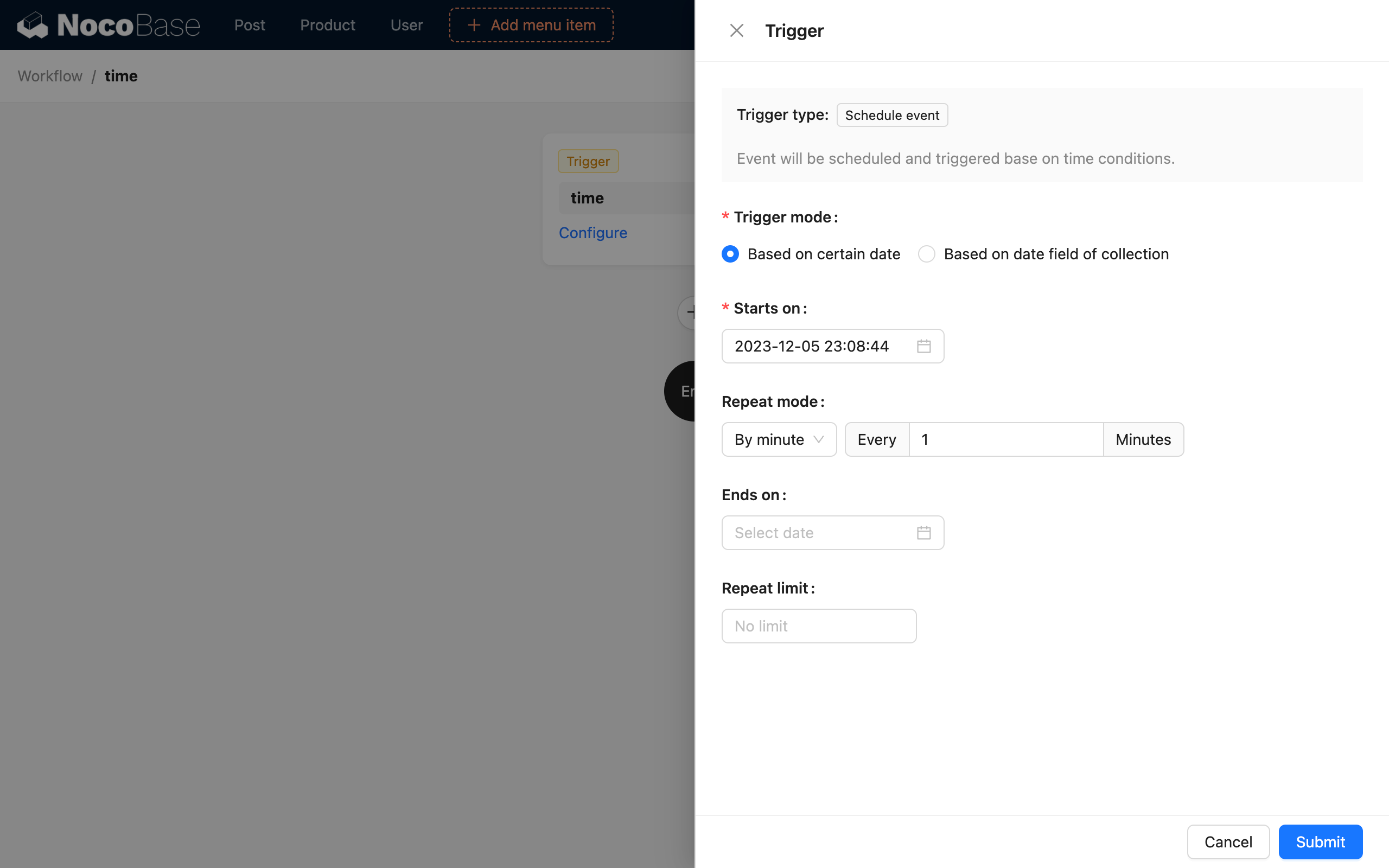
Custom time mode
Create a scheduled task-based workflow. In the trigger configuration, select "Custom time" mode, set the start time to any point not later than the current time, select "Every minute" for the repeat rule, and leave the end condition blank:
Then, configure other nodes according to the process logic, calculate the time 30 minutes ago, and change the status of unpaid orders created before that time to cancelled:
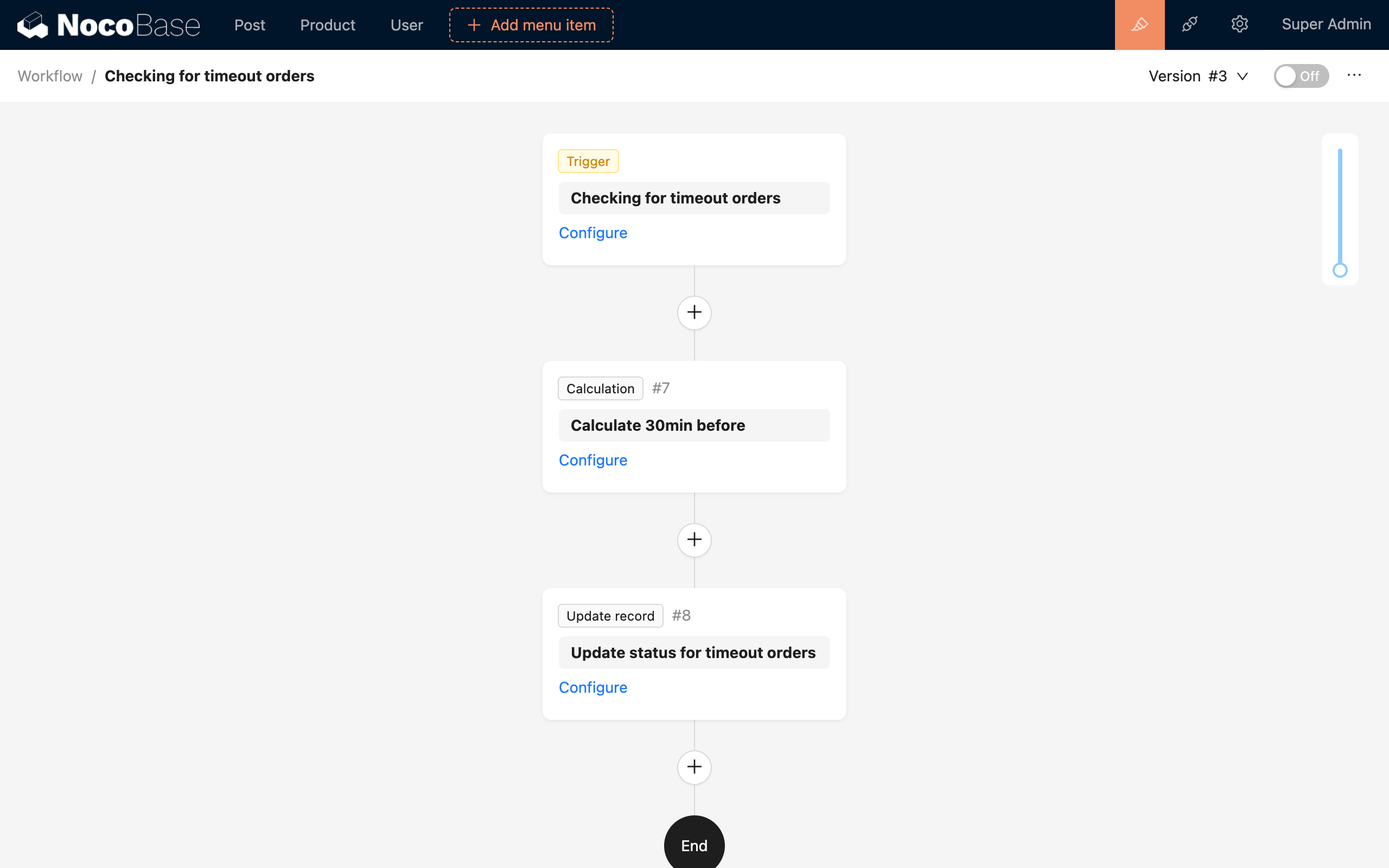
After the workflow is enabled, it will be triggered once every minute from the start time, calculating the time 30 minutes ago to update the status of orders created before that time point to cancelled.
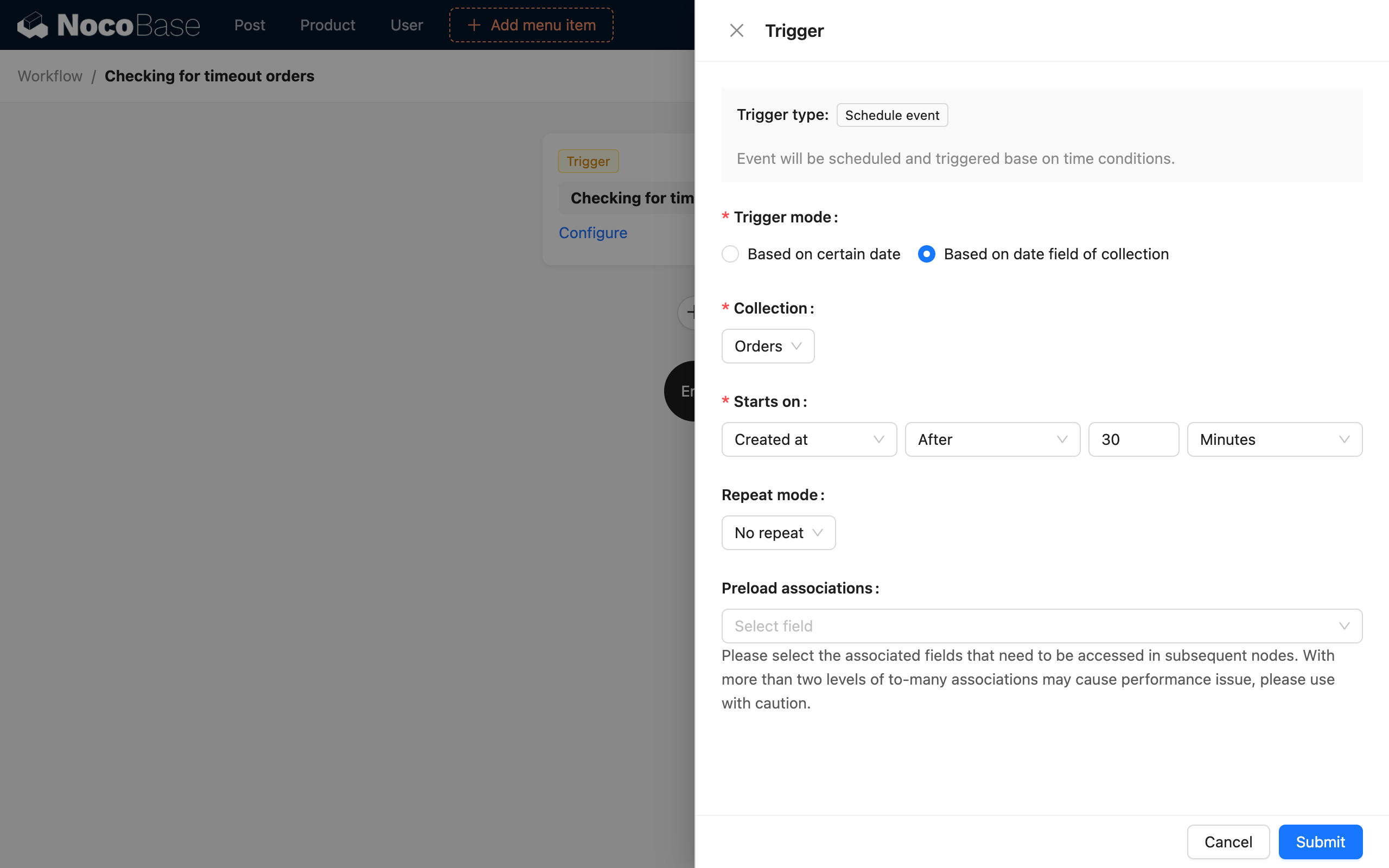
Collection time field mode
Create a scheduled task-based workflow. In the trigger configuration, select "Collection time field" mode, select the "Orders" collection, set the start time to 30 minutes after the order's creation time, and select "No repeat" for the repeat rule:
Then, configure other nodes according to the process logic to update the status of the order with the trigger data ID and a status of "unpaid" to cancelled:
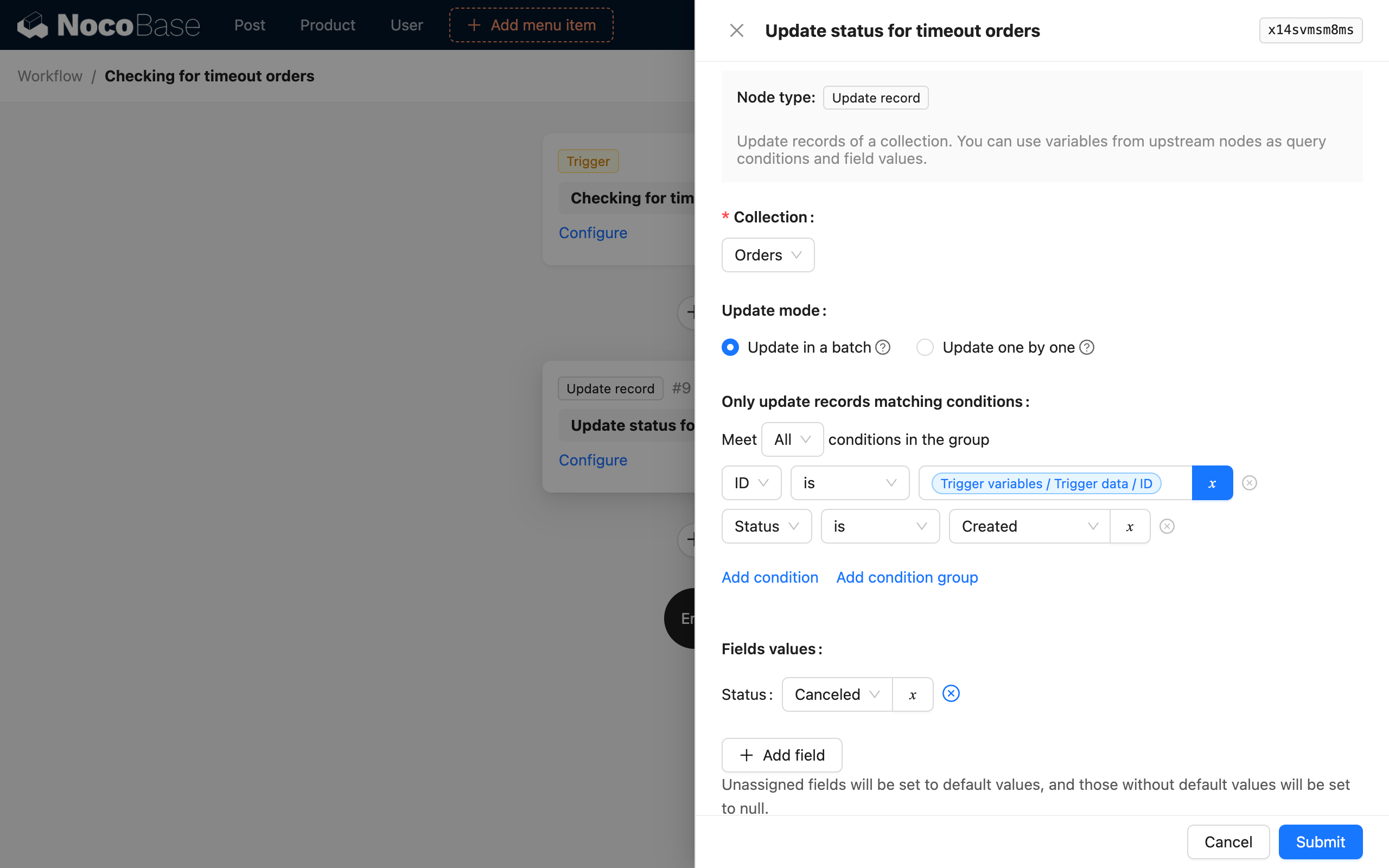
Unlike the custom time mode, there is no need to calculate the time 30 minutes ago here, because the trigger data context contains the data row that meets the time condition, so you can directly update the status of the corresponding order.

