Advanced Configuration
Execution Mode
Workflows are executed either asynchronously or synchronously, based on a trigger type selected during creation. Asynchronous mode means that after a specific event is triggered, the workflow enters a queue and is executed one by one by background scheduling. Synchronous mode, on the other hand, does not enter the scheduling queue after being triggered; it starts executing directly and provides immediate feedback upon completion.
Collection events, after action events, custom action events, scheduled events, and approval events are executed asynchronously by default. Before action events are executed synchronously by default. Both collection events and form events support both modes, which can be selected when creating a workflow:
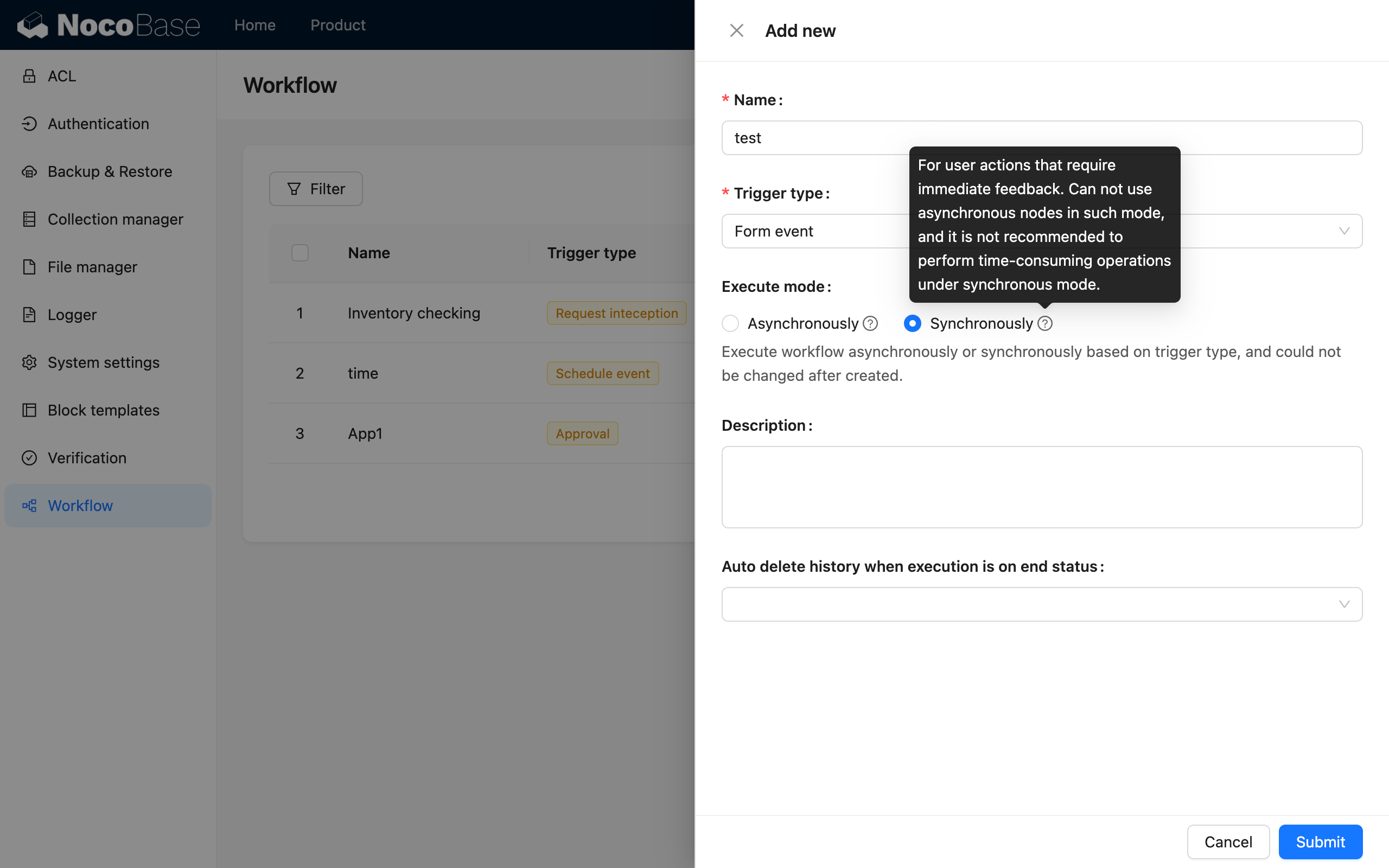
Due to their nature, synchronous workflows cannot use nodes that produce a "waiting" state, such as "Manual processing".
Auto-delete Execution History
When a workflow is triggered frequently, you can configure auto-deletion of execution history to reduce clutter and alleviate storage pressure on the database.
You can also configure whether to automatically delete the execution history for a workflow in its creation and editing dialogs:
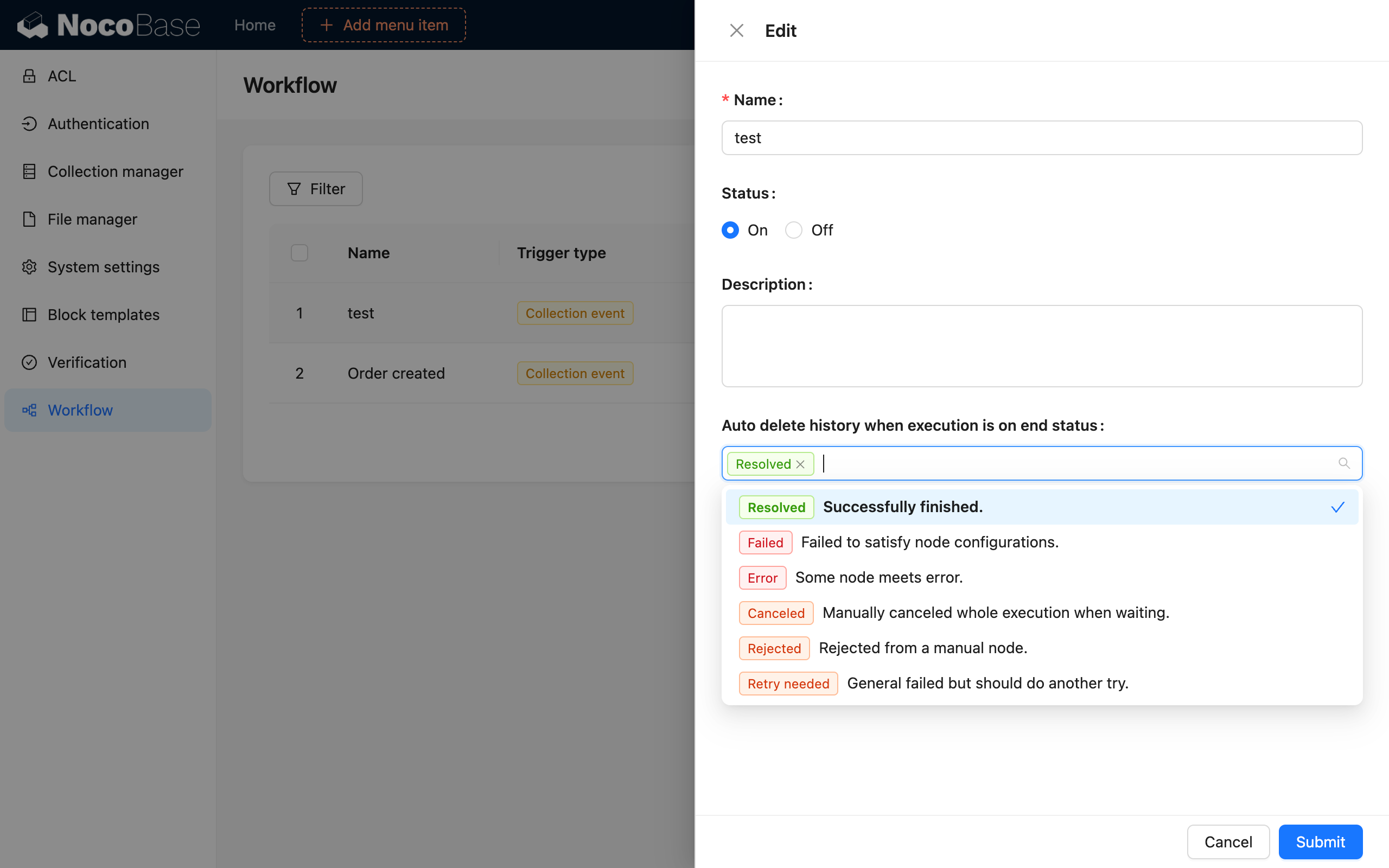
Auto-deletion can be configured based on the execution result status. In most cases, it is recommended to only check the "Completed" status to preserve records of failed executions for future troubleshooting.
It is recommended not to enable auto-deletion of execution history when debugging a workflow, so you can use the history to check if the workflow's execution logic is as expected.
Deleting a workflow's history does not reduce its execution count.

