SQL Action
This feature is provided by the plugin «Workflow: SQL node»Introduction
In some special scenarios, the simple collection action nodes mentioned above may not be able to handle complex operations. In such cases, you can use the SQL node directly to have the database execute complex SQL statements for data manipulation.
The difference between this and directly connecting to the database for SQL operations outside the application is that within a workflow, you can use variables from the process context as parameters in the SQL statement.
Installation
Built-in plugin, no installation required.
Create Node
In the workflow configuration interface, click the plus ("+") button in the flow to add an "SQL Action" node:
Node Configuration
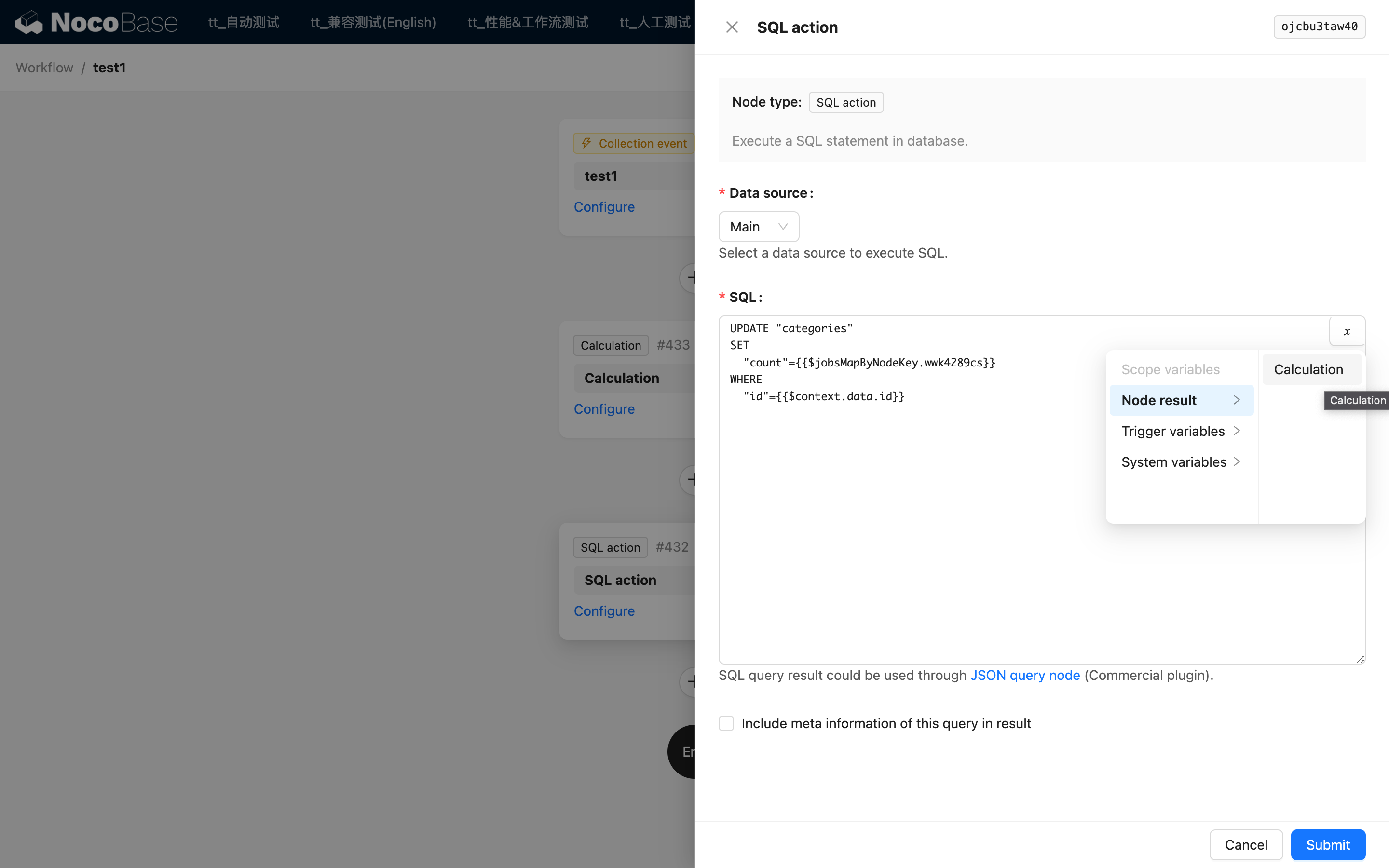
Data Source
Select the data source to execute the SQL.
The data source must be a database type, such as the main data source, PostgreSQL, or other Sequelize-compatible data sources.
SQL Content
Edit the SQL statement. Currently, only one SQL statement is supported.
Insert the required variables using the variable button in the upper right corner of the editor. Before execution, these variables will be replaced with their corresponding values through text substitution. The resulting text will then be used as the final SQL statement and sent to the database for querying.
Node Execution Result
Since v1.3.15-beta, the result of a SQL node execution is an array of pure data. Before that, it was the native Sequelize return structure containing query metadata (see: sequelize.query()).
For example, the following query:
Result before v1.3.15-beta:
Result after v1.3.15-beta:
FAQ
How to use the result of a SQL node?
If a SELECT statement is used, the query result will be saved in the node in Sequelize's JSON format. It can be parsed and used with the JSON-query plugin.
Does the SQL action trigger collection events?
No. The SQL action sends the SQL statement directly to the database for processing. The related CREATE / UPDATE / DELETE operations occur in the database, while collection events occur at the Node.js application layer (handled by the ORM), so collection events will not be triggered.

