Variable
This feature is provided by the commercial plugin «Workflow: Custom variable», please purchase to useIntroduction
You can declare variables in a flow or assign values to declared variables. This is typically used to store temporary data within the flow.
Create Node
In the workflow configuration interface, click the plus ("+") button in the flow to add a "Variable" node:

Configure Node
Mode
The variable node is similar to variables in programming; it must be declared before it can be used and assigned a value. Therefore, when creating a variable node, you need to select its mode. There are two modes to choose from:
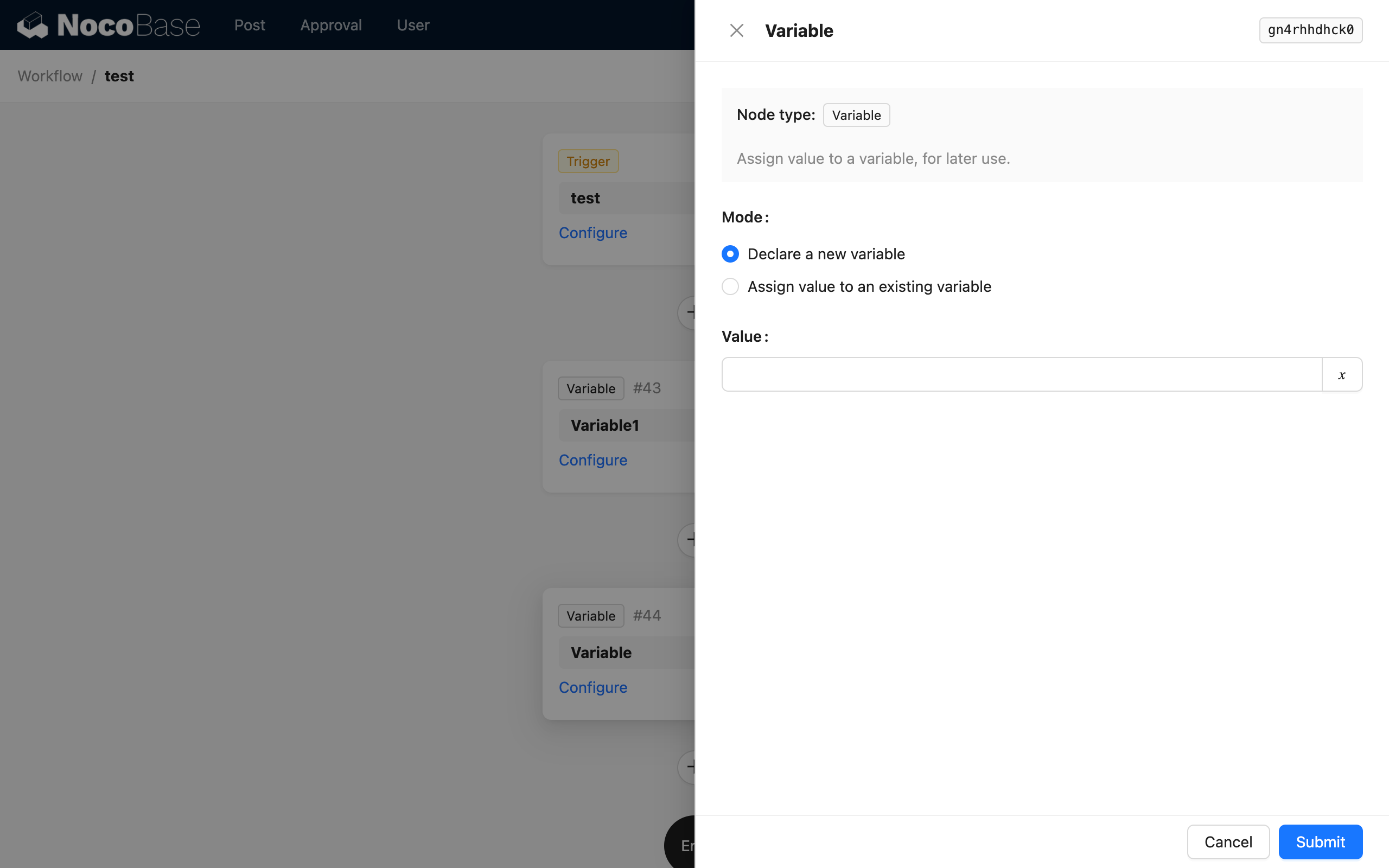
- Declare a new variable: Creates a new variable.
- Assign to an existing variable: Assigns a value to a variable that has been declared earlier in the flow, which is equivalent to modifying the variable's value.
When the node being created is the first variable node in the flow, you can only select the declare mode, as there are no variables available for assignment yet.
When you choose to assign a value to a declared variable, you also need to select the target variable, which is the node where the variable was declared:
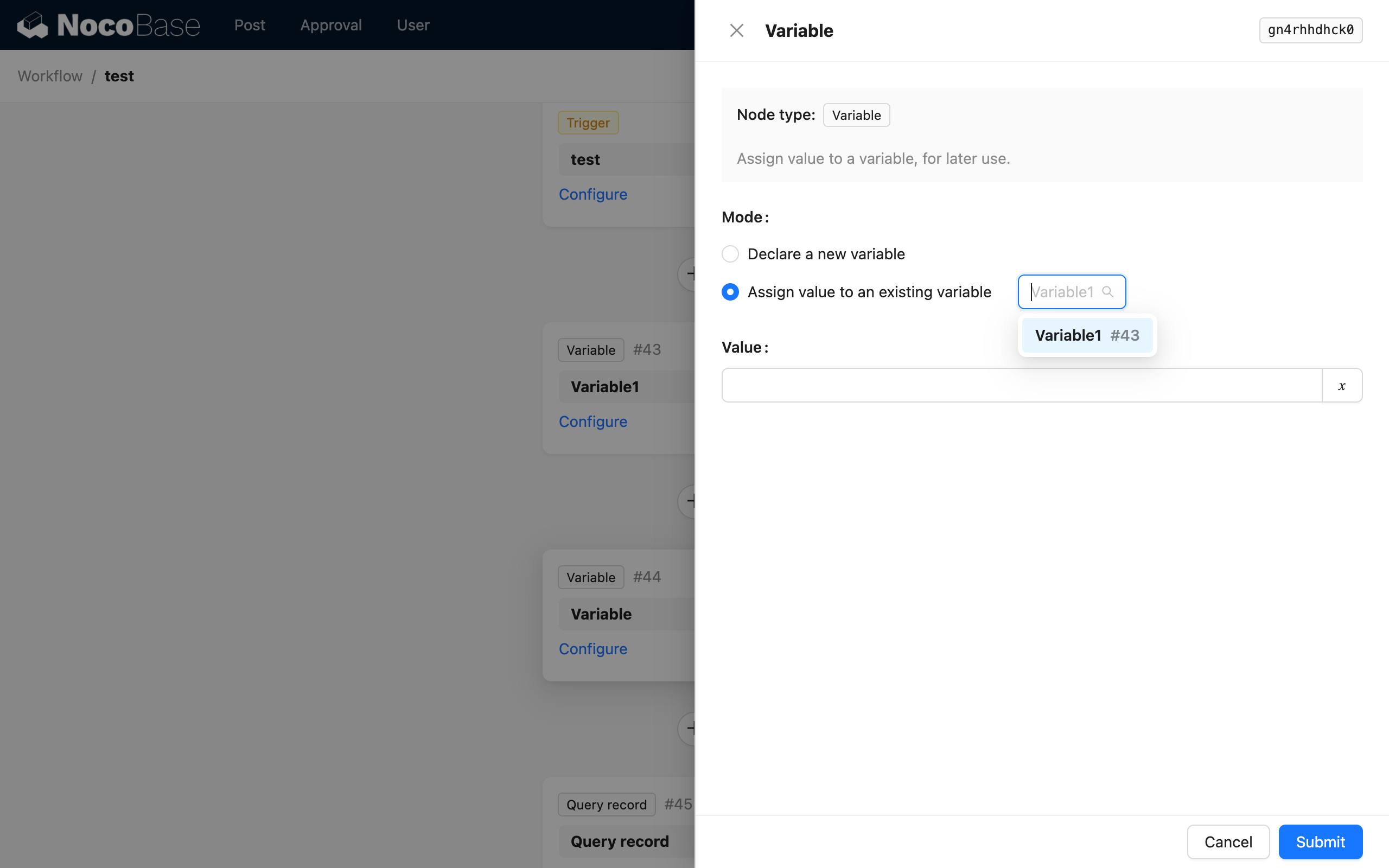
Value
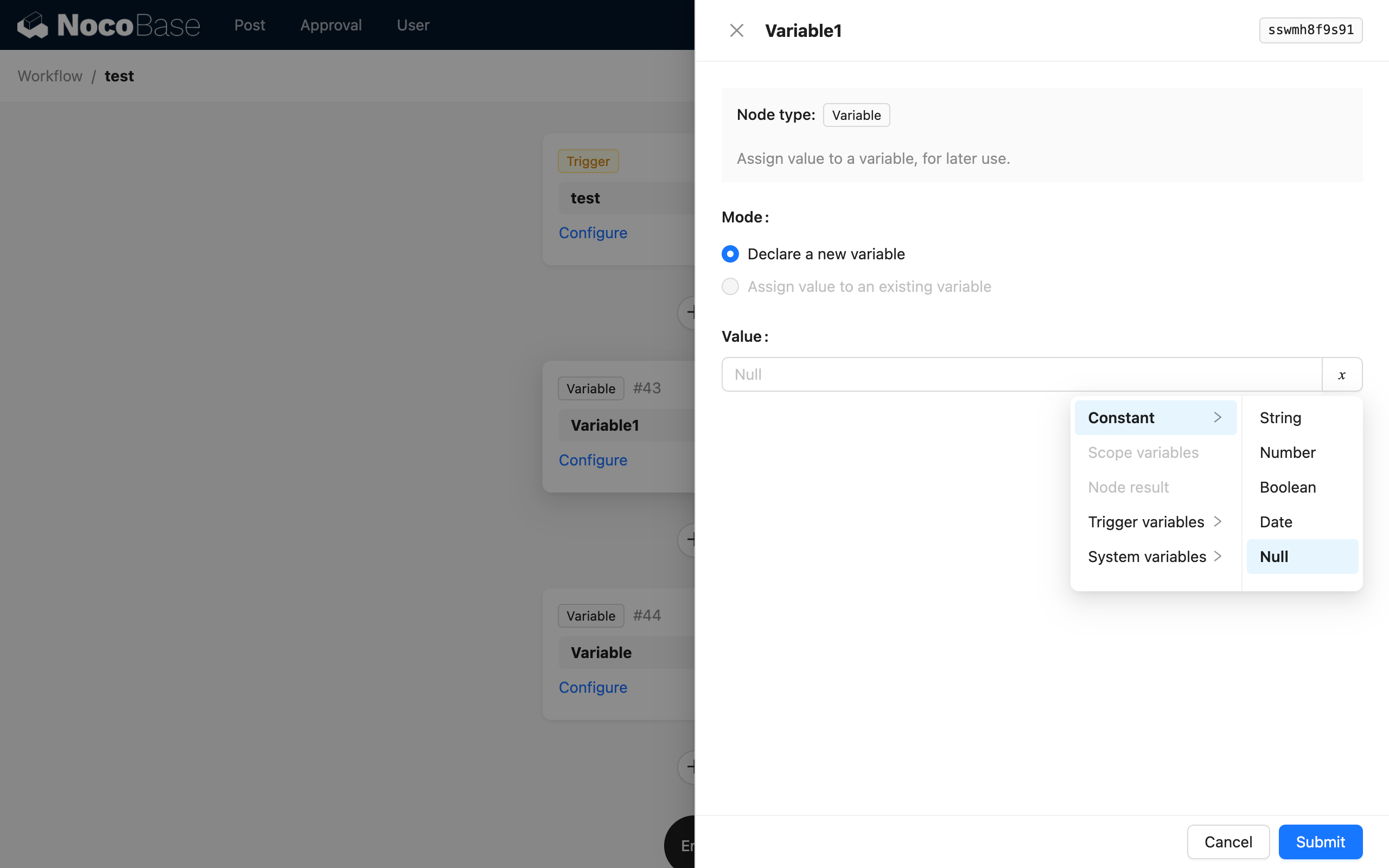
The value of a variable can be of any type. It can be a constant, such as a string, number, boolean, or date, or it can be another variable from the flow.
In declare mode, setting the variable's value is equivalent to assigning it an initial value.
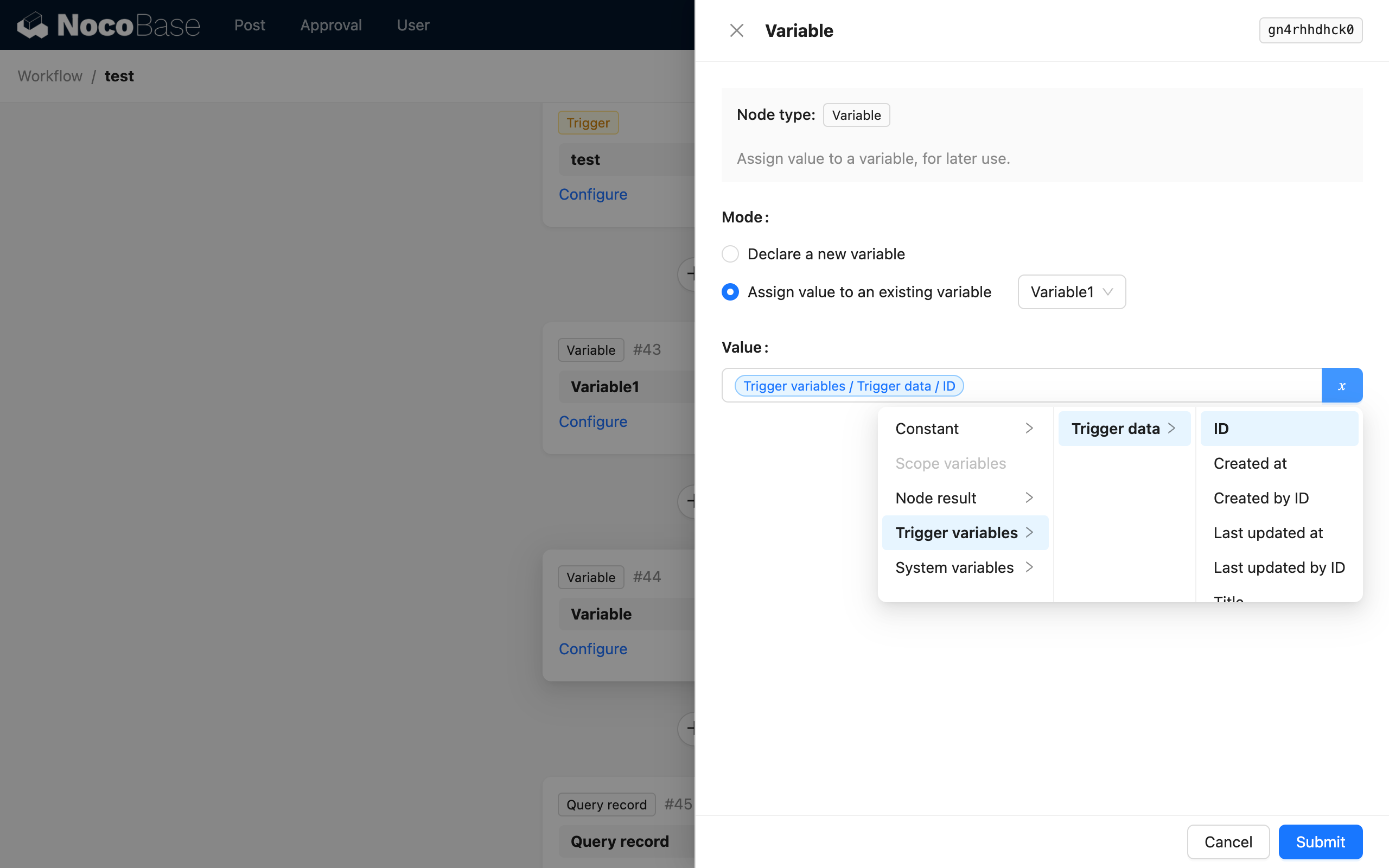
In assignment mode, setting the variable's value is equivalent to modifying the value of the declared target variable to a new value. Subsequent uses will retrieve this new value.
Using the Variable's Value
In subsequent nodes after the variable node, you can use the variable's value by selecting the declared variable from the "Node Variables" group. For example, in a query node, use the variable's value as a query condition:
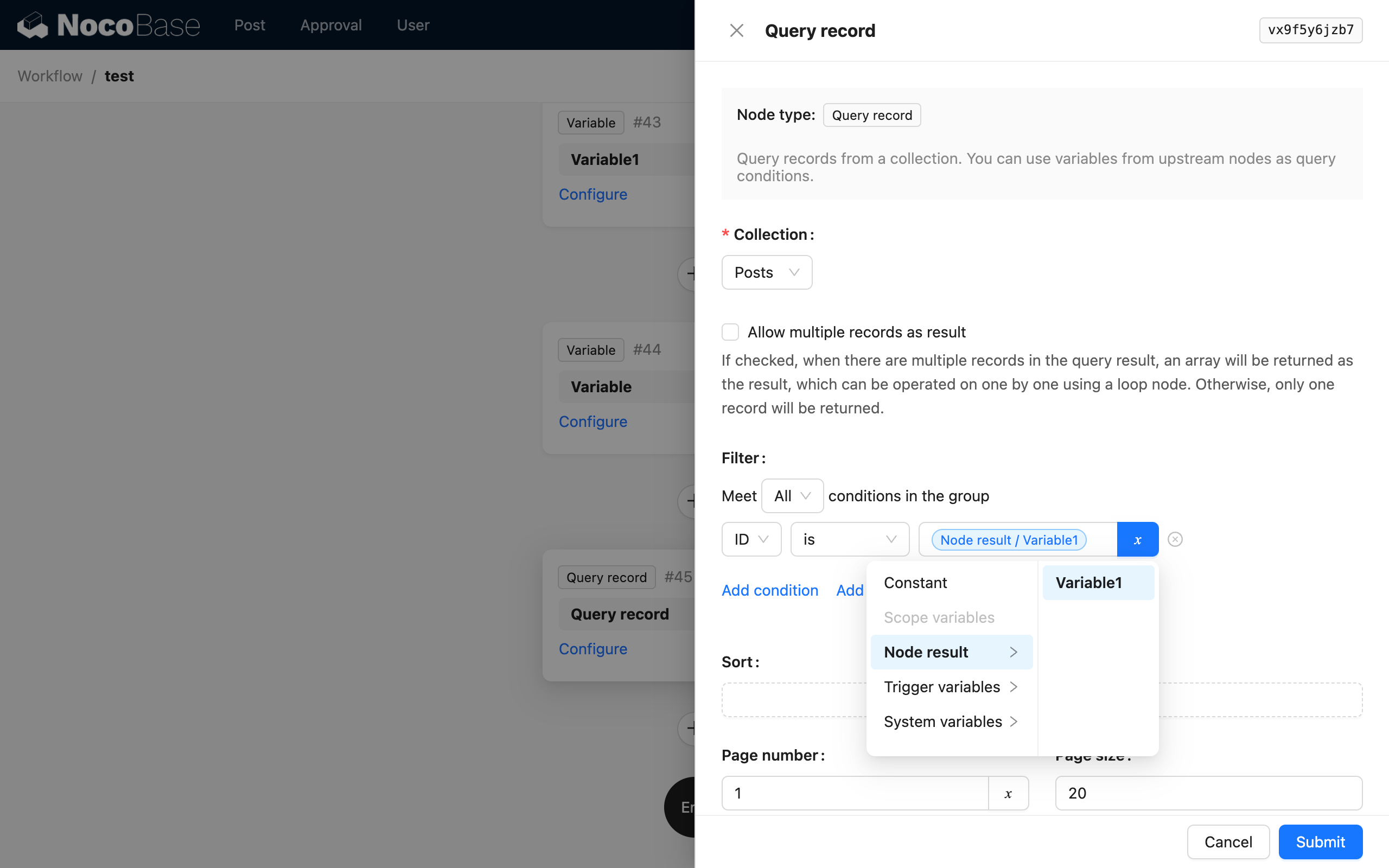
Example
A more useful scenario for the variable node is in branches, where new values are calculated or merged with previous values (similar to reduce/concat in programming), and then used after the branch ends. The following is an example of using a loop branch and a variable node to concatenate a recipient string.
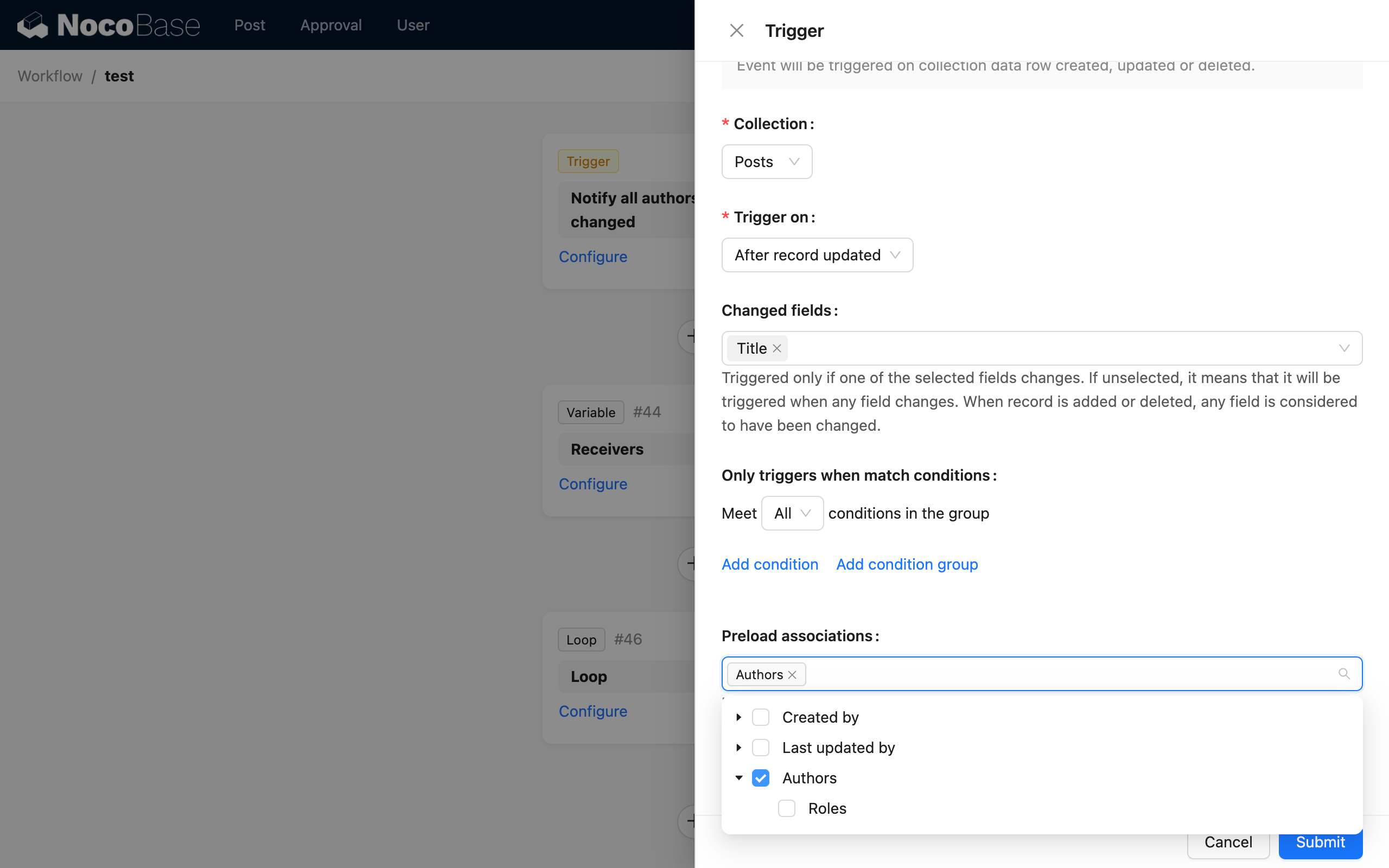
First, create a collection-triggered workflow that triggers when "Article" data is updated, and preload the related "Author" association data (to get recipients):
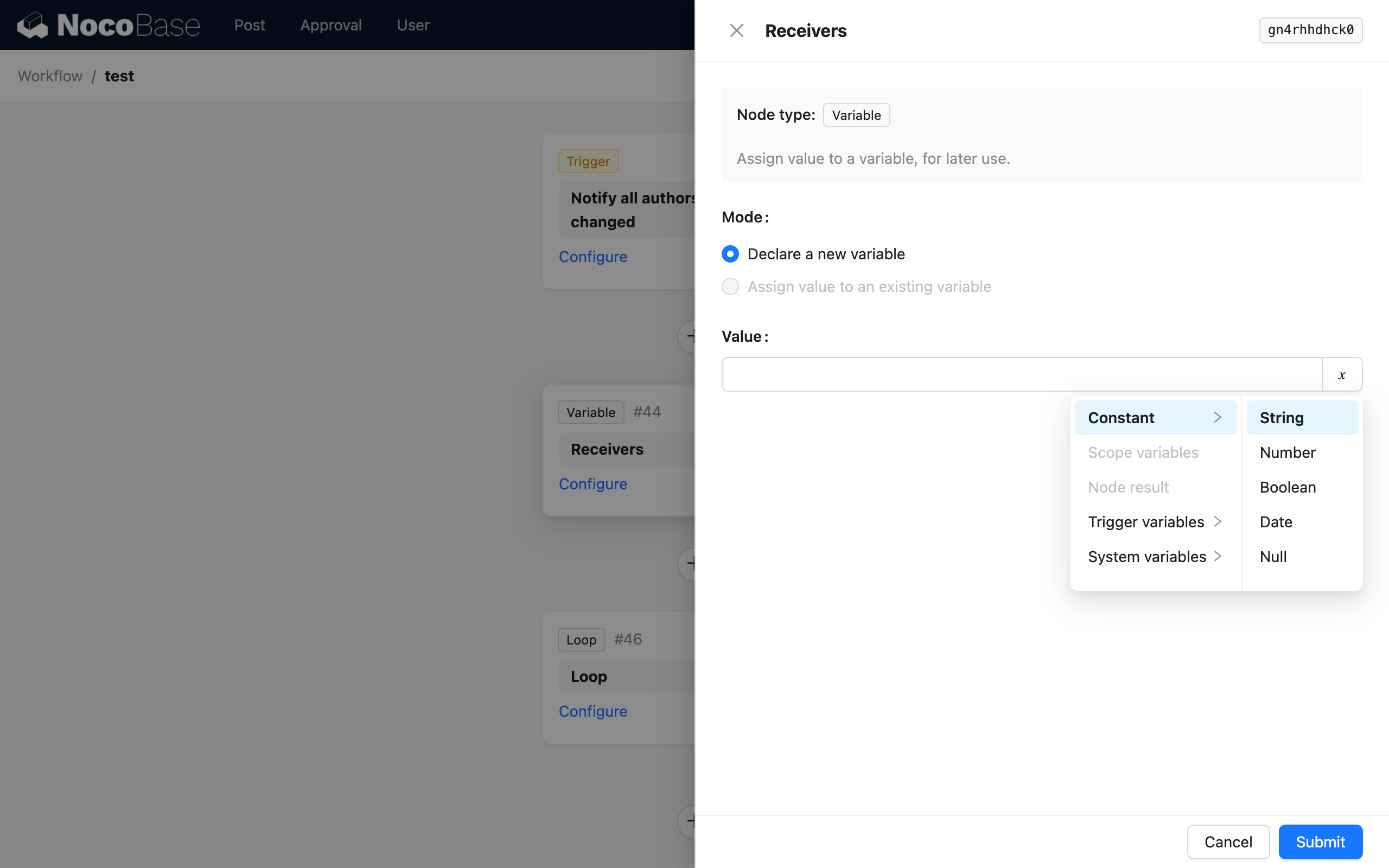
Then, create a variable node to store the recipient string:
Next, create a loop branch node to iterate through the article's authors and concatenate their recipient information into the recipient variable:
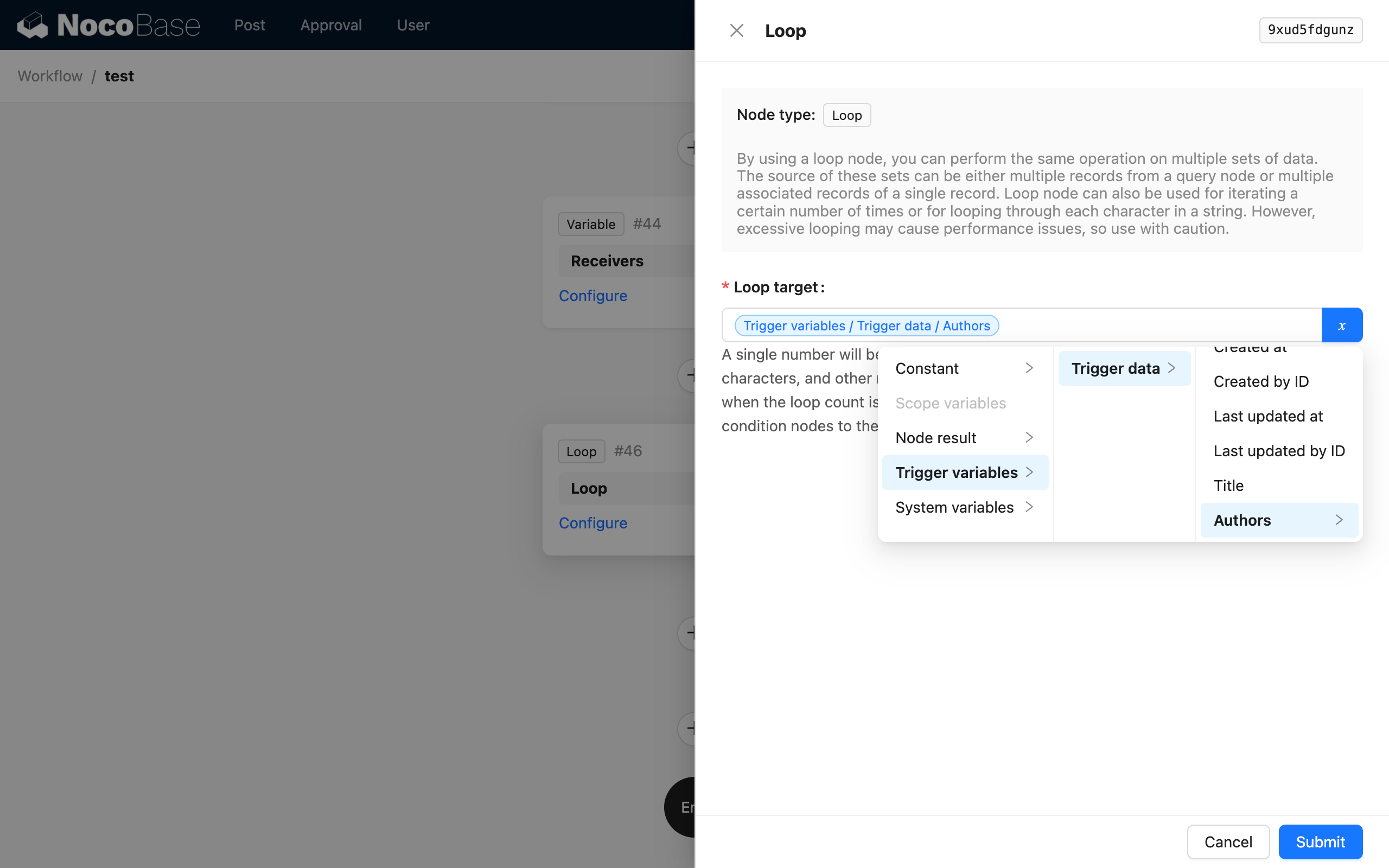
Inside the loop branch, first create a calculation node to concatenate the current author with the already stored author string:
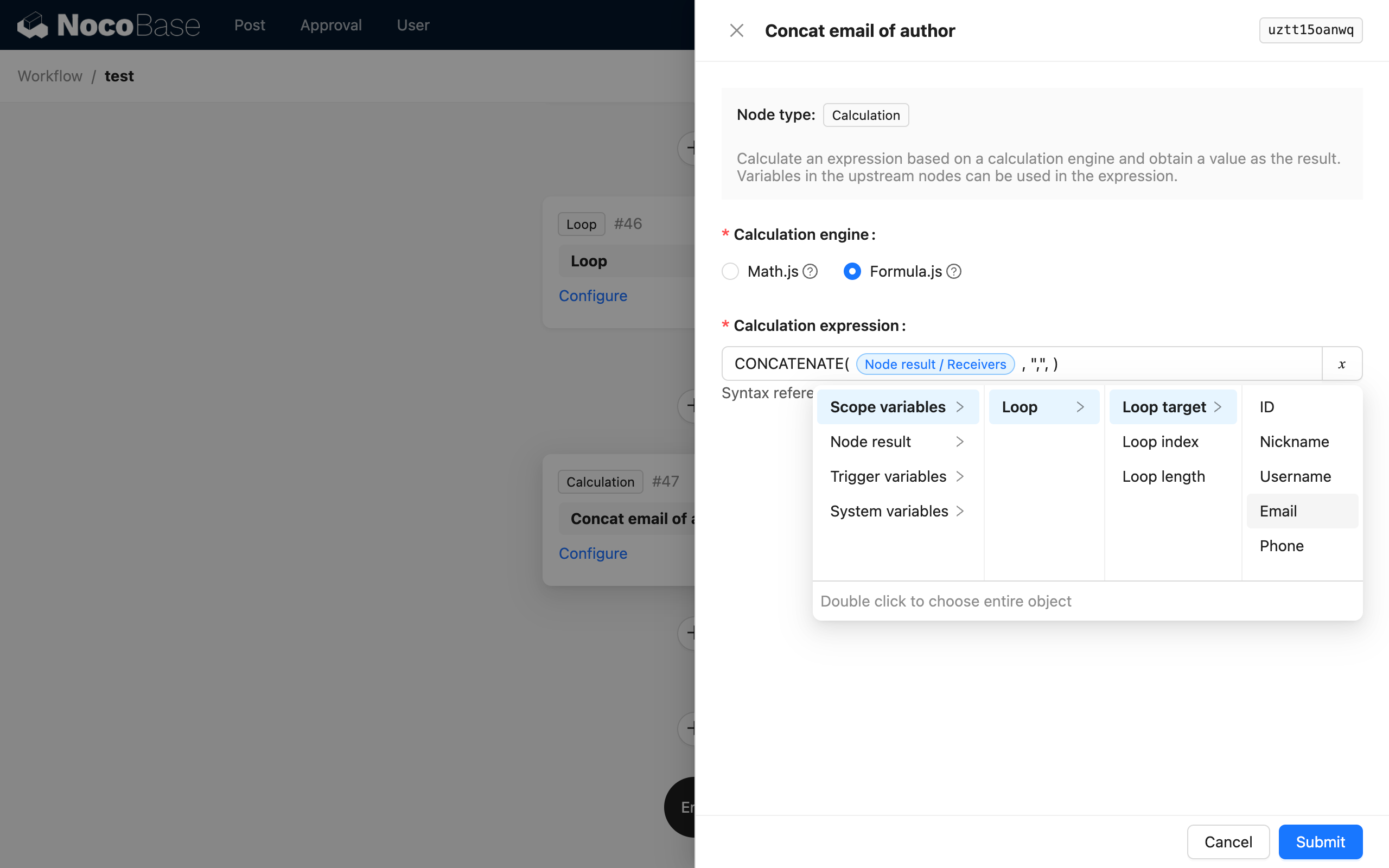
After the calculation node, create another variable node. Select the assignment mode, choose the recipient variable node as the assignment target, and select the result of the calculation node as the value:
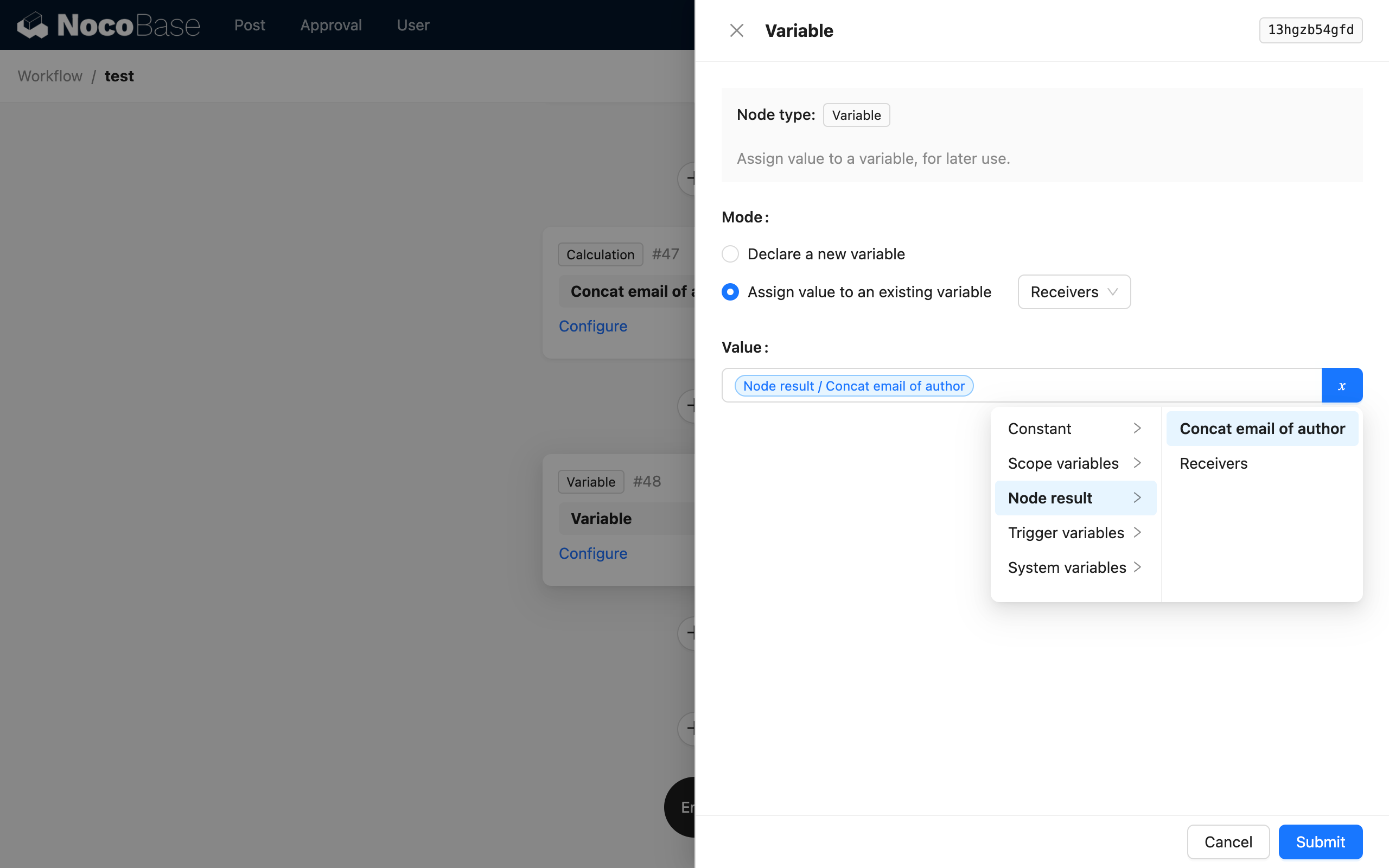
This way, after the loop branch finishes, the recipient variable will store the recipient string of all the article's authors. Then, after the loop, you can use an HTTP Request node to call a mail sending API, passing the value of the recipient variable as the recipient parameter to the API:
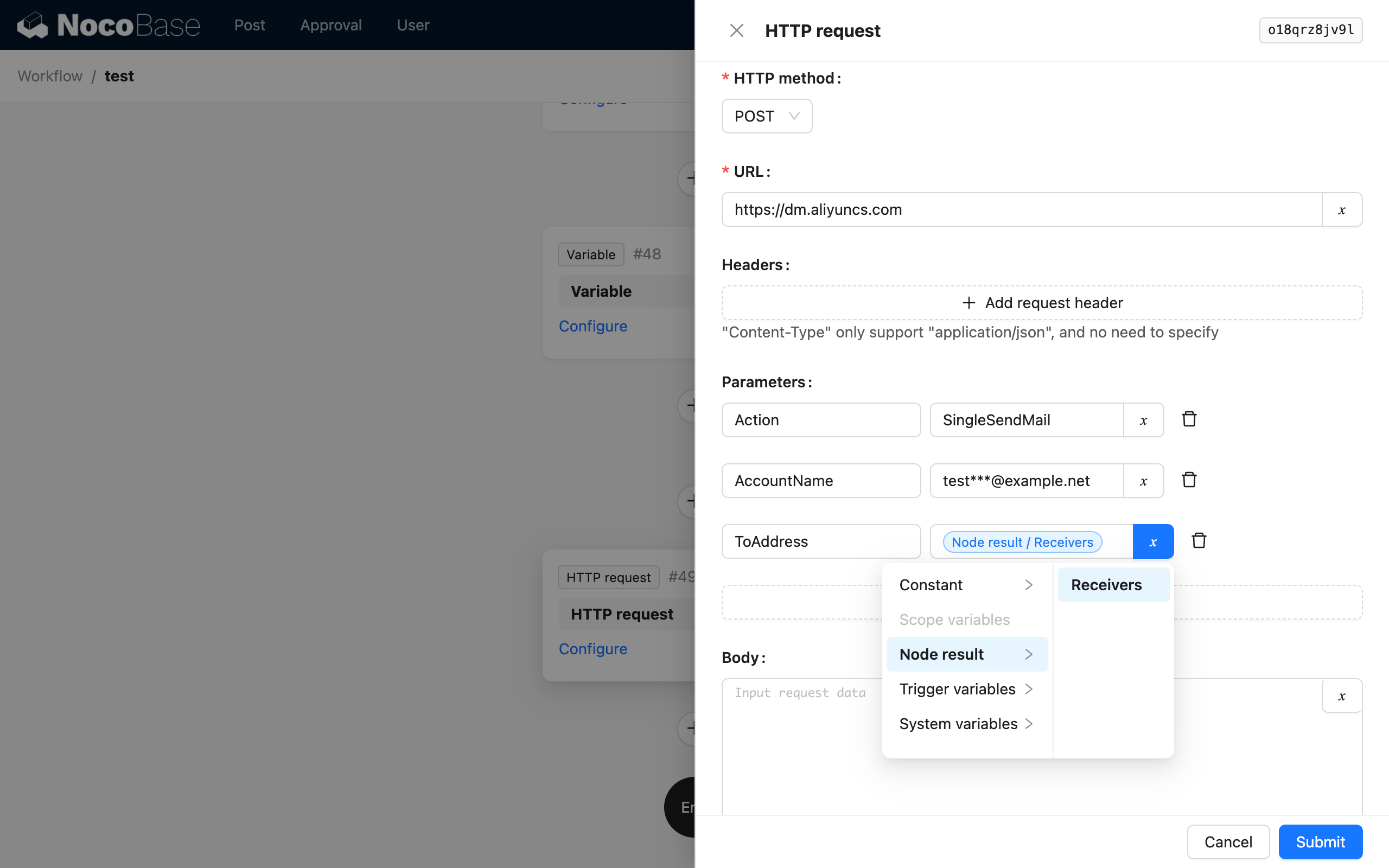
At this point, a simple bulk email feature has been implemented using a loop and a variable node.

