JSON Calculation
This feature is provided by the plugin «Workflow: JSON calculation»Introduction
Based on different JSON calculation engines, it calculates or transforms complex JSON data generated by upstream nodes for use by subsequent nodes. For example, the results of SQL operation and HTTP request nodes can be transformed into the required values and variable formats through this node for use by subsequent nodes.
Create Node
In the workflow configuration interface, click the plus ("+") button in the process to add a "JSON Calculation" node:
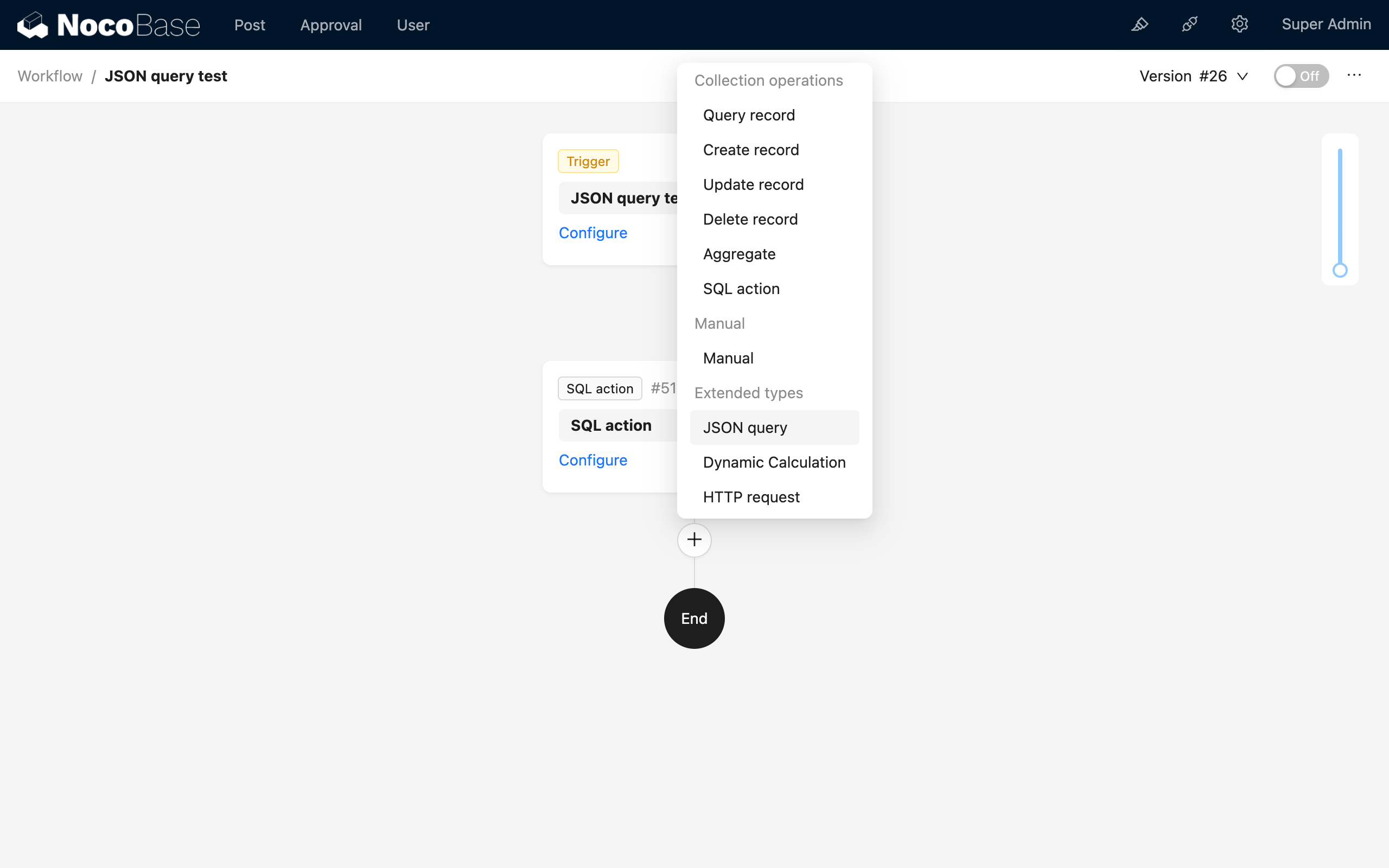
Usually, the JSON Calculation node is created below other data nodes to parse them.
Node Configuration
Parsing Engine
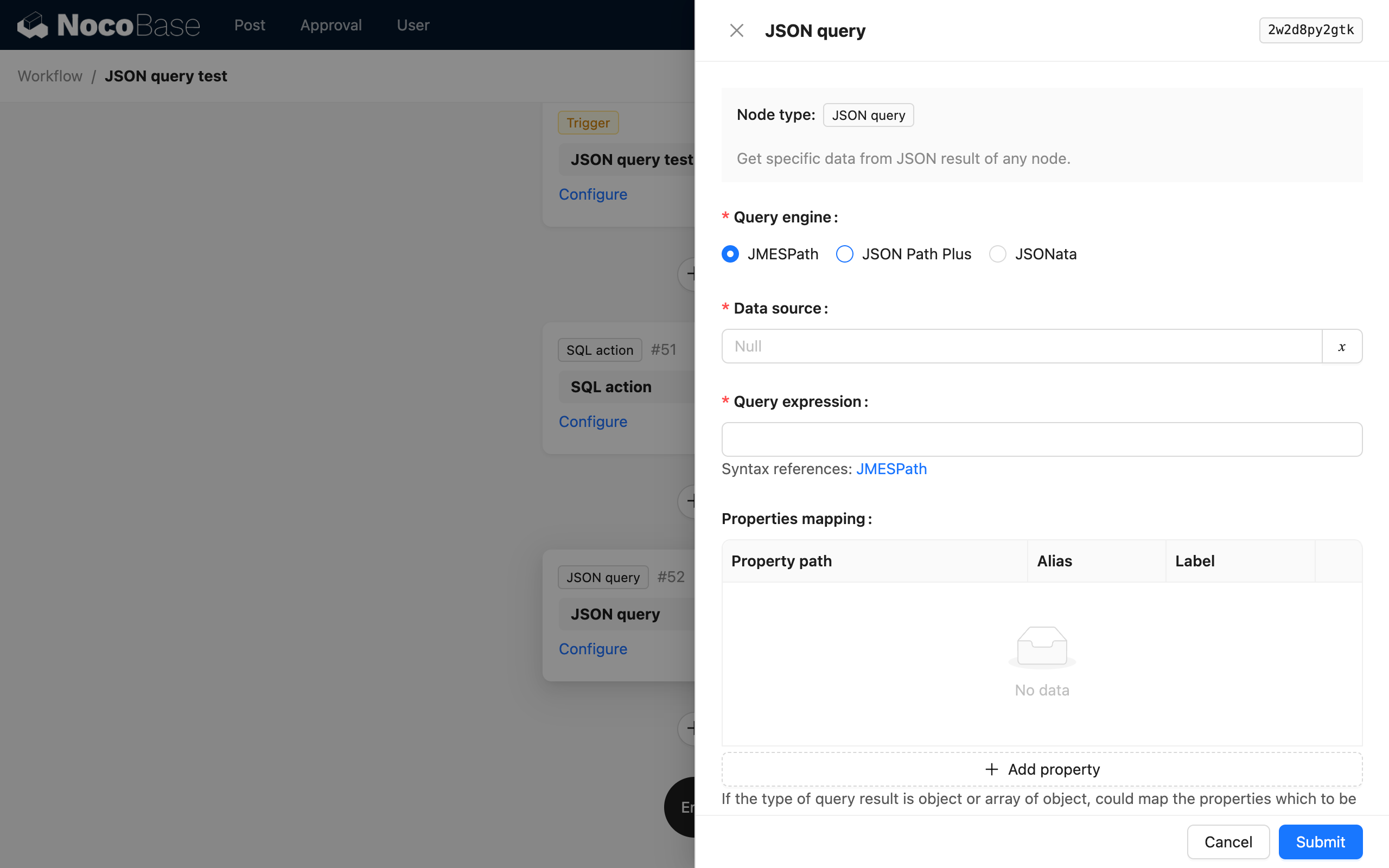
The JSON Calculation node supports different syntaxes through different parsing engines. You can choose based on your preferences and the features of each engine. Currently, three parsing engines are supported:
Data Source
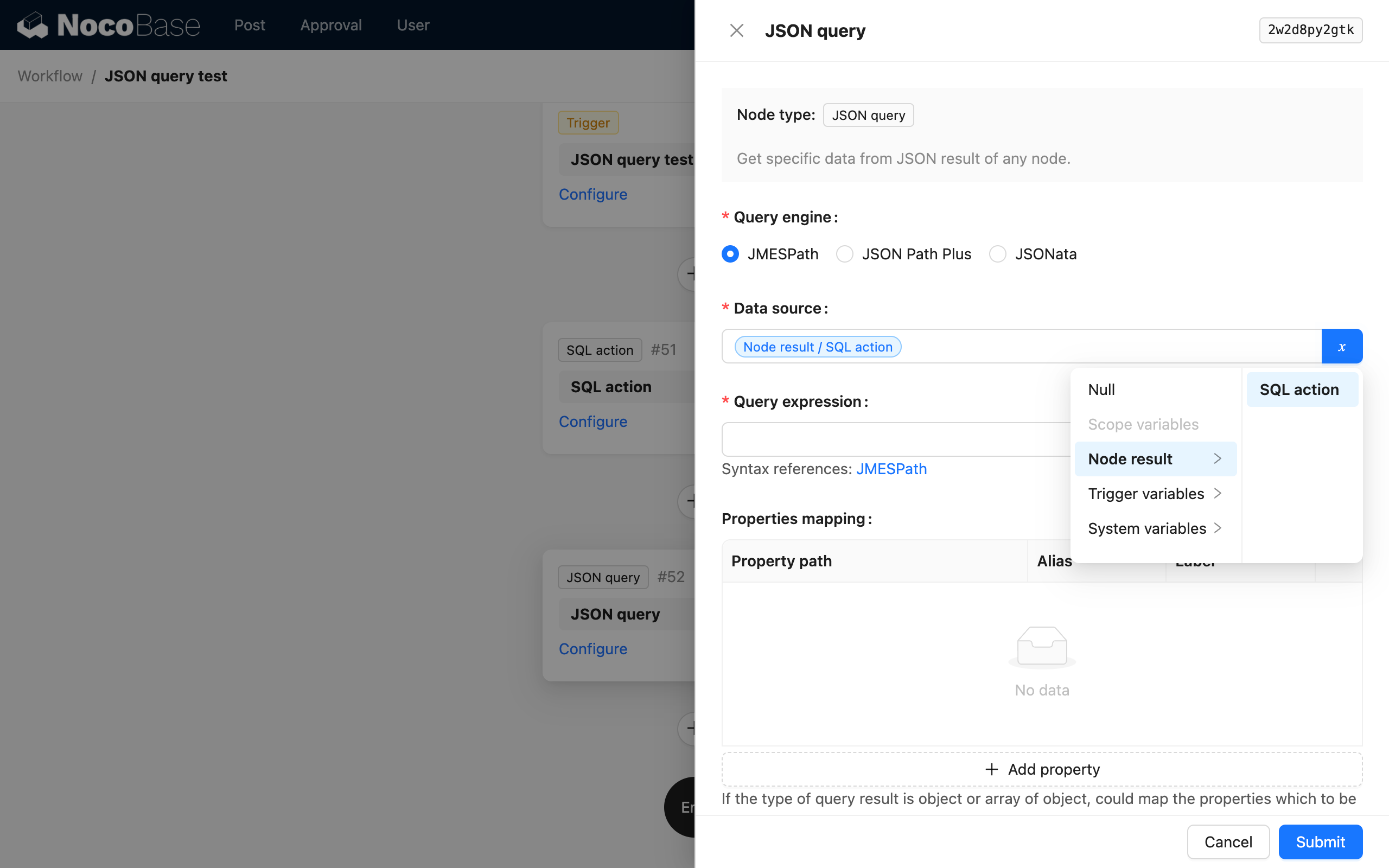
The data source can be the result of an upstream node or a data object in the workflow context. It is usually a data object without a built-in structure, such as the result of an SQL node or an HTTP request node.
Usually, the data objects of collection-related nodes are structured through collection configuration information and generally do not need to be parsed by the JSON Calculation node.
Parsing Expression
Custom parsing expressions based on parsing requirements and the chosen parsing engine.
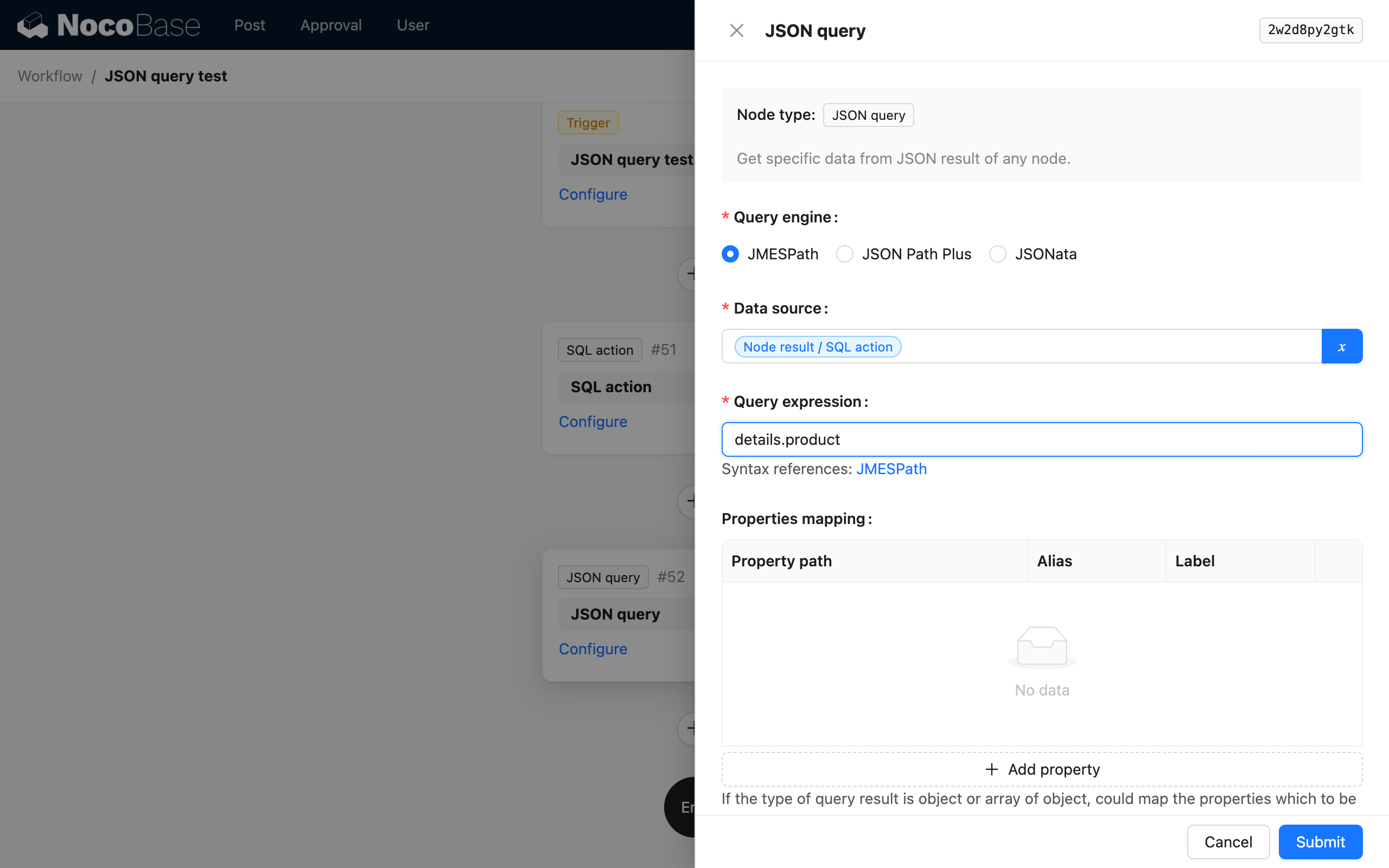
Different engines provide different parsing syntaxes. For details, please refer to the documentation in the links.
Since v1.0.0-alpha.15, expressions support variables. Variables are pre-parsed before the specific engine executes, replacing the variables with specific string values according to string template rules, and concatenating them with other static strings in the expression to form the final expression. This feature is very useful when you need to dynamically build expressions, for example, when some JSON content needs a dynamic key for parsing.
Property Mapping
When the calculation result is an object (or an array of objects), you can further map the required properties to child variables through property mapping for use by subsequent nodes.
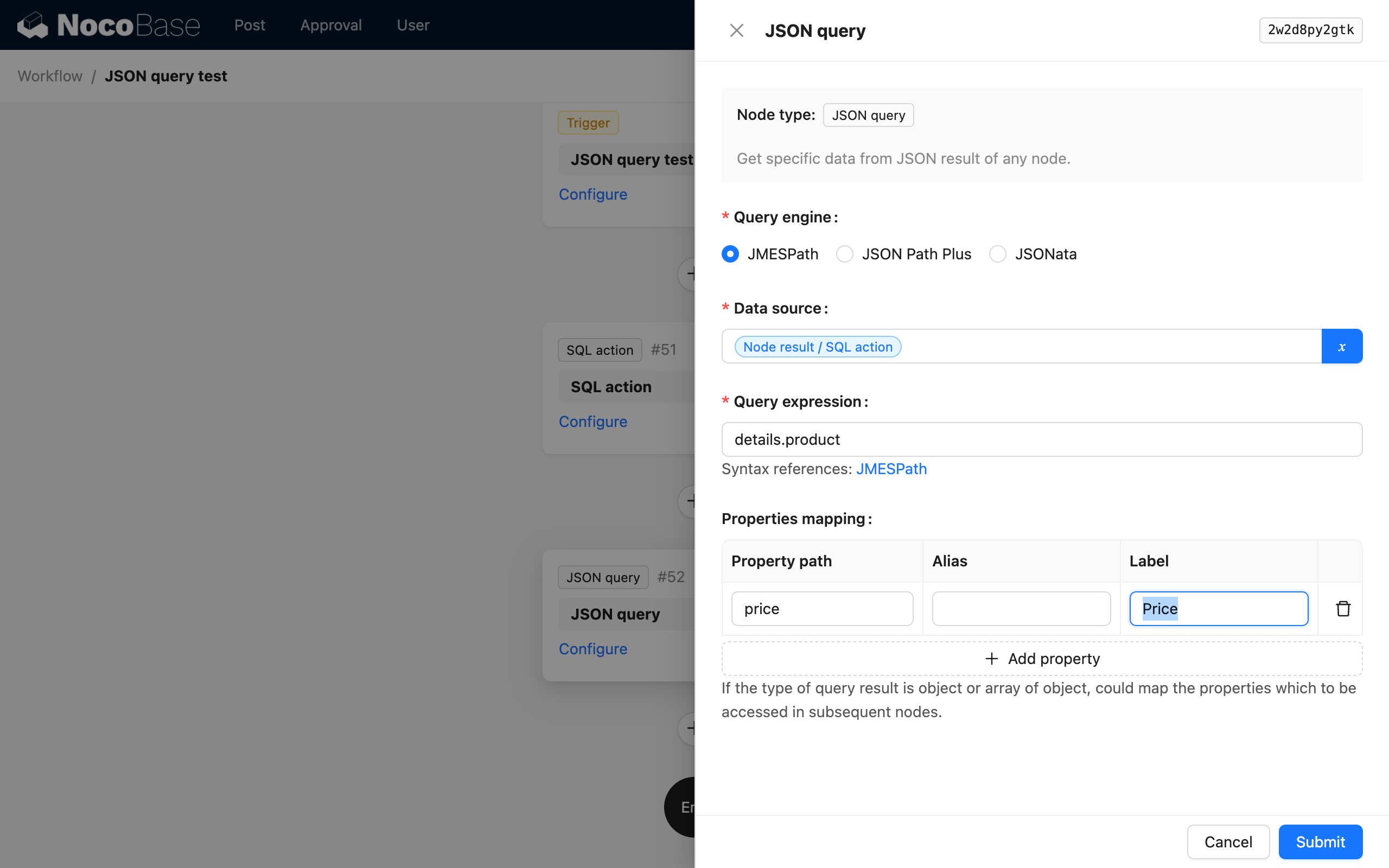
For an object (or array of objects) result, if property mapping is not performed, the entire object (or array of objects) will be saved as a single variable in the node's result, and the property values of the object cannot be used directly as variables.
Example
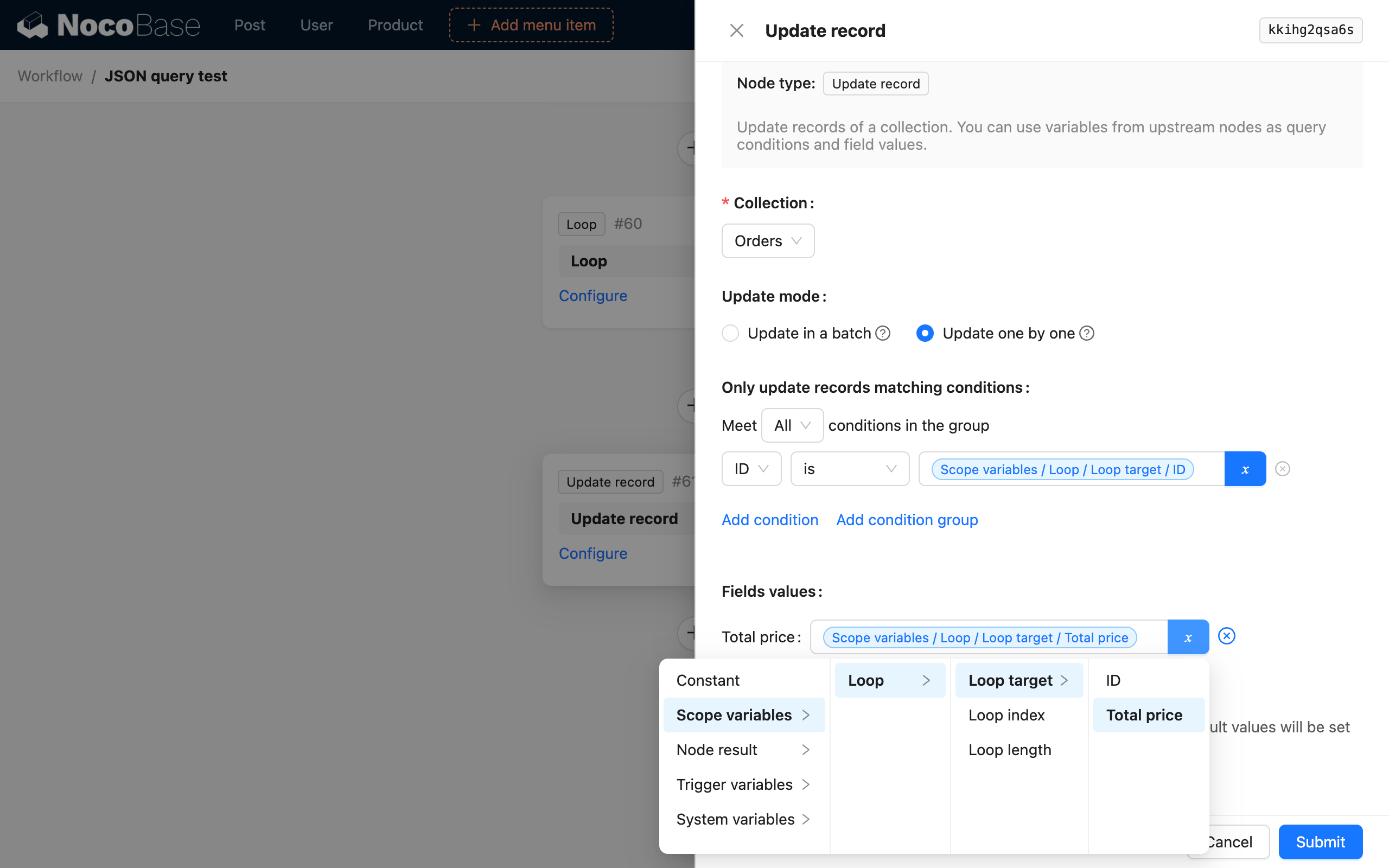
Suppose the data to be parsed is from a preceding SQL node used to query data, and its result is a set of order data:
If we need to parse and calculate the total price of the two orders in the data, and assemble it with the corresponding order ID into an object to update the order's total price, we can configure it as follows:
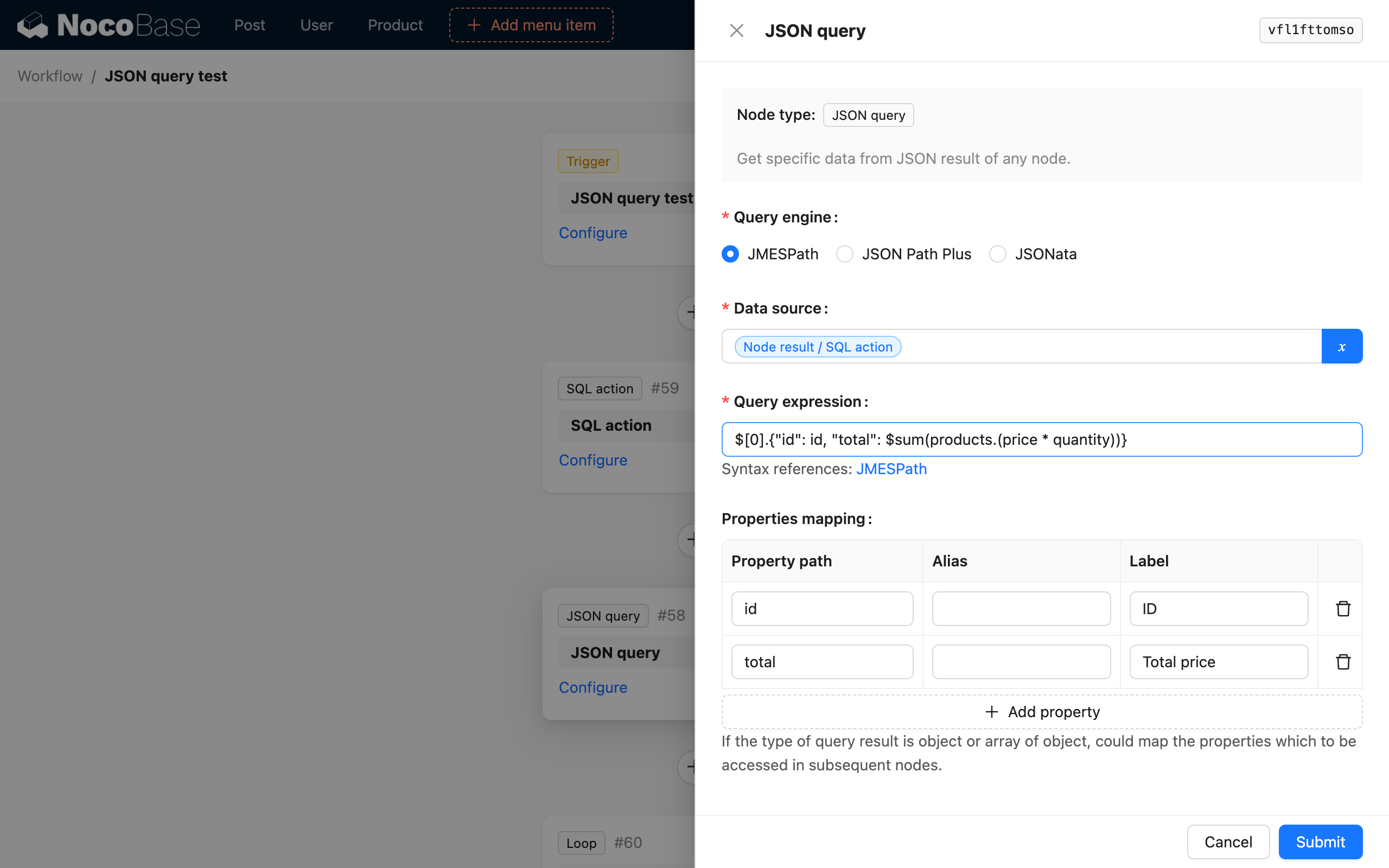
- Select the JSONata parsing engine;
- Select the result of the SQL node as the data source;
- Use the JSONata expression
$[0].{"id": id, "total": products.(price * quantity)}to parse; - Select property mapping to map
idandtotalto child variables;
The final parsing result is as follows:
Then, loop through the resulting order array to update the total price of the orders.