JavaScript Script
This feature is provided by the commercial plugin «Workflow: JavaScript», please purchase to useIntroduction
The JavaScript Script node allows users to execute a custom server-side JavaScript script within a workflow. The script can use variables from upstream in the workflow as parameters, and its return value can be provided to downstream nodes.
The script runs in a worker thread on the NocoBase application's server and supports most Node.js features, but there are some differences from the native execution environment. For details, see Feature List.
Create Node
In the workflow configuration interface, click the plus ("+") button in the flow to add a "JavaScript" node:
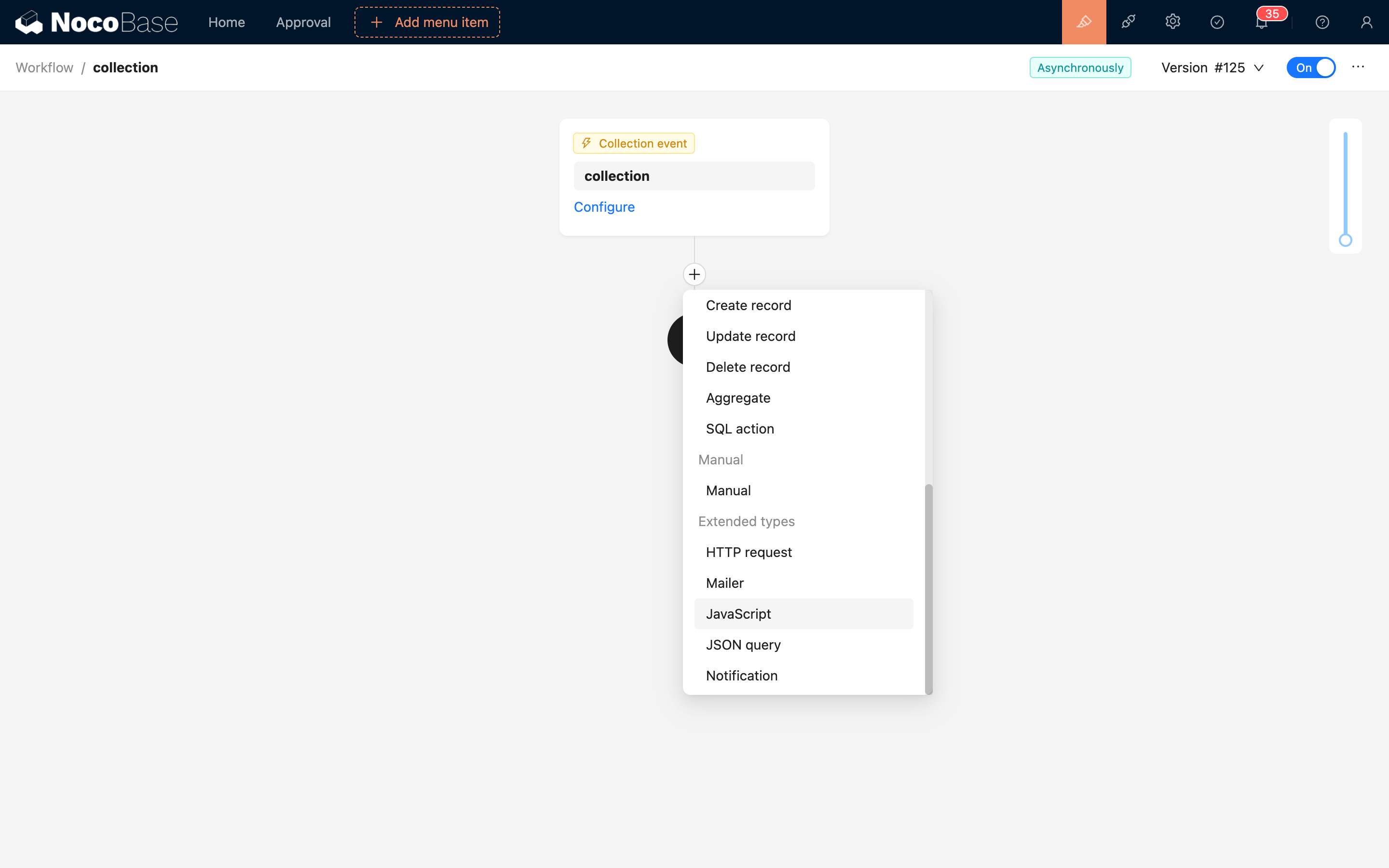
Node Configuration
Parameters
Used to pass variables or static values from the workflow context into the script for use in the code logic. name is the parameter name, which becomes the variable name once passed into the script. value is the parameter value, which can be a variable or a constant.
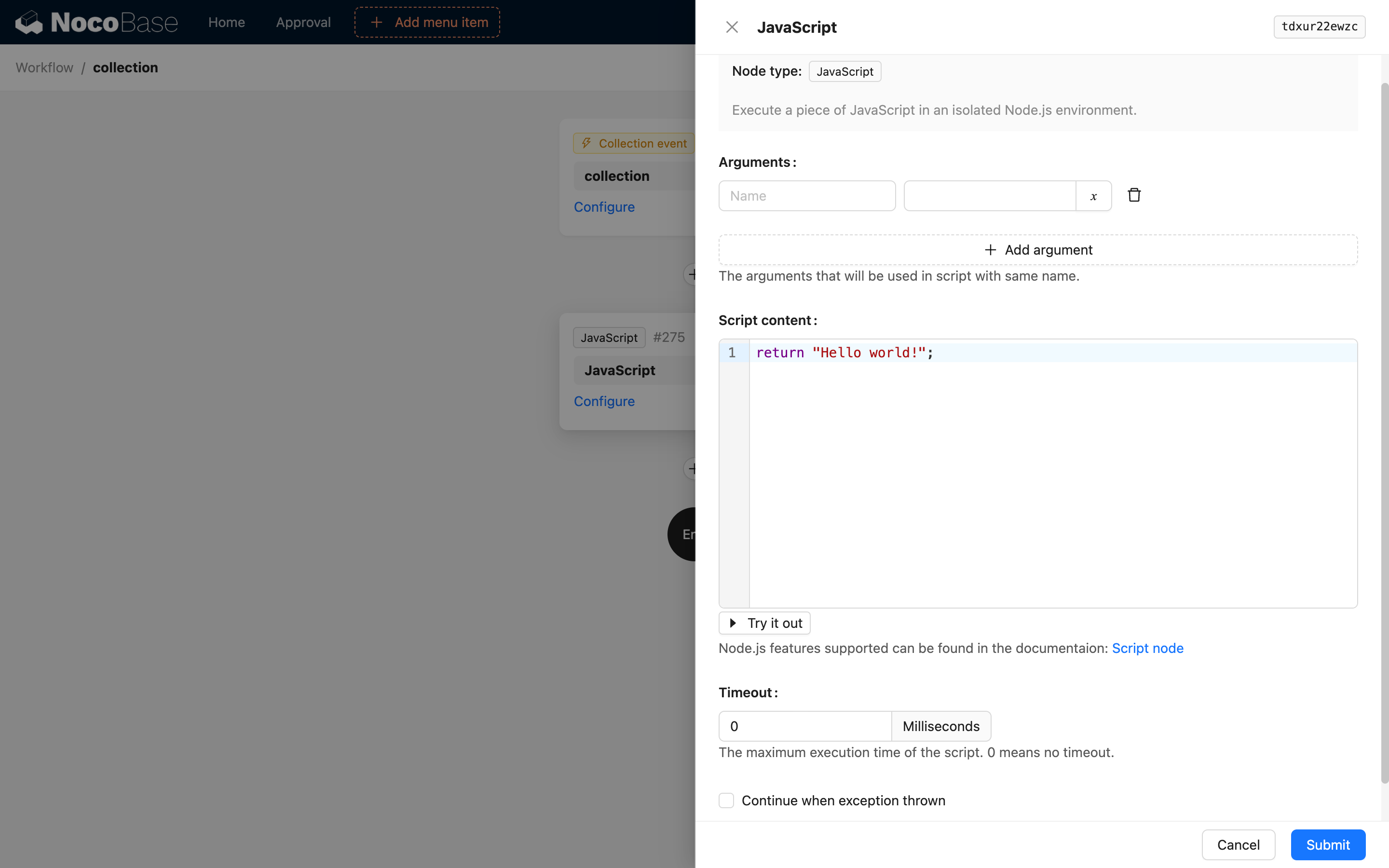
Script Content
The script content can be considered a function. You can write any JavaScript code supported in the Node.js environment and use the return statement to return a value as the node's execution result, which can be used as a variable by subsequent nodes.
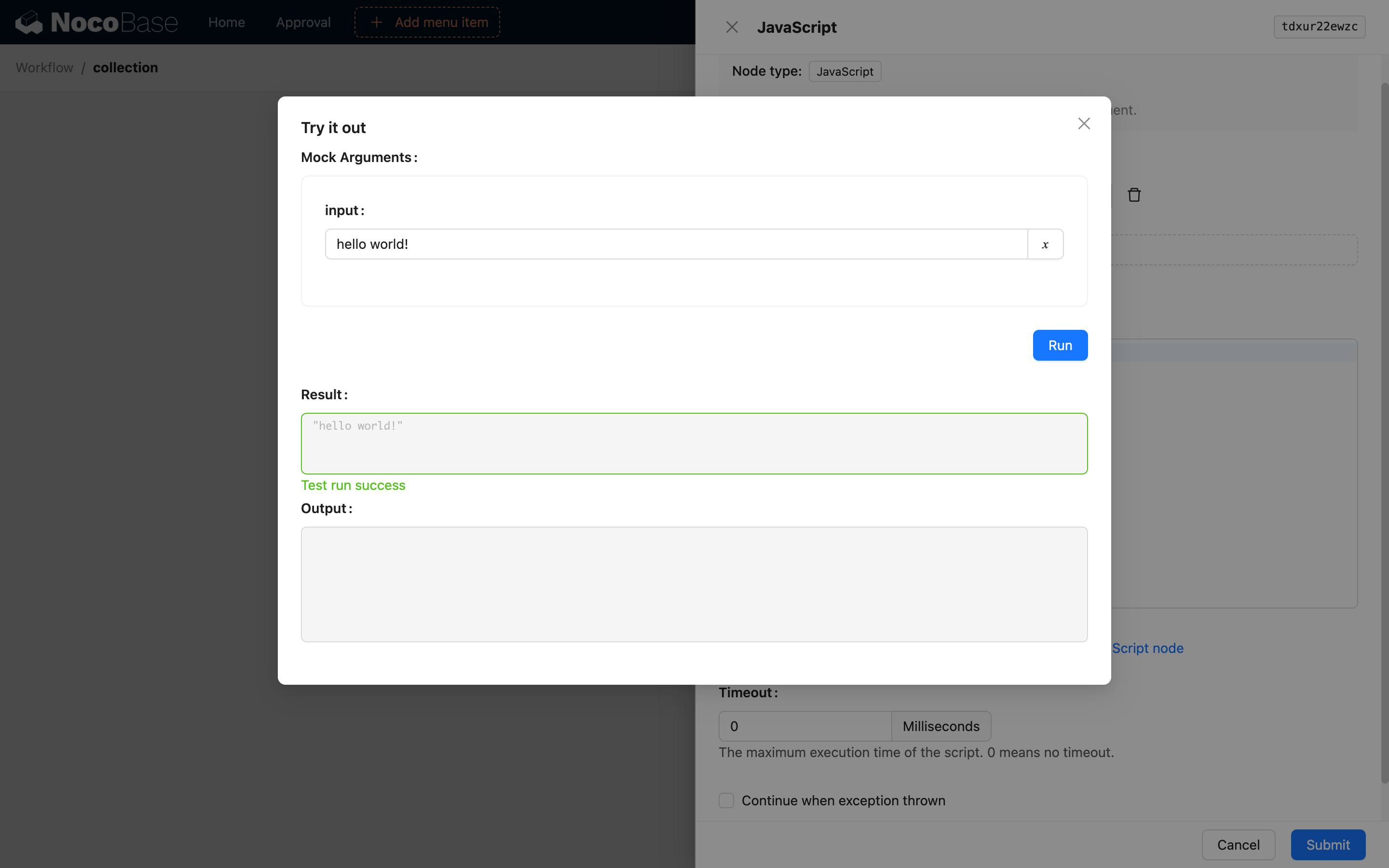
After writing the code, you can click the test button below the editor to open a test execution dialog, where you can fill in parameters with static values for a simulated run. After execution, you can see the return value and output (log) content in the dialog.
Timeout Setting
The unit is milliseconds. A value of 0 means no timeout is set.
Continue on error
If checked, subsequent nodes will still be executed even if the script encounters an error or times out.
If the script errors out, it will have no return value, and the node's result will be populated with the error message. If subsequent nodes use the result variable from the script node, it should be handled with caution.
Feature List
Node.js Version
Same as the Node.js version running the main application.
Module Support
Modules can be used in the script with limitations, consistent with CommonJS, using the require() directive to import modules.
Supports native Node.js modules and modules installed in node_modules (including dependencies already used by NocoBase). Modules to be made available to the code must be declared in the application's environment variable WORKFLOW_SCRIPT_MODULES, with multiple package names separated by commas, for example:
Modules not declared in the WORKFLOW_SCRIPT_MODULES environment variable cannot be used in the script, even if they are native to Node.js or already installed in node_modules. This policy can be used at the operational level to control the list of modules available to users, preventing scripts from having excessive permissions in some scenarios.
When in a non-source-deployed environment, if a module is not installed in node_modules, you can manually install the required package into the storage directory. For example, to use the exceljs package, you can perform the following steps:
Then add the package's relative (or absolute) path based on the application's CWD (current working directory) to the environment variable WORKFLOW_SCRIPT_MODULES:
You can then use the exceljs package in your script (as the name used in require must match exactly with that defined in the environment variable):
Global Variables
Does not support global variables such as global, process, __dirname, and __filename.
Input Parameters
Parameters configured in the node become global variables within the script and can be used directly. Parameters passed to the script only support basic types, such as boolean, number, string, object, and arrays. A Date object will be converted to an ISO format string when passed in. Other complex types, such as instances of custom classes, cannot be passed directly.
Return Value
The return statement can be used to return basic data types (same rules as parameters) to the node as its result. If the return statement is not called in the code, the node execution will have no return value.
Output (Log)
Supports using console to output logs.
When the workflow is executed, the output of the script node is also recorded in the corresponding workflow's log file.
Asynchronous
Supports using async to define asynchronous functions and await to call them. Supports using the Promise global object.
Timers
To use methods like setTimeout, setInterval, or setImmediate, you need to import them from the Node.js timers package.

