Using Variables
Core Concepts
Just like variables in a programming language, variables in a workflow are an important tool for connecting and organizing processes.
When each node is executed after a workflow is triggered, some configuration items can use variables. The source of these variables is the data from the upstream nodes of the current node, including the following categories:
- Trigger context data: In cases like action triggers or collection triggers, a single row data object can be used as a variable by all nodes. The specifics vary depending on the implementation of each trigger.
- Upstream node data: When the process reaches any node, it's the result data of previously completed nodes.
- Local variables: When a node is within some special branch structures, it can use specific local variables within that branch. For example, in a loop structure, the data object of each iteration can be used.
- System variables: Some built-in system parameters, such as the current time.
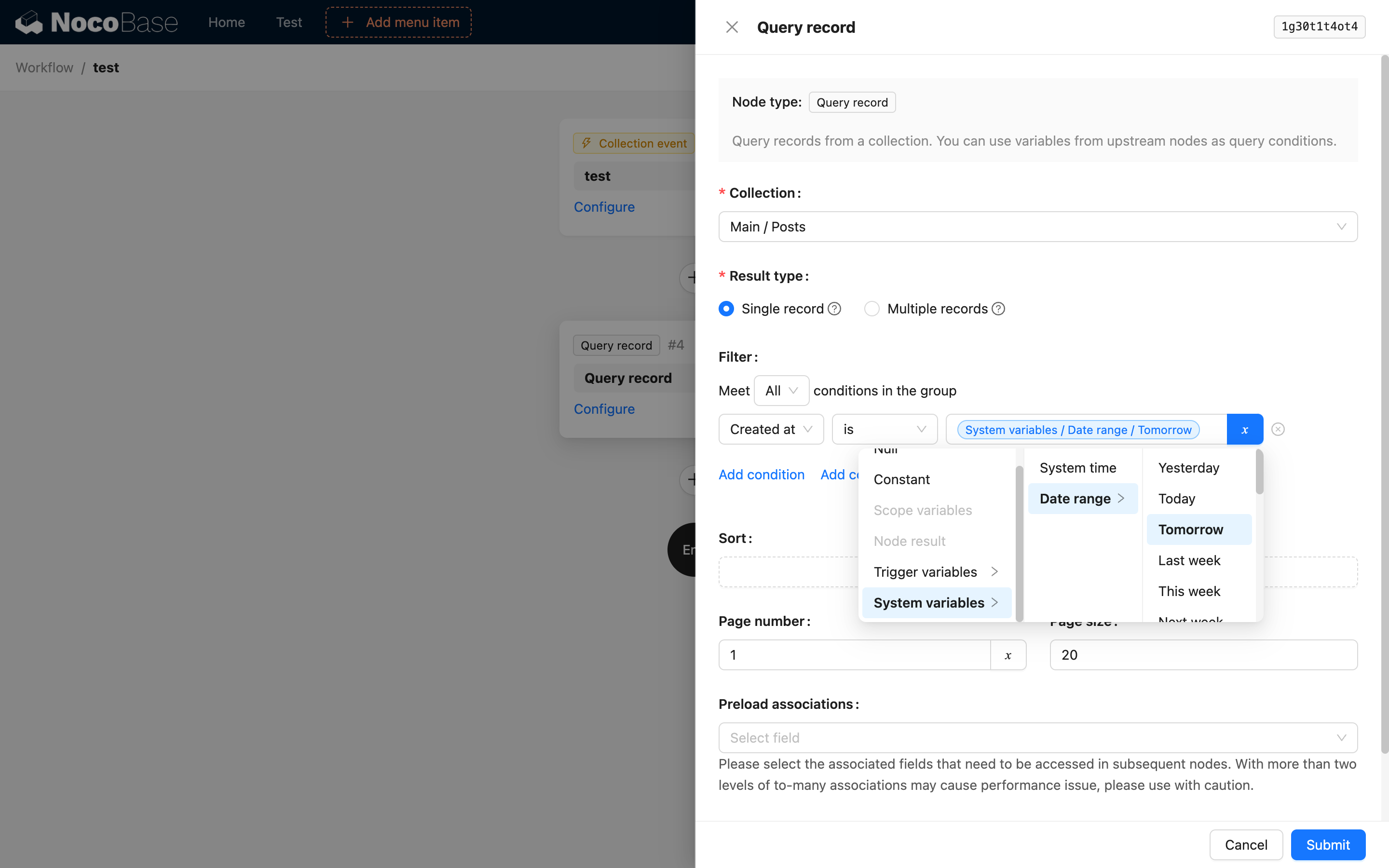
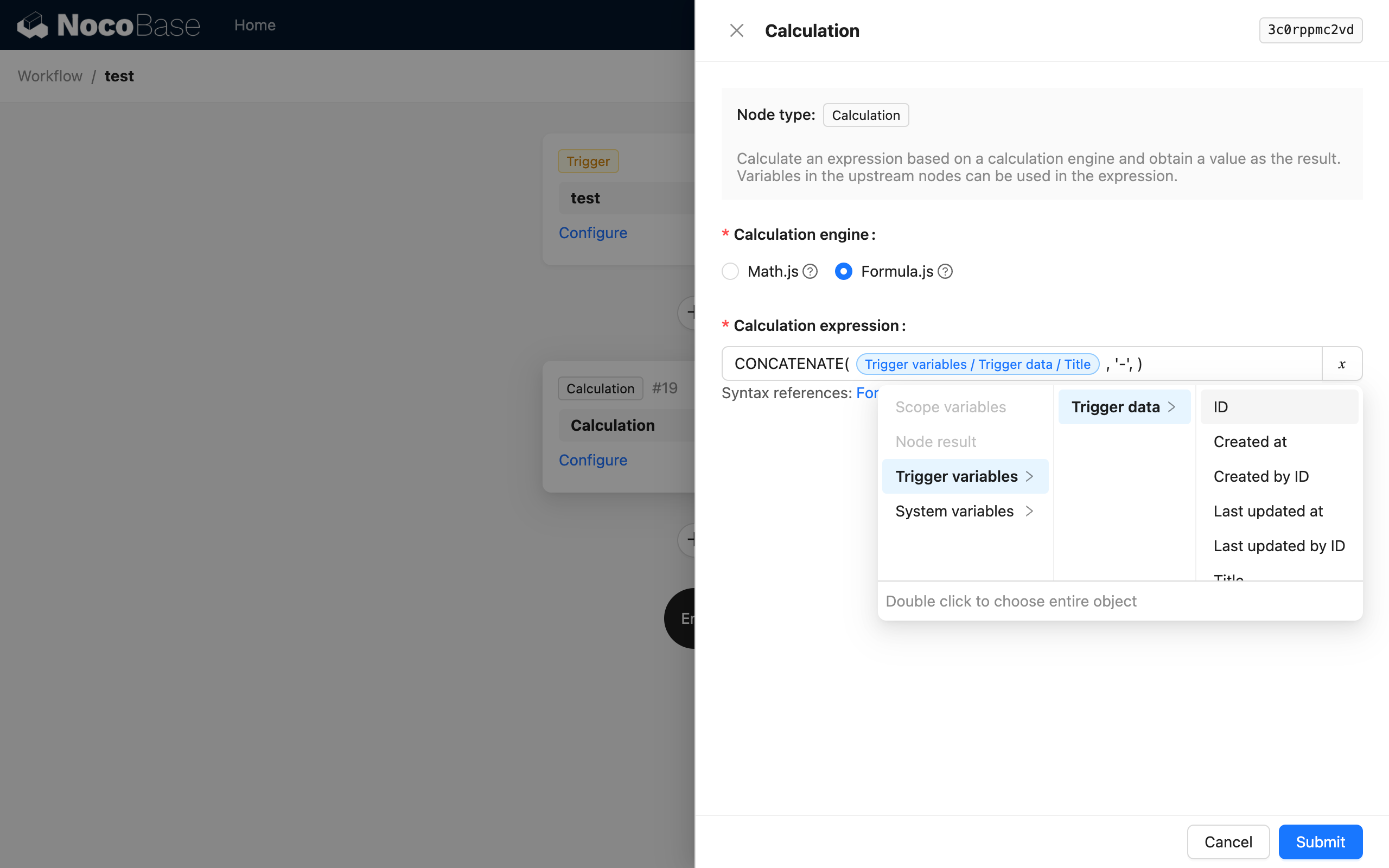
We have used the variable feature multiple times in Getting Started. For example, in a calculation node, we can use variables to reference trigger context data for calculations:
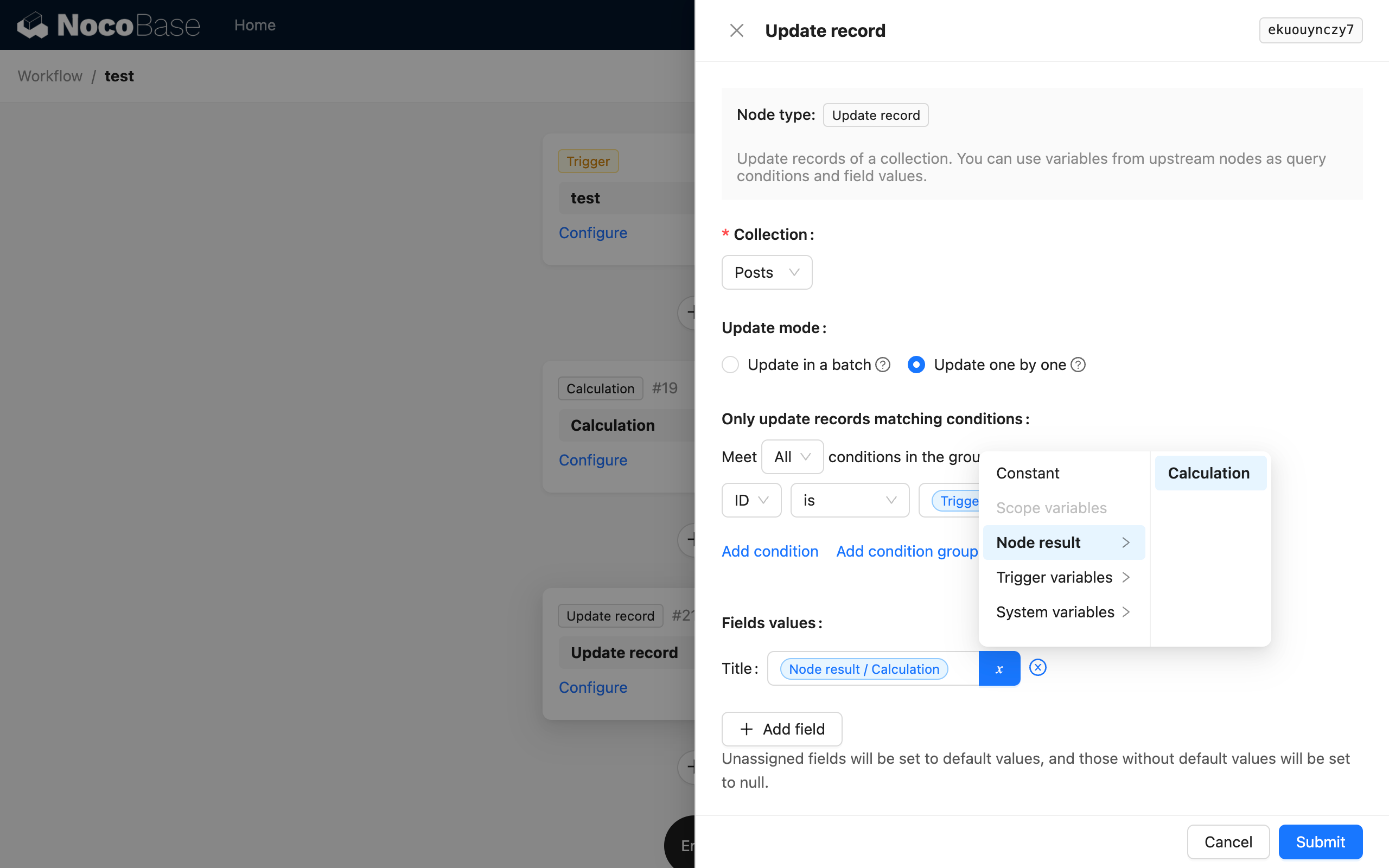
In an update node, use the trigger context data as a variable for the filter condition, and reference the result of the calculation node as a variable for the field value to be updated:
Data Structure
A variable is internally a JSON structure, and you can usually use a specific part of the data by its JSON path. Since many variables are based on NocoBase's collection structure, association data will be structured hierarchically as object properties, forming a tree-like structure. For example, we can select the value of a specific field from the association data of the queried data. Additionally, when the association data has a to-many structure, the variable may be an array.
When selecting a variable, you will most often need to select the last-level value attribute, which is usually a simple data type like a number or a string. However, when there is an array in the variable hierarchy, the last-level attribute will also be mapped to an array. Only if the corresponding node supports arrays can the array data be processed correctly. For example, in a calculation node, some calculation engines have functions specifically for handling arrays. Another example is in a loop node, where the loop object can also be an array.
For example, when a query node queries multiple pieces of data, the node result will be an array containing multiple rows of homogeneous data:
However, when using it as a variable in subsequent nodes, if the selected variable is in the form of Node data/Query node/Title, you will get an array mapped to the corresponding field values:
If it is a multi-dimensional array (such as a many-to-many association field), you will get a one-dimensional array with the corresponding field flattened.
System Built-in Variables
System Time
Gets the system time at the moment the node is executed. The time zone of this time is the one set on the server.
Date Range Parameters
Can be used when configuring date field filter conditions in query, update, and delete nodes. It is only supported for "is" comparisons. Both the start and end times of the date range are based on the time zone set on the server.